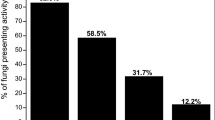
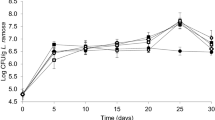
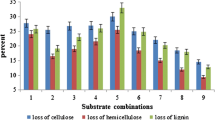
Abstract
Four mushroom strains ofPleurotus spp. were cultivated on sugar cane crop residues for 30 days at 26°C. Biochemical changes affected the substrate as a result of fungal growth, in terms of nitrogen, lignin, cellulose and hemicellulose contents. All strains showed a strong ligninolytic activity together with variable cellulolytic and xylanolytic action.Pleurotus sajor-caju attacked lignin and cellulose at the same rate, showing a degradation of 47% and 55%, respectively. A better balance was shown by theP. ostreatus-P. pulmonarius hybrid, which exhibited the poorest cellulolytic action (39%) and the highest ligninolytic activity (67%). The average composition of mushroom fruit bodies, in terms of nitrogen, carbohydrates, fats and amino acid profiles, was determined. Crude protein and total carbohydrate varied from 23% to 33% and 36% to 68% of dry matter, respectively. Fat ranged from 3.3% to 4.7% and amino acid content from 12.2% to 22.2%. Slight evidence for a nitrogen fixing capability was encountered in the substrate to fruit body balance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Association of Official Analytical Chemists 1980Official Methods of Analysis. Washington, DC:AOAC.
Benzing-Purdie, L. 1981 Glucosamine and galactosamine distribution in a soil as determined by gas liquid chromatography of soil hydrolysates: effect of acid strength and cations.Soil Science Society of America, Journal 45, 65–70.
Bisaria, R., Madan, M. & Bisaria, V.S. 1987 Biological efficiency and nutritive value ofPleurotus sajor-caju cultivated on different agro-wastes.Biological Wastes 19, 239–255.
Bourbonnais, R. & Paice, M G. 1988 Veratryl-alcohol oxidase from the lignin-degrading basidiomycetePleurotus sajor-caju.Biochemical Journal 255, 445–450.
Cabello, A. J. & Conde, J. 1985 Evaluation of newer methods of pretreament for biological utilization of cellulosic residues.Acta Biotechnologica,5, 191–196.
Chang, S. T., Lau, O.W. & Cho, K. Y. 1981 The cultivation and nutritional value ofPleurotus sajor-caju.European Journal of Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 12, 58–62.
Ginterova, A. 1973 Nitrogen fixation by higher fungi.Biologia (Bratislava) 28, 199–202.
Ginterova, A. & Lazarova, A. 1987 Amino acid composition of wood-rotting fungi (Pleurotus) and total amino acid balance of the cultivating system.Food Chemistry 23, 35–41.
Ginterova, A. & Maxianova, A. 1975 The balance of nitrogen and composition of proteins inPleurotus ostreatus grown on natural substrates.Folia Microbiologica 20, 246–250.
Guillen, F., Martinez, A. T. & Martinez, M.J. 1990 Production of hydrogen peroxide by aryl-alcohol oxidase from the ligninolytic fungusPleurotus eryngii.Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 32, 465–469.
Higuchi, T. 1990 Lignin biochemistry: Biosynthesis and biodegradation.Wood Science Technology 24, 23–63.
Hodge, J.L. & Hofreiter, B.T. 1962 Determination of reducing sugars and carbohydrates.Methods in Carbohydrate Chemistry 1, 380–394.
Kamra, D.N. & Zadrazil, F. 1986 Influence of gaseous phase, light and a substrate pretreatment on fruit-body formation, lignin degradation andin vitro digestibility of wheat straw fermented withPleurotus spp.Agricultural Wastes 18, 1–17.
Kewalramani, N., Kamra, D.N., Lall, D. & Pathak, N.N. 1988 Bioconversion of sugar cane bagasse with white rot fungi.Biotechnology Letters 10, 369–372.
Kühn, S. 1991 Chemische und enzymatische untersuchungen über den abbau von Weizenstroh durch den weissfäulepilzPleurotus eryngii. Thesis. Karlsruhe Universität.
Kurtzman, Jr., R.-H. 1979 Nitrogen fixation byPleurotus.Mushroom Science 10, 427–435.
Levonen-Muñoz, E., Bone, D.H. & Daugulis, A.J. 1983 Solid state fermentation and fractionation of oat straw by basidiomycetes.European Journal of Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 18, 120–123.
Martinez, E.O., Ortega, G.M., Otero, M.A. & Gonzalez, A.E. 1990 Sugar cane crop residues degradation byPleurotus ostreatus. InAbstracts of the Fourth International Mycological Congress, Regensburg, Germany eds Reisinger, A. & Bresinsky. A. p. 244.
Nicolini, L., Von Hunolstein, C. & Carrilli A. 1987 Solid state fermentation of orange peel and grape stalks byPleurotus ostreatus, Agrocybe aegerita andArmillariella mellea.Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 26, 95–98.
Rangaswami, G., Kandaswami, T.K. & Ramasami, K. 1975Pleurotus sajor-caju, a protein rich nitrogen fixing mushroom fungus.Current Science 44, 403–404.
Valmaseda, M., Almendros, G. & Martinez, A.T. 1990 Substrate-dependent degradation patterns in the decay of wheat straw and beech wood by ligninolytic fungi.Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 33, 481–484.
Van Soest, P.J. & Wine, R.H. 1968 Determination of lignin and cellulose in acid-detergent fiber with permanganate.Journal of American Official Methods of Analysis 51, 780–785.
Zadrazil, F. 1977 The conversion of straw into feed by basidiomycetes.European Journal of Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 4, 273–281.
Zadrazil, F. 1980 Influence of ammonium nitrate and organic supplements on the yield ofPleurotus sajor caju (Fr.) Sing.European Journal of Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 9, 31–35.
Zadrazil, F. 1985 Screening of fungi for lignin decomposition and conversion of straw into feed.Angewandte Botanik 59, 433–452.
Zadrazil, F., Diedrichs, M., Janssen, H., Sghuchardt, F. & Park, J.S. 1990 Large scale solid-state fermentation of cereal straw withPleurotus spp. InAdvances in Biological Treatment of Lignocellulosic Materials eds Coughlan, M.P. & Amaral Collaco, M.T. pp. 43–58. London: Elsevier Applied Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ortega, G.M., Martínez, E.O., Betancourt, D. et al. Bioconversion of sugar cane crop residues with white-rot fungiPleurotus sp.. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 8, 402–405 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01198754
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01198754