Abstract
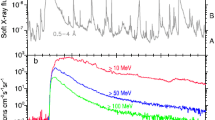
The first X-class flare in four years occurred on 9 July 1996. This X2.6/1B flare reached its maximum at 09:11 UT and was located in active region 7978 (S10° W30°) which was an old-cycle sunspot polarity group. We report the SOHO LASCO/EIT/MDI and SOONSPOT observations before and after this event together with Yohkoh SXT images of the flare, radio observations of the type II shock, and GOES disk-integrated soft X-ray flux during an extended period that included energy build-up in this active region.
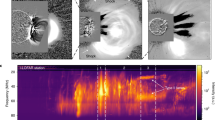
The LASCO coronagraphs measured a significant coronal mass ejection (CME) on the solar west limb beginning on 8 July at about 09:53 UT. The GOES 8 soft X-ray flux (0.1–0.8 nm) had started to increase on the previous day from below the A-level background (10-8 W m-2). At the start time of the CME, it was at the mid-B level and continued to climb. This CME is similar to many events which have been seen by LASCO and which are being interpreted as disruption of existing streamers by emerging flux ropes.
LASCO and EIT were not collecting data at the time of the X-flare due to a temporary software outage. A larger CME was in progress when the first LASCO images were taken after the flare. Since the first image of the 'big' CME was obtained after the flare's start time, we cannot clearly demonstrate the physical connection of the CME to the flare. However, the LASCO CME data are consistent with an association of the flare and the CME. No eruptive filaments were observed during this event.
We used the flare evidence noted above to employ in real time a simplified Shock-Time-of-Arrival (STOA) algorithm to estimate the arrival of a weak shock at the WIND spacecraft. We compare this prediction with the plasma and IMF data from WIND and plasma data from the SOHO/CELIAS instrument and suggest that the flare - and possibly the interplanetary consequences of the 'big' CME - was the progenitor of the mild, high-latitude, geomagnetic storm (daily sum of Kp=16+, Ap=8) on 12 July 1996. We speculate that the shock was attenuated enroute to Earth as a result of interaction with the heliospheric current/plasma sheet.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aurass, H.: 1997, in G. Trottet (ed.), Lecture Notes in Physics, in press.
Aurass, H., Mann, G., Dryer, M., Andrews, M. D., Michels, D. J., and Tappin, S. J.: 1997, 'On Signatures of Nonthermal Particles during CME Acceleration', Proceedings of SOHO V Workshop, ESA Conference Proc., SP-404 in The Corona and Solar Wind near Solar Minimum, pp. 183–187.
Brueckner, G. E., Howard, R. A., Koomen, M. J., Korendyke, G. M., Michels, D. J., Moses, J. D., Socker, D. G., Dere, K. P., Lamy, P. L., Llebaria, A., Bout, M. V., Schwenn, R., Simnett, G. M., Bedford, D. K., and Eyles, C. J.: 1995, Solar Phys. 162, 357.
Bruggmann, G., Benz, A. O., Magun, A., and Stehling, W.: 1990, Astron. Astrophys. 240, 506.
Burkepile, J. T. and St. Cyr, O. C.: 1993, A Revised and Expanded Catalogue of Mass Ejections Observed by the Solar Maximum Mission Coronagraph, NCAR/TN-369+STR, National Center for Atmospheric Research, UCAR, Boulder, CO.
Dryer, M.: 1982, Space Sci. Rev. 33, 233.
Dryer, M.: 1996, Solar Phys. 169, 421.
Dryer, M. and Maxwell, A.: 1979, Astrophys. J. 23, 960.
Dryer, M. and Smart, D. F.: 1984, Adv. Space Res. 4(7), 291.
Fleck, B., Domingo, V., and Poland A. I. (eds.): 1995, Solar Phys. 162, 1.
Garcia, H. A.: 1998, Astrophys. J., in press.
Gosling, J. T.: 1993, J. Geophys. Res. 98, 18937.
Howard, R. A., Sheeley, N. R., Jr., Koomen, M. J., and Michels, D. J.: 1985, J. Geophys. Res. 90, 8173.
Hundhausen, A. J.: 1993, J. Geophys. Res. 98, 13177.
Janardhan, P., Balasubramanian, V., Ananthakrishnan, S., Dryer, M., Bhatnagar, A., and McIntosh, P. S.: 1996, Solar Phys. 166, 379.
Kahler, S. W., Sheeley, N. R., Jr., and Ligget, M.: 1989, Astrophys. J. 344, 1026.
