Abstract
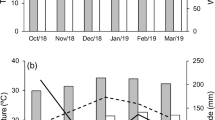
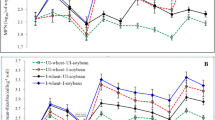
The effect of rice culture on changes in the number of a strain of soybean root-nodule bacteria, (Bradyrhizobium japonicum CB1809), already established in the soil by growing inoculated soybean crops, was investigated in transitional red-brown earth soils at two sites in south-western New South Wales. At the first site, 5.5 years elapsed between the harvest of the last of four successive crops of soybean and the sowing of the next. In this period three crops of rice and one crop of triticale were sown and in the intervals between these crops, and after the crop of triticale, the land was fallowed. Before sowing the first rice crop, the number of Bradyrhizobium japonicum was 1.32×105 g−1 soil. The respective numbers of bradyrhizobia after the first, second and third rice crops were 4.52 ×104, 1.26×104 and 6.40×102 g−1 soil. In the following two years the population remained constant. Thus sufficient bradyrhizobia survived in soil to nodulate and allow N2-fixation by the succeeding soybean crop. At the second site, numbers of bradyrhizobia declined during a rice crop, but the decline was less than when the soil was fallowed (400-fold cf. 2200-fold). Multiplication of bradyrhizobia was rapid in the rhizosphere of soybean seedlings sown without inoculation in the rice bays. At 16 days after sowing, their numbers were not significantly different (p<0.05) from those in plots where rice had not been sown. Nodulation of soybeans was greatest in plots where rice had not been grown, but yield and grain nitrogen were not significantly different (p<0.05). Our results indicate that flooding soil has a deleterious effect on the survival of bradyrhizobia but, under the conditions of the experiments, sufficient B. japonicum strain CB 1809 survived to provide good nodulation after three crops of rice covering a total period of 5.5 years between crops of soybean.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bacon P E and Cooper J L 1985 Effect of rice stubble and nitrogen fertilizer management techniques on yield of wheat sown after rice. Field Crops Res. 10, 241–250.
Bergersen F J, Brockwell J, Gault R R, Morthorpe L, Peoples M B and Turner G L 1989 Effects of available soil nitrogen and rates of inoculation on nitrogen fixation by irrigated soybeans and evaluation of 15N methods for measurement. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 40, 763–780.
Bergersen F J, Turner G L, Chase D L, Gault R R and Brockwell J 1985 The natural abundance of 15N in an irrigated soybean crop and its use for the calculation of nitrogen fixation. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 36, 411–423.
Boonkerd N and Weaver R W 1982 Survival of cowpea rhizobia in soil as affected by soil temperature and moisture. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 43, 585–589.
Brockwell J, Diatloff A, Grassia A and Robinson A C 1975 Use of wild soybean (Glycine ussuriensis Regel and Maack) as a test plant in dilution-nodulation frequency tests for counting Rhizobium japonicum. Soil Biol. Biochem. 7, 305–311
Brockwell J, Roughley R J and Herridge D F 1987 Population dynamics of Rhizobium japonicum strains used to inoculate three successive crops of soybean. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 38, 61–74.
Chapman A L and Meyers R J K 1987 Nitrogen contributed by grain legumes to rice grown in rotation on the Cununurra soils of the Ord irrigation area, Western Australia. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 27, 155–163.
Date R A 1969 A decade of legume inoculant quality control in Australia. J. Aust. Inst. Agric. Sci. 35, 27–37.
De Datta S K 1981 Principles and Practices of Rice Production. John Wiley and Sons, New York. 618p.
Dialoff A and Brockwell J 1976 Ecological studies of root-nodule bacteria introduced into field environments. 4. Symbiotic properties of Rhizobium japonicum and competitive success in nodulation of two Glycine max cultivars by effective and ineffective strains. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. Anim. Husb. 16, 514–521.
