Summary
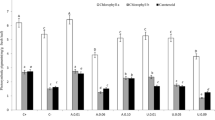
The effects of different nitrogen sources (NH4, NO3, and NH4 NO3) on the uptake of copper by wheat and barley growing in solution culture were compared in three experiments. Both the copper concentration and weight gain of shoots and roots were found to decrease in the order NO3>NH4 NO3>NH4 irrespective of the solution copper concentration. Ammonium nitrogen was also found to decrease the copper concentration of wheat grown on a copper deficient soil compared with a nitrate source of nitrogen.
Increasing concentrations of ammonium ions in solution culture caused ammonium toxicity and reduced both plant copper concentrations and vegetative yield. Biochemical investigations using paper chromatography revealed that the amino acid asparagine was the major detoxification product of ammonia in wheat. Copper deficient plants were found to have elevated levels of amino acids compared with controls, irrespective of the nitrogen source.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blair, G. J., Miller, M. H. and Mitchell, W. A. 1970 Nitrate and ammonium as sources of nitrogen for corn and their influence on the intake of other ions. Agron. J.62, 530–532.
Brown, J. C. and Clark, R. B. 1977 Copper as essential to wheat reproduction. Plant and Soil48, 509–523.
Cox, W. J. and Reisenauer, H. M. 1973 Growth and ion uptake by wheat supplied nitrogen as nitrate, or ammonium, or both. Plant and Soil38, 363–380.
Cox, W. J. and Reisenauer, H. M. 1977 Ammonium effects on nutrient cation absorption by wheat. Agron. J.69, 868–871.
Dijkshoorn, W. and Ismanadja, M. 1972 Nitrogen nutrition of rice plants measured by growth of nutrient content in pot experiments. 3. Change during growth. Neth. J. Agric. Sci.20, 133–144.
van Egmond, F. 1978 Nitrogen nutritional aspects of the ionic balance of plants.In Nitrogen in the Environment. Eds. D. R. Nielsen and J. G. Mac Donald. Vol. 2. Academic Press, New York, USA 528 p.
Fleming, G. A. and Delaney, J. 1961 Copper and nitrogen in the nutrition of wheat on cutaway peat. Ir. J. Agric. Res.1, 81–82.
Gasser, J. K. R. 1961 Transformations, leaching and uptake of fertilizer nitrogen applied in autumn and spring to winter wheat on a heavy soil. J. Sci. Food Agric.12, 375–380.
Gilbert, S. G., Lagasse, F. S., Sims, G. T., Hamilton, J. and Mason, A. 1945 Proc. Am. Tung Oil Ass.11, 55.
Harmsen, G. W. and Kolenbrander, G. J. 1965 Soil inorganic nitrogen.In Soil Nitrogen. Eds. W. V. Bartholomew and F. E. Clark. Am. Soc. Agron. Inc., Wisconsin, USA.
Hewitt, E. J. and Smith, T. A. 1975 Plant Mineral Nutrition The English Universities Press, London, 298 p.
Hiatt, A. J. 1978 Critique of absorption and utilization of ammonium nitrogen by plants.In Nitrogen in the Environment Eds. D. R. Nielsen and J. G. Mac Donald. Vol. 2. Academic Press, New York, USA 528 p.
Hiatt, A. J. and Legget, J. E. 1974In The Plant Root and its Environment. Ed. E. W. Carson p 101 Univ. Press of Virginia, Charlottesville, USA.
Kirkby, E. A. 1968 Influence of ammonium and nitrate nutrition of the cation-anion balance and nitrogen and carohydrate metabolism of white mustard grown in dilute nutrient solutions. Soil Sci.105, 133–141.
Kirkby, E. A. and Hughes A. D. 1970 Some aspects of ammonium and nitrate nutrition in plant metabolism.In Nitrogen Nutrition of the Plant. Ed. E. A. Kirkby, Waverley Press, Leeds.
Kirkby, E. A. and Mengel, K. 1967 Ionic balance in different tissues of tomato plant in relation to nitrate, urea or ammonium nutrition. Plant Physiol.42, 6–14.
Lorenz, H. 1976 Free amino acids in tomato plants in relation to form and concentration of nitrogen in the rooting medium. Plant and Soil45, 163–168.
Matsumoto, H., Wakiuchi, N. and Takehashi, E. 1971 Changes of some mitochondrial enzyme activities of cucumber leaves during ammonium toxicity. Physiol. Plant.25, 353–357.
Mulder, E. J. 1950 Trace Elements in Plant Physiology. Symposium Int. Union Biol. Sci.
Nightingale, G. T. 1948 The nitrogen nutrition of green plants II. Bot. Rev.14, 185–221.
Penning de Vries, F. W. T., Brunsting, A. H. M. and van Laar, H. M. 1974 Products, requirements and efficiency of biosynthesis: A quantitative approach. J. Theor. Biol.45, 339–377.
Pill, W. G. and Lambeth, V. N. 1977 Effect of NH4 and NO3 nutrition with and without pH adjustment on tomato growth, ion composition and water relations. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci.102, 78–81.
Prasad, R., Rajale, G. B. and Lekhdive, B. A. 1971 Nitrification retarders. Adv. Agron.23, 337–383.
Puritch, G. S. and Barker, A. V. 1967 Structure and function of tomato leaf chloroplasts during ammonium toxicity. Plant Physiol.42, 1229–1238.
Rao, K. P. and Rains, D. W. 1976 Nitrate absorption by barley. I. Kinetics. Plant Physiol.57, 55–58.
Raven, J. A. and Smith, F. A. 1976 Nitrogen assimilation and transport in vascular land plants in relation to intracellular pH regulation. New Phytol.76, 415–431.
Reisenauer, H. M. 1978 Absorption and utilization of ammonium nitrogen by plants.In Nitrogen in the Environment. Eds. D. R. Nielsen and J. G. Mac Donald. Vol. 2. Academic Press, New York, USA. 528 p.
Richter, R., Dijkshoorn W. and Vonk, C. R. 1975 Amino acids of barley plants in relation to nitrate, urea or ammonium nutrition. Plant and Soil42, 601–618.
Tills, A. R. and Alloway, B. J. 1981 Subclinical copper deficiency in crops on the Breckland in East Anglia. J. Agric. Sci. Camb. (in the press).
Vines, H. M. and Wedding, R. T. 1960 Some effects of ammonia on plant metabolism and a possible mechanism for ammonia toxicity. Plant Physiol.35, 820–825.
Zadoks, J. C., Chang, T. T. and Konzak, C. F. 1974 A decimal code for the growth stages of cereals. Weed Res.14, 415–421.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tills, A.R., Alloway, B.J. The effect of ammonium and nitrate nitrogen sources on copper uptake and amino acid status of cereals. Plant Soil 62, 279–290 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02374091
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02374091