Abstract
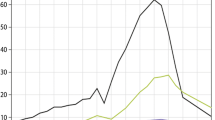
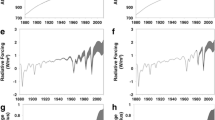
Computer assessments of the atmospheric chemistry and air quality of the past, present, and future rely in part on inventories of emissions constructed on appropriate spatial and temporal scales and with appropriate chemical species. Accurate inventories are also of substantial utility to field measurement scientists and the regulatory and policy communities. The production of global emissions inventories is the task of the Global Emissions Inventory Activity (GEIA) of the International Global Atmospheric Chemistry Project (IGAC). This paper presents a summary of recent emissions inventories from GEIA and other programs for reference year 1985, with special attention directed to emissions of the acid-related compounds CO2 (≈6.2 Pg C yr−1 anthropogenic), SOx (≈65 Tg S yr−1 anthropogenic and 15 Tg S yr−1 natural), NOx (≈21 Tg N yr−1 anthropogenic and 15–20 Tg N yr−1 natural), HCl (≈55 Tg Cl yr−1 total), and NH3 (≈45 Tg N yr−1 total). The global acid-equivalent flux of about 4.2 Teq H+yr−1 is about equally attributable to SOx and NOx emissions. For some of the acid-related species, historic inventories are available for a century or more; all show dramatic emissions increases over that period. IPCC scenario IS92a is used here as the basis for constructing global acid-related emissions estimates for selected years to 2100; among the results are that acid equivalent emissions are expected to more than double in the coming century.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreae, M.O.: 1991, in Global Biomass Burning: Atmospheric, Climatic, and Biospheric Implications, Levine, J.S., Ed., pp. 3–21, MIT Press, Cambridge, Mass.
Andreae, M.O.: 1995, Paper presented at AGU Chapman Conference on Biomass Burning and Global Change, Williamsburg, VA.
Andres, R.J., Marland, G., Fung, I., and Matthews, E.: 1995, Global Biogeochem. Cycles, submitted.
Baughcum, S.L., Metwally, M., Seals, R.K., and Wuebbles, D.J.: 1993, in The Atmospheric Effects of Stratospheric Aircraft: A Third Program Report, edited by R.S. Stolarski and H.L. Wesoky, pp. 185–208, NASA Ref. Pub. 1313, Nat. Aeronautics and Space Admin., Washington, D.C.
Bates, T.S., Lamb, B.K., Guenther, A., Dignon, J., and Stoiber, R.E.: 1992: J. Atmos. Chem., 14, 315–337.
Benkovitz, C.M., Berkowitz, C.M., Easter, R.C., Nemesure, S., Wagener, R., and Schwartz, S.E.: 1994: J. Geophys. Res., 99, 20725–20756.
Benkovitz, C.M., Scholtz, M.T., Pacyna, J., Tarrason, L., Dignon, J., Voldner, E.C., Spiro, P.A., Logan, J.A., and Graedel, T.E.: 1995, J. Geophys. Res., submitted.
Bottger, A., Ehhalt, D.H. and Gravenhorst, G.:1978, Atmospheric Cycles of Nitrogen Oxides and Ammonia (in German), Report 1558, KFA Julich, Germany.
Chameides, W.L., and Stelson, A.W.: 1992, J. Geophys. Res., 97, 20565–20580.
Charlson, R.J., Schwanz, S.E., Hales, J.M., Cess, R.D., Coakley, J.A., Hansen, J.E., and Hofmann, D.J.: 1992, Science, 255, 423–430.
Demener, F., and Crutzen, P.J.: 1994, J. Atmos. Chem., 19, 331–369.
Enting, I.G., Wigley, T.M.L., and Heimann, M.: 1994, Future Emissions and Concentrations of Carbon Dioxide: Key Ocean/Atmosphere/Land Analyses, Tech. Pap. 31, CSIRO Div. of Atmos. Res., Mordialloc, Vic., Australia.
Graedel, T.E., and Keene, W.C.: 1995, Global Biogeochem. Cycles, 9, 47–77.
Graedel, T.E., Bates, T.S., Bouwman, A.F., et al.: 1993, Global Biogeochem. Cycles, 7, 1–26.
Gschwandtner, G., Gschwandtner, K., Eldridge, K., Mann, C., and Mobley, D.: 1986, J. Air Pollut. Contr. Assoc., 36, 139–149.
Guenther, A., Hewitt, C.N., Erickson, D., et al., 1995: J. Geophys. Res., 100, 8873–8892.
Hameed, S., and Dignon, J.: 1992, J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc., 42, 159–163.
Houghton, J., Callander, B., and Vamey, S.: 1992, Climate Change 1992: The IPCC Supplementary Report, Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge University Press.
Husar, R.B.: 1994, in Industrial Metabolism: Restructuring for Sustainable Development, Ayres, R.U., and Simonis, U.E., Eds., Tokyo: United Nations University Press.
Langner, J., and Rodhe, H.: 1991, J. Atmos. Chem., 13, 225–265.
Lee, D., Bouwman, A.F., Dentener, F., et al.: 1995, in preparation.
Marland, G., Andres, R.J., and Boden, T.A.: 1994a, in Trends '93: A Compendium of Data on Global Change, Boden, T.A., Kaiser, D.P., Sepanski, R.J., and Stoss, F.W., Eds., pp. 505–584, Rpt. ORNL/CDIAC-65, Oak Ridge National Lab., Oak Ridge, TN.
Marland, G., Andres, R.J., and Boden, T.: 1994b, in Global Climate Change: Science, Policy and Mitigation Strategies, C.V. Mathai and G. Stensland, Eds., Proc. Intl. Spec. Conf., Air and Waste Mgt. Assoc., Pittsburgh, PA.
Moore, B. III, and Braswell, B.H., Jr.: 1994, Ambio, 23, 4–12.
Mylona, S.: 1993, Trends of Sulphur Dioxide Emissions, Air Concentrations and Depositions of Sulphur in Europe Since 1880, EMEP/MSC-W Rpt. 2/93, Norwegian Meteorological Institute, Oslo.
Rinsland, C.P., Levine, J.S., Goldman, A., Sze, N.D., Ko, M.K.W., and Johnson, D.W.: 1991, J. Geophys. Res., 96, 15523–15540.
Rodhe, H., et al.: 1995, in preparation.
Schlesinger. W.H. and Hartley, A.E.: 1992, Biogeochemistry, 15, 191–211.
Soderlund, R. and Svennson, B.H.: 1976, in Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Sulfur Global Cycles, SCOPE Report 7, Ecological Bulletin, Stockholm, Sweden.
Stoiber, R.E., Williams, S.N., and Huebert, B.: 1987. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res., 33, 1–8.
Symonds, R.B., Rose, W.I., and Reed, M.H.: 1988, Nature, 334, 415–418.
Tans, P.P., Fung, I.Y., and Takahashi, T.: 1990, Science, 247, 1431–1438.
Williams, S.N., Schaefer, S.J., Calvache V., M.L., and Lopez, D.: 1992, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 56, 1765–1770.
World Energy Council: 1993, Energy for Tomorrow's World, St. Martin's Press, New York.
Yienger, J.J., and Levy, H. II: 1995, J. Geophys. Res., 100, 11447–11464.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Graedel, T.E., Benkovitz, C.M., Keene, W.C. et al. Global emissions inventories of acid-related compounds. Water Air Soil Pollut 85, 25–36 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00483686
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00483686