Fehr W R, Caviness C E, Bumood D T and Pennington J S 1971 Stage of development descriptions for soybeans, Glycine max (L.) Merrill. Crop Sci. 11, 929–931.
Gibson A H, Curnow B C, Bergersen F J, Brockwell J and Robinson A C 1975 Studies of field populations of Rhizobium. Effectiveness of strains of Rhizobium trifolii associated with Trifolium subterraneum L. pastures in south-eastern Australia. Soil Biol. Biochem. 7, 95–102.
Gibson A H, Demezas D H, Gault R R, Bhuvaneswari T V and Brockwell J 1990 Genetic stability in rhizobia in the field. Plant and Soil 129, 37–44.
Hartley R A, Lawn R J and Byth D E 1993 Genotypic variation in growth and seed yield of soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) in saturated soil culture. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 44, 689–702.
Herridge D F, O'Connell P and Donnelly K 1988 The soybean ureide assay of nitrogen fixation: Sampling procedures and sources of error. J. Exp. Bot. 39, 12–22.
Herridge D F and Peoples M B 1990 Ureide assay for measuring nitrogen fixation by nodulated soybean calibrated by 15N methods. Plant Physiol. 93, 495–503.
Hughes R M and Herridge D F 1989 Effect of tillage on yield, nodulation and nitrogen fixation of soybean in far north-coastal New South Wales. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 29, 671–677.
Lawn R J and Byth D E 1989 Saturated soil culture-a technology to expand the adaptation of soybean. In Proc. of the World Soybean Res. Conf. IV. Ed. A JPascale. pp 576–585. Asociasion Argentine de la Soja, Buenos Aires.
Nathanson K, Lawn R J, de Jabrun P L M and Byth D E 1984 Growth, nodulation and nitrogen accumulation by soybean in saturated soil culture. Field Crops Res. 8, 73–92.
Northcote K H, Hubble G D, Isbell R F, Thompson C H and Bettenay E 1975 A Description of Australian Soils. CSIRO, Melbourne. 170p.
Osa-Afiana L O and Alexander M 1979 Effect of moisture on the survival of Rhizobium in soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 43, 925–930.
Peoples M B, Faizah A W, Rerkasem B and Herridge D F 1989 Methods for Evaluating Nitrogen Fixation by Nodulated Legumes in the Field. ACIAR Monograph No. 11. ACIAR, Canberra. 76p.
Peoples M B, Gault R R, Lean B, Sykes J D and Brockwell J 1995 Nitrogen fixation by soybean in commercial irrigated crops of central and southern New South Wales. Soil Biol. Biochem. 27 (In press).
Sharpe A N and Jackson A K 1972 Stomaching: a new concept in bacteriological sample preparation. Appl. Microbiol. 24, 175–179.
Sykes J D, Morthorpe L J, Gault R R and Brockwell J 1988 Soybean inoculation. NSW Agric. Fish. Agfacts P. 5.2.9. 7p.
Troedson R J, Lawn R J, Byth D E and Wilson G L 1989 Response of field-grown soybean to saturated soil culture. I. Patterns of biomass and nitrogen accumulation. Field Crops Res. 21, 171–187.
Turner G L, Gault R R, Morthorpe L, Chase D L and Bergersen F J 1987 Differences in the natural abundance of 15N in the extractable mineral nitrogen of cropped and fallowed surface soils. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 38, 15–25.
Wang G, Peoples M B, Herridge D F and Rerkasem B 1993 Nitrogen fixation, growth and yield of soybean grown under saturated soil culture and conventional irrigation. Field Crops Res. 32, 257–268.
Weaver R W, Morris D R, Boonkerd N and Sij J 1987 Populations of Bradyrhizobium japonicum in fields cropped with soybean-rice rotations. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 51, 90–92.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roughley, R.J., Gault, R.R., Gemell, L.G. et al. Autecology of Bradyrhizobium japonicum in soybean-rice rotations. Plant Soil 176, 7–14 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00017670
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00017670