Abstract
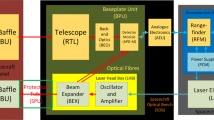
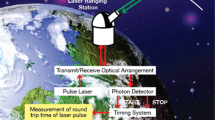
In 1999 after a 3-year transit, the Near-Earth Asteroid Rendezvous (NEAR) spacecraft will enter a low-altitude orbit around the asteroid, 433 Eros. Onboard the spacecraft, five facility instruments will operate continuously during the planned one-year orbit at Eros. One of these instruments, the NEAR Laser Rangefinder (NLR), will provide sufficiently high resolution and accurate topographical profiles that when combined with gravity estimates will result with quantitative insight into the internal structure, rotational dynamics, and evolution of Eros. Developed at the Applied Physics Laboratory (APL), the NLR instrument is a direct-detection laser radar using a bistatic arrangement. The transmitter is a gallium arsenide (GaAs) diode-pumped Cr:Nd:YAG (1.064-µm) laser and the separate receiver uses an extended infrared performance avalanche-photodiode (APD) detector with 7.62-cm clear aperture Dall–Kirkham telescope. The lithium-niobate (LiNbO3) Q-switched transmitter emits 15-ns pulses at 15.3 mJ pulse-1, permitting reliable NLR operation beyond the required 50-km altitude. With orbital velocity of 5 m s-1 and a sampling rate of 1 Hz, the NLR spot size provides high spatial sampling of Eros along the orbital direction. Cross-track sampling, determined by the specific orbital geometry with Eros, defines the resolution of the global topographic model; this spacing is expected to be <500 m on the asteroid's surface. Combining the various sources of range errors results with an overall range accuracy of 6 m with respect to Eros' center-of-mass. The NLR instrument design, perfomance, and validation testing is decribed. In addition, data derived from the NLR are discussed. Using altimetry data from the NLR, we expect to estimate the volume of 433 Eros to 0.01% and its mass to 0.0001% accuracies; significantly greater accuracies than ever possible before NEAR.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Binzel, R., Gehrels, T., and Matthews, M. (eds.): 1989, Asteroids II, The University of Arizona Press, Tucson, AZ.
Boies, M. T., Cole, T. D., El-Dinary, A. S., and Reiter, R. A.: 1996, 'Optical System Development and Performance Testing of the Near Laser Rangefinder', Photonics for Space Environments IV, SPIE, Vol. 2811, pp. 169–184.
Burns, H. N.: 1994, NEAR Laser Radar (NLR) Tilt/Decenter Analysis, Technical Report to APL, Burns Engineering, Inc.
Cole, T. D. and Davidson, F. M.: 1996, 'Performance Evaluation of the Near-Earth Asteroid Rendezvous (NEAR) Laser Rangefinder', Photonics for Space Environments IV, SPIE, Vol. 2811, pp. 156–168.
Cole, T.D. et al.: 1996, 'Laser Rangefinder for the Near-Earth Asteroid Rendezvous (NEAR) Mission', Lidar Techniques for Remote Sensing II, SPIE, Vol. 2581, EUROPTO, Paris, France, pp. 2–26.
Culpepper, C., Kushina, M., Wiswall, C., and Cole, T.: 1995, 'Laser Transmitter for the Near-Earth Asteroid Rendezvous Spacecraft', IEEE/OSA CLEO/QELS '95, Baltimore.
El-Dinary, A. S.: 1995, NEAR Laser Ranger Test Plan, APL/JHU Technical Report No. 7361- 3007.
El-Dinary, A. S., Cole, T. D., Boies, M. T., Reiter, R. A., and Rodriguez, D. E.: 1996, 'Pre-Launch and Post-Launch Testing of the Near-Earth Asteroid Rendezvous (NEAR) Laser Rangefinder', Photonics for Space Environments IV, SPIE, Vol. 2811, pp. 222–231.
Jelalian, A. V.: 1992, Laser Radar Systems, chapter 1.7, Artech House Publishers, p. 29.
Moore, R. C.: 1994, NEAR NLR Flight Software Requirements Specification, APL/JHU Report 7352- 9069.
Penn, J.: 1994, GaAs Design for Laser Rangefinder Timer, APL Technical Memorandum No. S2R-94- 050.
Reiter, A.: 1993, Timing Precision of the NEAR Navigation Laser Rangefinder (NLR) Analog Electronics, APL Technical Memorandum No. S2A-93- 0201.
Rodriguez, D.: 1994, NEAR Laser Rangefinder Digital Processor - Electrical Design Data Package, APL Technical Memorandum No. S2F-94- 0315.
Swenson, T.: 1994, Specification of Microplasma 1064 nm Narrow Band Filter, Application Note, Optical Corporation of America.
Zuber, M. T., Smith, D. E., Cheng, A. F., and Cole, T. D.: 1997, 'The NEAR Laser Ranging Experiment', J. Geophys. Res. - Planets, submitted.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cole, T.D., Boies, M.T., El-Dinary, A.S. et al. The Near-Earth Asteroid Rendezvous Laser Altimeter. Space Science Reviews 82, 217–253 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005056828065
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005056828065