Karlický, M. and Jiřička, K.: 1996, Solar Phys. 163, 171.
Karlický, M. and Odstrčil, D.: 1994, Solar Phys. 155, 71.
Mann, G., Jansen, F., MacDowall, R. J., Kaiser, M., and Stone, R. G.: 1998, Astron. Astrophys., in press.
Manoharan, P. K., Ananthakrishnan, S., Dryer, M., Detman, T. R., Leinbach, H., Kojima, M., Watanabe, T., and Khan, J.: 1995, Solar Phys. 156, 377.
Odstrčil, D., Smith, Z., and Dryer, M.: 1996, Geophys. Res. Lett. 23(18), 2521.
Pick, M., Maia, D., Howard, R., Kerdraon, A., Schwenn, R., Brueckner, G. E., Lamy, P., Paswaters, S., Lanzerotti, L. J., Simnett, G., and Aurass, H.: 1997. 'Joint Nançay Radioheliograph and LASCO Observations of Coronal Mass Ejections', preprint.
Sheeley, N. R., Jr., Wang, Y.-M., Hawley, S. H., Brueckner, G. E., Dere, K. P., Howard, R. A., Koomen, M. J., Korendyke, C. M., Michels, D. J., Paswaters, S. E., Socker, D. G., St. Cyr, O. C., Wang, D., Lamy, P. L., Llebaria, A., Schwenn, R., Simnett, G. M., Plunkett, S., and Biesecker, D. A.: 1997, Astrophys. J. 484, 472.
Simnett, G. M., Tappin, S. J., Plunkett, S. P., Bedford, D. K., Eyles, C. J., St. Cyr, O. C., Howard, R. A., Brueckner, G. E., Michels, D. J., Moses, J. D., Socker, D., Dere, K. P., Korendyke, C. M., Paswaters, S. E., Wang, D., Schwenn, R., Lamy, P., Llebaria, A., and Bout, M. V.: 1997, Solar Phys. 175, 685.
Smith, Z. and Dryer, M.: 1990, Solar Phys. 129, 387.
Smith, Z. K. and Dryer, M.: 1995, The Interplanetary Shock Propagation Model: A Model for Predicting Solar-Flare-Caused Geomagnetic Sudden Impulses Based on the 2–1/2D, MHD Numerical Simulation Results from the Interplanetary Global Model (2D IGM), NOAA Tech. Memo ERL/SEL-89.
Solar Geophysical Data: 1996, Prompt Reports, Part I, Number 626, NOAA National Geophysical Data Center, p. 34.
Solar Geophysical Data: 1997, Prompt Reports, Part II, Number 629, NOAA National Geophysical Data Center, p. 20.
Space Weather Operations: 1996, Preliminary Report 1088, NOAA Space Environment Center, Boulder, CO.
Watanabe, T. and Schwenn, R.: 1989, Space Sci. Rev. 51, 147.
Watanabe, T., Kakinuma, T., Kojima, M., and Schwenn, R.: 1989, Proceedings of the Research Institute of Atmospherics, Nagoya University 36, 11.
Wu, S. T. and Guo, W. P.: 1997, in N. Crooker, J. A. Joselyn, and J. Feynmann (eds.) 'A Self-consistent Numerical Magnetohydrodynamic Model of Helmet Streamer and Flux-rope Interactions: Initiation and Propagation of Coronal Mass Ejections', Coronal Mass Ejections, AGU Geophysical Monograph Series, No. 99, American Geophysical Union, Washington, D.C., p. 83.
Wu, S. T., Guo, W. P., and Wang, J. F.: 1995, Solar Phys. 157, 325.
Wu, S. T., Guo, W. P., and Dryer, M.: 1997, Solar Phys. 170, 265.
Wu, S. T., Guo, W. P., Andrews, M. D., Brueckner, G. E., Howard, R. A., Koomen, M. J., Korendyke, C. M., Michels, D. J., Moses, J. D., Socker, D. G., Dere, K. P., Lamy, P. L., Llebaria, A., Bout, M. V., Schwenn, R., Simnett, G. M., Bedford, D. K., and Eyles, C. J.: 1997, Solar Phys. 175, 719.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
presently at High Altitude Observatory, Boulder, CO80309, U.S.A.
presently at Naval Research Laboratory, Washington DC, 20375, U.S.A.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dryer, M., Andrews, M.D., Aurass, H. et al. The Solar Minimum Active Region 7978, Its X2.6/1B Flare, CME, and Interplanetary Shock Propagation of 9 July 1996. Solar Physics 181, 159–183 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016522812668
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016522812668