Abstract
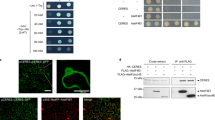
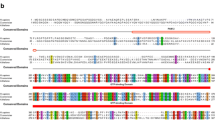
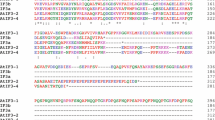
The eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) emerged recently as a target for different types of regulation affecting translation. In animal and yeast cells, eIF4E-binding proteins modulate the availability of eIF4E. A search for plant eIF4E-binding proteins from Arabidopsis thaliana using the yeast genetic interaction system identified a clone encoding a lipoxygenase type 2 (AtLOX2). In vitro and in vivo biochemical assays confirm an interaction between AtLOX2 and plant eIF4E(iso) factor. A two-hybrid assay revealed that AtLOX2 is also able to interact with both wheat initiation factors 4E and 4E(iso). Deletion analysis maps the region of AtLOX2 involved in interaction with AteIF(iso)4E between amino acids 175 and 232. A sequence related to the conserved motif present in several eIF4E-binding proteins was found in this region. Furthermore, the wheat p86 subunit, a component of the plant translation eIF(iso)4F complex, was found to interfere with the AteIF(iso)4E-AtLOX2 interaction suggesting that p86 and AtLOX2 compete for the same site on eIF(iso)4E. These results may reflect a link between eIF4Es factors mediating translational control with LOX2 activity, which is probably conserved throughout the plant kingdom.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altmann, M., Schmitz, N., Berset, C. and Trachsel, H. 1997. A novel inhibitor of cap-dependent translation initiation in yeast: p20 competes with the eIF4G for binding to eIF4E. EMBO J. 16: 1114–1121.
Bartel, P.L., Chien, C., Sternglanz, R. and Fields, S. 1993. Using the two hybrid system to detected protein-protein interactions. In: D.A. Hartley (Ed.) Cellular Interactions in Development: A Practical Approach, IRL Press. Oxford, UK, 153–179.
Bell, E. and Mullet, J.E. 1993. Characterization of an Arabidopsis lipoxygenase gene response to methyl jasmonate and wounding. Plant Physiol. 103: 1133–1137.
Bell, E., Creelman, R. and Mullet, J. 1995. A chloroplastic lipoxygenase is required for wound-induced jasmonic acid accumulation in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92: 8675–8679.
Benichou, S., Bomsel, M., Bodeus, M., Durand, H., Doute, M., Letourneur, F., Camonis, J. and Benarous, R. 1994. Physical interaction of the HIV-1 Nef protein with ?-COP, a component of non-clathrin-coated vesicles essential for membrane traffic J. Biol. Chem. 269: 30073–30076.
Boyer, H. and Roulland-Dussoix, D. 1969. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 41: 459–472.
Breeden, L. and Nasmyth, K. 1985. Regulation of the yeast Ho gene. Cold Spring Symp. Quant. Biol. 50: 643–650.
Browning, K.S. 1996. The plant translation apparatus. Plant Mol. Biol. 32: 107–144.
Browning, K.S., Webster, C., Roberts, J.K.M. and Ravel, J.M. 1992. Identification of an isozyme from protein synthesis initiation factor 4F in plants. J. Biol. Chem. 267: 10096–10100.
Boutry, M., Nagy, F., Poulsen, C., Aoyagi, K. and Chua, N. 1987. Targeting of bacterial chloramphenicol acethyltransferase to mitocondria in transgenic plants. Nature 328: 340–342.
Creelman, R.A. and Mullet, J.E. 1997. Biosynthesis and action of jasmonates in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 48: 355–381.
Durfee, T., Becherer, K., Chen, P.L., Yeh, S.H., Yang, Y., Kilburn, A.E., Lee, W.H. and Elledge, S.J. 1993. The retinoblastoma protein associates with the protein phophatase type 1 catalytic subunit. Genes Dev. 4: 555–569.
Fields, S. and Song, O. 1989. A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature 340: 245–246.
Gietz, D., Jean, A.S., Woods, R.A. and Schiestl, R.H. 1992. Improved method for high efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells. Nucl. Acids Res. 20: 1425.
Gorschen, E., Dunaeva, M., Reech, I. and Wasternack, C. 1997. Overexpression of the jasmonate-inducible 23 kDa protein (JIP23) from barley in transgenic tobacco leads to the repression of leaf proteins. FEBS Lett. 419: 58–62
Jackson, R.J. and Wickens, M. 1997. Translation controls impinguing on the 5'-untranslated region and initiation factor proteins. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 7: 233–241.
Laemmli, U.K. 1970. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685.
Lawrence, J.C. Jr. and Abraham, R.T. 1997. PHAS/4E-BPs as regulators of mRNA translation and cell proliferation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 22: 345–349.
Marcotrigiano, J., Gringas, A.-C., Sonenberg, N. and Burley, S.K. 1997. Cocrystal structure of the messenger RNA 5' cap-binding protein (eIF4E) bound to 7-methyl-GDP. