Abstract
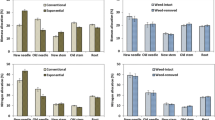
Nutrient loaded and non-loaded Chinese fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata (Lamb) Hook) seedlings were transplanted in a pot trial to examine effects of exponential nutrient loading and fertilization treatments on first season growth and N nutrition. The treatments tested four rates of N (0, 30, 60, and 90 mg tree-1) as a mixed NPK fertilizer applied before planting to create a soil fertility gradient, and two topdressings applied only to non-loaded seedlings later in the season. Nutrient loading alone consistently enhanced seedling growth on the four soil fertility classes, increasing respective biomass and N uptake 42, 45, 20 and 8%, and 65, 67, 29 and 18% more than non-loaded seedlings. The positive response was attributed to increased N retranslocation from higher nutrient reserves built up by loading during nursery culture. Net retranslocation from old shoots to new growth was highest soon after planting when nutrient stress was most severe. Pre-plant soil fertilization and post-plant topdressings were also effective in promoting seedling productivity, but equivalent additions yielded less biomass than that from nutrient loading alone. Implications are that exponential nutrient loading may be more efficient in improving early growth performance of Chinese fir seedlings than traditional field fertilization practices at plantation establishment, and may on competitive sites avoid problems of stimulating surrounding vegetation rather than trees.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burdett A N 1990 Physiological process in plantation establishment and the development of specifications for forest planting stock. Can. J. For. Res. 20, 415–427.
Burdett A N, Herring I J and Thompson C F 1984 Early growth of planted spruce. Can. J. For. Res. 14, 644–651.
Chapin F S III and Moilanen 1991 Nutritional controls over nitrogen and phosphorus resorption from Alaskan birch leaves. Ecology 71, 709–715.
Chen B 1992 Status, causes and improvement strategy of soil degradation in timber plantations. In Research on Site Degradation of Timber Plantation. Eds Division of Forest Ecology, Chinese Society of Forestry. pp 20–26. Chinese Press of Science and Technology, Beijing (in Chinese).
Eastin E F 1978 Use of an AutoAnalyzer for total N determination in plants. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 9, 107–113.
Fan S H, Yu X and Zhong A 1995 Studies on nutrition management of Chinese fir seedling cultivation. J. Fujian Coll. For. 15, 293–300 (in Chinese with English Abstract).
He Z Y and Yu X T 1992 Study on problems of soil degradation in continuously cropped Chinese fir plantation. In Research on Site Degradation of Timber Plantation. Eds Division of Forest Ecology, Chinese Society of Forestry. pp 243–250. Chinese Press of Science and Technology, Beijing (in Chinese).
Hong J S 1994 Selection of superior provenances of Chinese fir for plantations. For. Res. 7, 1–25 (in Chinese with English Abstract).
Huang S 1993 Silvicultural Techniques in China. Chinese Press of Science and Technology, Beijing, China (in Chinese).
Imo I and Timmer V R 1999 Vector competition analysis of black spruce seedling responses to nutrient loading and vegetation control. Can. J. For. Res. 29, 474–486.
Ingestad T and Lund A 1986 Theory and techniques for steady-state mineral nutrition and growth of plants. Scand. J. For. Res. 1, 439–453.
Ingestad T and Ågren G I 1995 Plant nutrition and growth: Basic principles. Plant Soil 168–169, 15–20.
Li Y Q 1992 Study on effects of fertilization on Chinese fir plantation. In Research on Site Degradation of Timber Plantation. Eds Division of Forest Ecology, Chinese Society of Forestry. pp 243–250. Chinese Press of Science and Technology, Beijing (in Chinese).
Lowther J R 1980 Use of a single sulphuric-hydrogen peroxide digest for the analysis of Pinus radiata needles. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 11, 175–188.
Malik V and Timmer V R 1995 Interaction of nutrient loaded black spruce seedlings with neighboring vegetation in greenhouse environments. Can. J. For. Res. 25, 1017–1023.
Malik V and Timmer V R 1996 Growth, nutrient dynamics, and interspecific competition of nutrient-loaded black spruce seedlings on a boreal mixedwood site. Can. J. For. Res. 26, 1651–1659.
Malik V and Timmer. V R 1998. Biomass partitioning and nitrogen retranslocation in black spruce seedlings on competitive mixedwood sites: a bioassay study. Can. J. For. Res. 28, 206–215.
McAlister J A and Timmer V R 1998 Nutrient enrichment of white spruce seedlings during nursery culture and initial plantation establishment. Tree Physiol. 18, 195–202.
Millard P and Proe M F 1993 Nitrogen uptake, partitioning and internal cycling in Picea sitchensis (Bong.) Carr. as influenced by nitrogen supply. New Phytol 125, 113–119.
Munson A D, Margolis H A and Brand D G 1995 Seasonal nutrient dynamics in white pine and white spruce in response to environmental manipulation. Tree Physiol. 15, 141–149.
Nambiar E K S and Fife D N 1991 Nutrient retranslocation in temperate conifers. Tree Physiol. 9, 185–207.
Nambiar E K S and Fife D N 1987 Growth and nutrient retranslocation in needles of radiata pine in relation to nitrogen supply. Ann. Bot. 60, 147–156.
Proe M F and Millard P 1994 Relationships between nutrient supply, nitrogen partitioning and growth in young Sitka spruce (Picea sitchensis). Tree Physiol. 14, 75–88.
SAS Institute, Inc. 1989 SAS/STAT user's guide. SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC.
Sheng W T 1992 Soil degradation and its control techniques for Chinese fir timber plantation. In Research on site degradation of timber plantation. Eds Division of Forest Ecology, Chinese Society of Forestry. pp 49–71. Chinese Press of Science and Technology, Beijing.
Timmer V R 1997 Exponential nutrient loading: a new fertilization technique to improve seedling performance on competitive sites. New Forests 13, 279–299.
Timmer V R and Aidelbaum A S 1996 Manual for exponential nutrient loading of seedlings to improve outplanting performance on competitive forest sites. Natural Resources Canada, Canadian Forest Service, NODA/NFP Tech. Rep. TR-25.
Timmer V R and Munson A D 1991 Site-specific growth and nutrient uptake of planted Picea mariana in the Ontario Clay Belt. IV. Nitrogen loading response. Can. J. For. Res. 21, 1058–1065.
van den Driessche R 1985 Late-season fertilization, mineral nutrient reserves, and retranslocation in planted Douglas-fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii (Mirb.) Franco) seedlings. For. Sci. 31, 485–496.
Xu X J and Timmer V R 1998 Biomass and nutrient dynamics of Chinese fir seedlings under conventional and exponential fertilization regimes. Plant Soil 203, 313–322.
Yu X T 1997 Chinese Fir Silviculture. Fujian Press of Science and Technology, Fuzhou, China (in Chinese).
Zeng L Z, Chen L J and Huang Q L 1994 Soil factors limiting the growth of Chinese fir plantation. J. Fujian Coll. For. 14(1), 11–15 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Q S 1997 Effects of soil extracts from repeated plantation woodland of Chinese-fir on microbial activities and soil nitrogen mineralization dynamics. Plant Soil 191, 205–212.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Timmer, V.R. Growth and nitrogen nutrition of Chinese fir seedlings exposed to nutrient loading and fertilization. Plant and Soil 216, 83–91 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004733714217
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004733714217