Summary
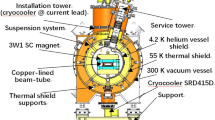
A superconducting wiggler has been designed and built at Laboratori Nazionali INFN in Frascati, Italy, in collaboration with Ansaldo Componenti-Genova, to be used as an insertion device in the Adone storage ring. It will be used as a light source on the 1.5 GeV, 100 mA electron beam of the accelerator, to produce about 1012 photons/s/mrad in 0.1% band width, in the short X-ray wavelength range. In order to minimize the electron beam orbit disortion and to obtain the best phase space distribution of the generated synchrotron radiation (a single bright spot), a superconducting dipole, producing a sharp vertical field peak (6 T, 12 cm FWHM), between two normal conducting side dipoles (0.8T), to compensate the field integral, has been manufactured. The s.c. dipole is made up of 2NbTi coils, separated by a central plate and kept together by two 356 kg total weight iron yokes. The magnet gap is 6 cm and the design current is 360A. The system is contained in a warm bore cryostat and cooled by boiling helium at 4.6K. The static cryostat helium consumption is of 41/h and, when the cryomagnet is energized, it is cooled by a 1430S Koch liquefier/refrigerator on line with it through transfer lines. The stored energy is 184 kJ. This paper describes the latest status of the facility and the verification tests.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. U. Luccio:Status report on the Adone wiggler and X-ray beam line, inWiggler Meeting, Frascati, June 29–30, 1978.
H. Hsieh et al.:IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., Vol. NS-28, No. 3 (June 1981).
S. Pissanetzky:The new version of the finite element 3 D magnetostatics program Magnus, inComputational Electromagnetics, edited byZ. J. Cendes (Elsevier Science Publishers B. V., North Holland, IMACS, 1986).
R. Coisson, S. Guiducci andM. Preger:Nucl. Instrum. Methods,201, p. 3 (1982).
M. Helm, M. J. Lee andP. L. Morton:Evaluation of synchrotron radiation integrals, SLAC/PUB-1193 (March 1973).
R. P. Walker:An improved wiggler model: calculation of beam parameters and comparison with experiment, SRS/APN/82/41.
M. N. Wilson:Superconducting Magnet (Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1983), p. 200.
C. Sanelli:Progetto magnetico dei compensatori per S.CO.W., LNF-85/64 (R) (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barone, M., Cattoni, A., Gambardella, U. et al. Superconducting wiggler for adone: Design and present status. Il Nuovo Cimento D 13, 579–613 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02451285
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02451285