Abstract
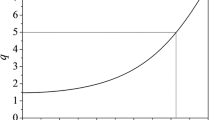
Studies of large-size (R=1.5 m,a=0.5 m), moderate current (I <750 kA) reversed-field pinch (RFP) plasmas are carried out in the Madison Symmetric Torus in order to evaluate and improve RFP confinement, study general toroidal plasma MHD issues, determine the mechanism of the RFP dynamo, and measure fluctuation-induced transport and anomalous ion heating. MST confinement scaling falls short of the RFP scaling trends observed in smaller RFPs, although the plasma resistance is classical. MHD tearing modes with poloidal mode numberm=1 and toroidal mode numbersn=5–7 are prevalent and nonlinearly couple to produce sudden relaxations akin to tokamak sawteeth. Edge fluctuation-induced transport has been measured with a variety of insertable probes. Ions exhibit anomalous heating, with increases of ion temperature occurring during strong MHD relaxation. The anomalous heating fraction decreases with increasing density, such that ion temperatures approach the lower limit given by electron-ion friction. The RFP dynamo has been studied with attention to various possible mechanisms, including motion-EMF drive, the Hall effect, and superthermal electrons. The toroidal field capacity of MST will be upgraded during Summer 1993 to allow low-current tokamak operation as well as improved RFP operation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. B. Taylor (1986).Rev. Mod. Phys. 58, 741.
J. W. Johnson (1981).Plasma Phys. 23, 187.
K. F. Schoenberg, R. F. Gribble, and J. A. Phillips (1982).Nucl. Fusion 22, 1433.
J. C. Sprott (1988).Phys. Fluids 31, 2266.
W. Shen and J. C. Sprott (1991).Phys. Fluids B 3, 1225.
C. G. Gimblett (1990).Europhys. Lett. 11, 541.
Z. Yoshida (1991).Nucl. Fusion 31, 386.
N. Mattor, S. C. Prager, and P. Terry (1993).Comments Plasma Phys. Contr. Fusion 15, 65.
E. Scime, S. Hokin, N. Mattor, and C. Watts (1992).Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 2165.
E. Scime, M. Cekic, D. J. Den Hartog, S. Hokin, D. Holly, and C. Watts (1992).Phys. Fluids B 4, 4062.
F. Najmabadiet al. (1990). UCLA Report UCLA-PPG-1200, UCLA.
K. A. Werley (1991).Nucl. Fusion 31, 567.
R. N. Dexter, D. Kerst, T. W. Lovell, S. C. Prager, and J. C. Sprott (1991).Fus. Technol. 19, 131.
G. Malesani (1987). inProceedings of the International School of Plasma Physics Workshop on Physics of Mirrors, Reversed Field Pinches and Compact Tori, Varenna, Italy, 1986. S. Ortolani and E. Sindoni (eds.) (Societá Italiana di Fisica, Bologna) p. 359.
Y. Yagi, Y. Maejima, Y. Hirano, T. Shimada, K. Hattori, I. Hirota, and P. R. Brunsell (1992).Plasma Physics and Controlled Nuclear Fusion Research, 1992. International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna. To be published.
Earl Scime and Samuel Hokin (1992).Rev. Sci. Instrum. 63, 4527.
S. Hokin, A. Almagri, S. Assadi, M. Cekic, B. Chapman, G. Chartas, N. Crocker, M. Cudzinovic, D. J. Den Hartog, R. Dexter, G. Fiksel, J. Henry, D. Holly, S. Prager, T. Rempel, J. Sarff, E. Scime, W. Shen, C. Sprott, M. Stoneking, and C. Watts (1992).Plasma Physics and Controlled Nuclear Fusion Research, 1992. International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna. To be published.
K. F. Schoenberg, R. W. Moses, and R. L. Hagenson (1984). Phys. Fluids 27, 1671.
T. R. Jarboe and B. Alper (1987).Phys. Fluids 30, 1177.
H. Y. W. Tsui (1988).Nucl. Fusion 28, 1543.
A. F. Almagri, S. Assadi, S. C. Prager, J. S. Sarff, and D. W. Kerst (1992).Phys. Fluids B 4, 4080.
D. J. Den Hartog, M. Cekic, G. Fiksel, S. Hokin, R. Kendrick, S. Prager, and M. Stoneking (1993).J. Nucl. Mater. 200, 177.
S. Assadi, S. C. Prager, and K. L. Sidikman (1992).Phys. Rev. Lett. 69, 281.
J. Sarff, S. Assadi, A. Almagri, M. Cekic, D. J. Den Hartog, G. Fiksel, S. Hokin, H. Ji, S. Prager, W. Shen, K. Sidikman, and M. Stoneking (1993).Phys. Fluids B 5, 2540.
R. J. Hayden and B. Alper (1989).Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 31, 193.
T. Tamano, W. D. Bard, C. Chu, Y. Kondoh, R. J. LaHaye, P. S. Lee, M. T. Saito, M. J. Schaffer, and P. L. Taylor (1987). Phys. Rev. Lett. 59, 1444.
George Chartas and Samuel Hokin (1992).Phys. Fluids B 4, 4019.
W. Shen, R. N. Dexter, and S. C. Prager (1992).Phys. Rev. Lett 68, 1319.
T. D. Rempel, C. W. Spragins, S. C. Prager, S. Assadi, D. J. Den Hartog, and S. A. Hokin (1991).Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 1438.
T. D. Rempel, A. F. Almagri, S. Assadi, D. J. Den Hartog, S. A. Hokin, S. C. Prager, J. S. Sarff, W. Shen, K. L. Sidikman, C. W. Spragins, J. C. Sprott, M. R. Stoneking, and E. J. Zita (1992).Phys. Fluids B 4, 2136.
G. Fiksel, J. Frank, and D. Holly (1993).Rev. Sci. Instrum. Submitted.
P. G. Carolan, A. R. Field, A. Lazaros, M. G. Rusbridge, H. Y. W. Tsui, and M. V. Bevir (1987).Proceedings of the 14th European Conf. on Contr. Fusion and Plasma Physics, Madrid, EPS, Petit-Lancy, Vol. 2, p. 469.
G. A. Wurdenet al. (1988).Proceedings of the 15th European Conf. on Contr. Fusion and Plasma Physics, Dubrovnik, EPS, Petit-Lancy, p. 331.
H. Ji, H. Toyama, A. Fujisawa, S. Shinohara, and K. Miyamoto (1992).Phys. Rev. Lett. 69, 616.
A. al-Karkhy, P. K. Browning, G. Cunningham, S. J. Gee, and M. G. Rusbridge (1993).Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1814.
W. Shen and S. C. Prager (1993).Phys. Fluids B 5, 1931.
A. R. Jacobson and R. W. Moses, Jr. (1984).Phys. Rev. A 29, 3335.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hokin, S., Almagri, A., Cekic, M. et al. Reversed-field pinch studies in the Madison Symmetric Torus. J Fusion Energ 12, 281–287 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01079671
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01079671