Abstract
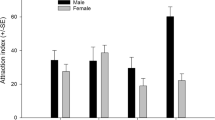
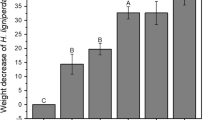
MaleIps paraconfusus Lanier bored and fed in cellulose powder substrates treated with solvent extracts of ponderosa pine phloem in preference to cellulose powder alone. Stimuli that elicit boring and feeding behavior occurred in the water extracts and the combined solvent extracts. No significant boring or feeding occurred in the methanol extract. There was a preference for, but no significant feeding in, the water partition of the ether extract. Feeding, but no preferential boring, occurred in the ether extracts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, J.E., andNorris, D.M. 1967. A feeding stimulant forScolytus multistriatus isolated from the bark ofUlmus americana.Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 60:1213–1215.
Baker, J.E., Rainey, D.P., Norris, D.M., andStrong, F.M. 1968.p-Hydroxy-benzaldehyde and other phenolics as feeding stimulants for the small European bark beetle.For. Sci. 14:91–95.
Browne, L.E. 1972. An emergence cage and refrigerated collector for wood-boring insects and their associates.J. Econ. Entomol. 65:1499–1501.
Dethier, V.G. 1953. Host plant perception in phytophagous insects.Trans. 9th Int. Congr. Amsterdam 1951. 2:81–88.
Doskotch, R.W., Chatterji, S.K., andPeacock, J.W. 1970. Elm bark derived feeding stimulants for the smaller European bark beetle.Science 167:380–382.
Doskotch, R.W., Mikhajr, A.A., andChatterji, S.K. 1973. Structure of the water soluble feeding stimulant forScolytus multistriatus: A revision.Phytochemistry 12:1153–1155.
Elkinton, J.S., andWood, D.L. 1980. Feeding and boring behavior of the bark beetleIps paraconfusus on the bark of a host and non-host tree species.Can. Entomol. 112:797–809.
Elkinton, J.S., Wood, D.L., andHendry, L.B. 1980. Pheromone production by the bark beetleIps paraconfusus in non-host, white fir.J. Chem. Ecol. 6:979–987.
Gilbert, B.L., Baker, J.E., andNorris, D.M. 1967. Juglone (5-hydroxy-1, 4-naphthoquinone) fromCarya ovata, a deterrent to feeding byScolytus multistriatus.J. Insect Physiol. 13:1453–1459.
Gupta, P.D., andThorsteinson, A.J. 1960. Food plant relationships of the diamond-back moth (Plutella maculipennis (Curt.)), I. Gustation and olfaction in relation to botanical specificity of the larva.Entomol. Exp. Appl. 3:241–250.
Hedin, P.A., Maxwell, F.G., andJenkins, J.N. 1974. Insect plant attractants, feeding stimulants, repellents, deterrents, and other related factors affecting insect behavior, pp. 494–527,in F.G. Maxwell and F.A. Harris (eds.). Proceedings of the Summer Institute on Biological Control of Plant Insects and Diseases. University Press of Mississippi, Jackson.
Jermy, T. 1966. Feeding inhibitors and food preference in chewing phytophagous insects.Entomol. Exp. Appl. 9:1–12.
Levy, E.C., Ishaaya, I., Gurevitz, E., Cooper, R., andLavie, D. 1974. Isolation and identification of host compounds eliciting attraction and bite stimuli in the fruit tree bark beetle,Scolytus mediterraneus.J. Agr. Food Chem. 22:376–379.
Miller, R.G. 1966. Simultaneous Statistical Inferences. McGraw-Hill, New York. 272 pp.
Schoonhoven, L.M. 1968. Chemosensory bases of host plant selection.Annu. Rev. Entomol. 13:115–136.
Schoonhoven, L.M. 1972. Plant recognition by lepidopterous larvae, pp. 87–99,in H.F. van Emden (ed.). Insect/Plant Relationships. Symposia of the Entomological Society of London, No. 6. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Coleoptera: Scolytidae.
Research supported by the Rockefeller Foundation, an NIH Training Grant, USDA/SEA Regional Research Project W-110, and the USDA Forest Service.
From a thesis submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy, by J.S.E., 1979, University of California, Berkeley, California.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elkinton, J.S., Wood, D.L. & Browne, L.E. Feeding and boring behavior of the bark beetle,Ips paraconfusus, in extracts of ponderosa pine phloem. J Chem Ecol 7, 209–220 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00988649
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00988649