Abstract
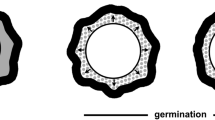
Sporosarcina halophila forms endospores. Electron micrographs revealed ultrastructural similarity to spores of S. ureae. Spore germination indicated by loss of refractility, darkening, swelling and formation of new vegetative cells was followed by phase contrast light microscopy. To induce spore germination, the endospores needed to be heat avtivated. After activation, they were inoculated into nutrient broth medium supplemented with sea-water. Double concentrated sea-water was found to be optimal for germination. Similar to other bacterial endospores, the spores were found to be resistant to heat and ethanol. An ultraviolet absorbing substance was isolated from suspensions of free spores; it was identified to be pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic acid (DPA) usually present in bacterial spores. DPA was detected in amounts ranging from 5–7% of the spore dry weight; it was not detected in extracts of vegetative cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DPA:
-
2,6-pyridine-dicarboxylic acid
References
Bartholomew JW, Mittwer T (1950) A simplified bacterial spore stain. Stain Technol 25:153–156
Brown WL, Ordal ZJ, Halvorson HO (1957) Production and cleaning of spores of putrefactive anaerobe 3679. Appl Microbiol 5:156–159
Charney J, Fischer WP, Hegarty CP (1951) Manganese as an essential element for sporulation in the genus Bacillus. J Bacteriol 62:145–148
Church BD, Halvorson H (1959) Dependence of heat resistance of bacterial spores on their dipicolinic acid content. Nature 183:124–125
Claus D, Fahmy F, Rolf HJ, Tosunoglu N (1983) Sporosarcina halophila sp. nov., an obligate, slightly halophilic bacterium from salt marsh soils. Syst Appl Microbiol 4:496–506
Jannsen FW, Lund AJ, Anderson LE (1958) Colorimetric assay for dipicolinic acid in bacterial spores. Science 127:26–27
Koransky JR, Allen SD, Dowell VR (1978) Use of ethanol for selective isolation of sporeforming microorganisms. Appl Env Microbiol 35:762–765
Long SK, Williams OB (1958) Method for removal of vegetative cells from bacterial spore preparations. J Bacteriol 76:332
Martin HH, Foster JW (1958) On the chromatographic behaviour of dipicolinic acid. Arch Mikrobiol 31:171–178
Morton HE (1977) Alcohols. In: Block S (ed) Disinfection, sterilization and preservation, 2nd edn. Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia, pp 301–308
Perry JJ, Foster JW (1955) Studies on the biosynthesis of dipicolinic acid in spores of Bacillus cereus var. mycoides. J Bacteriol 69:337–346
Perry JJ, Foster JW (1956) Monoethyl ester of dipicolinic acid from bacterial spores. J Bacteriol 72:295–300
Powell JF (1953) Isolation of dipicolinic acid (pyridine-2:6-dicarboxylic acid) from spores of Bacillus megaterium. Biochem J 54:210–211
Robinson RW, Spotts ChR (1983) The ultrastructure of sporulation in Sporosarcina ureae. Can J Microbiol 29:807–814
Silva MT, Lima MP, Fonseca AF, Sousa JCF (1973) The fine structure of Sporosarcina ureae as related to its taxonomic position. J Submicr Cytol 5:7–22
Spurr AR (1969) A low viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res 26:31–43
Thompson RS, Leadbetter ER (1963) On the isolation of dipicolinic acid from endospores of Sarcina ureae. Arch Mikrobiol 45:27–32
Valentine RC, Shapiro BM, Stadtman ER (1968) Regulation of glutamine synthetase. XII. Electron microscopy of the enzyme from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 7:2143–2152
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fahmy, F., Mayer, F. & Claus, D. Endospores of Sporosarcina halophila: characteristics and ultrastructure. Arch. Microbiol. 140, 338–342 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00446974
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00446974