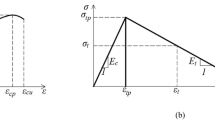
Abstract
The investigation reveals the main peculiarities (among which is the presence of a pronounced peak of moment before yielding) of the response to bending actions of slightly reinforced concrete structural members and shows that the trend in the reactive moments is strikingly different from what would result from the ‘classical’ analysis, especially in the region preceding yielding. One of the most interesting results in our opinion is the bringing to light of the role played by concrete which, with the same reinforcement, is capable of radically modifying the type of response and peak height, besides influencing the gap between the experimental yielding moment and the one that would results from the ‘classical’ procedure. Also shown is the fact that with particularly weak reinforcement (0.05%), high concrete strength is capable of bringing the cracking moment up to values far superior even to those of yielding. With weak reinforcement, hyper-strength does not relate only to the reinforcement percentage—as follows from various relationships proposed—but also, and in a determinant way, to concrete strength.
Résumé
L'étude révèle les principales caractéristiques (notamment la présence d'un pic significatif de moment avant le seuil de plasticité) de la réponse aux actions de flexion d'éléments structuraux de béton faiblement armé; il apparaît que les moments réactifs tendent à différer fortement des résultats qu'aurait donnés une analyse ‘classique’, en particulier dans la région précédant le seuil de plasticité.
L'un des résultats les plus intéressants, à notre avis, est la mise en lumière du rôle joué par le béton qui, avec une armature identique, a la capacité de modifier radicalement le type de réponse et la hauteur du ‘pic’, exerçant en outre une influence sur l'écart entre le seuil de plasticité et celui qui se produirait avec une méthode ‘classique’. Il apparaît également qu'avec une armature particulièrement faible (0,05%), le moment de fissuration du béton de haute résistance peut être porté à des valuers bien supérieures même à celles du seuil de plasticité.
Avec une faible armature, la sur-résistance ne correspond pas seulement au pourcentage d'armature—comme le mettent en évidence diverses relations avancées—mais aussi, et ceci de façon déterminante, à la résistance du béton.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Soretz, S., ‘Beitrag zur uberfestigkeit in biegebeauspruchten Stahlbeton balken’, Bulletin d'Information, No. 22 (CEB, 1960).
Bosco, C., ‘Confronto tra il momento di rottura teorico e sperimentale nelle sezioni in c.a. costituite con travetto precompresso e getto di completamento’ Atti del Dipartimento di Ing. Strutturale di Torino, Politecnico, No. 7 (1987).
Levi, F. and Debernardi, P. G., ‘Interpretazione del fenomeno d'iperresistenza nelle travi cementizie debolmente armate’—(Academy of Science of Turin, 1987).
Levi, F., Bosco, C. and Debernardi, P. G., ‘Two aspects of the behaviour of slightly reinforced structures’, CEB 25th Plenary Session, Treviso, May 1987.
Cossu, P., ‘Approccio al problema della iperresistenza e del regime fessurativo delle travi in calcestruzzo debolmente armate’, Università di Cagliari, Atti della Facoltà d'Ingegneria (1987).
Pozzo, E., ‘The influence of axial load and rate of loading on experimental post-elastic behaviour and ductility of reinforced concrete members’,Mater. Struct. 20 (1987).
Idem., Pozzo, E., ‘Influenza della velocità di deformazione sulla duttilità di membrature di c.a. pressoinflesse—Indagine sperimentale’, Proceedings of Giornate AICAP 87, Stresa (Italy), April 1987.
CEB-FIP Model Code (1978).
Chambaud, R., ‘Le calcul du béton armé à la rupture’ (Eyrolles, Paris, 1965).
Konig, G., ‘Restraint crack-width control and minimum reinforcement in thick concrete members’, Annual Journal on Concrete and Concrete Structures, Darmstad Concrete, Vol. 1 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cossu, P., Pozzo, E. Experimental behaviour and hyper-strength of slightly reinforced concrete members bent up to collapse. Materials and Structures 23, 204–212 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02473019
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02473019