Abstract
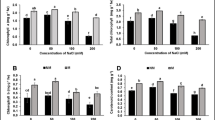
Maize (Zea mays) and sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) were inoculated with a range of VAM fungi and grown under water-stressed and unstressed conditions. There was considerable variation amongst the inocula in their effects on plant growth. Inoculation with Glomus clarum produced the biggest plants in each host, with Glomus monosporum and Acaulospora sp. giving the least growth overall. Root infection produced by the different inocula also varied, but levels were not correlated with effects on plant growth. Water-stress reduced plant growth, with the effects not being altered by mycorrhizal infection. VAM infection levels were not affected by water-stress. Spore production from most inocula was reduced by water-stress, both in total spore numbers and in terms of spores per gram plant weight. Sporulation of G. clarum, G. epigeum and G. monosporum were affected less by stress than were the other inocula. Spore production was in general greater on sorghum than on maize, but the host effect varied amongst the inocula.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott L K and Robson A D 1978 Growth of subterranean clover in relation to the formation of endomycorrhizas by introduced and indigenous fungi in a field soil. New Phytol. 81, 575–585.
Allen M F and Bossalis M G 1983 Effects of two species of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on drought tolerance of winter wheat. New Phytol. 93, 67–76.
Bethlenfalvay G J, Brown M S and Packvsky R S 1982 Parasitic and mutalistic associations between a mycorrhizal fungus and soybean. Phytopathology 72, 889–897.
Busse M D and Ellis J R 1985 Vesicular-arbuscula mycorrhizal (Glomus fasciculatum) influence on soybean drought tolerance in high-phosphorus soil. Can. J. Bot. 63, 2290–2294.
Carling D E and Brown M F 1980 Relative effect of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the growth and yield of soybeans. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 44, 528–532.
Daft M J and Hogarth B 1983 Competitive interaction among four species of Glumus on maize and onions. Tr. Br. Mycol. Soc. 80, 339–345.
Daniels B A and Menge J A 1981 Evaluation of the commercial potential of the V-A mycorrhizal fungus, Glomus epigaeus. New Phytol. 87, 345–354.
Ellis J R, Larsen H J and Boosalis M G 1985 Drought resistance of wheat plants inoculated with vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizae. Plant and Soil 86, 369–378.
Giovanneti M and Mosse B 1980 An evaluation of techniques for measuring vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal infection in roots. New Phytol. 84, 489–500.
Graham J H and Syvertson J P 1984 Influence of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza on the hydraulic conductivity of roots of two citrus rootstocks. New phytol. 97, 277–284.
Hetrick B A D, Gerschefske Kitt D and Thompson W G 1986 The influence of phosphorus fertilisation, drought, fungal species and non-sterile soil on mycorrhizal growth response in tall-grass prairie plants. Can. J. Bot. 64, 1199–1203.
Nelson C E and Safir G R 1982 Increased drought tolerance of mycorrhizal onion plants caused by improved phosphorus nutrition. Planta 154, 407–413.
Phillips J M and Hayman D S 1970 Improved procedures for clearing roots and staining parasitic and vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for rapid assessment of infection. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 55, 158–161.
Sieverding E 1981 Influence of soil water regimes on vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza. 1. Effect on plant growth, water utilisation and development of mycorrhiza. Z. Acker-Pflanzenb. 150, 400–411.
Sieverding E 1983 Influence of soil regimes on vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza. 2. Effect of soil temperature and water regime on growth, nutrient uptake and water utilisation of Eupatorium odoratum. Z. Acker-Pflanzenb. 152, 56–67.
Son C L and Smith S E 1988 Mycorrhizal growth responses: Interactions between photon irradiance and phosphorus nutrition. New Phytol. 108, 305–314.
Stahl P D and Smith W K 1984 Effects of different geographical isolates of Glomus on the water relations of Agropyron smithii. Mycologia 76, 261–267.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simpson, D., Daft, M.J. Interactions between water-stress and different mycorrhizal inocula on plant growth and mycorrhizal development in maize and sorghum. Plant Soil 121, 179–186 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00012310
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00012310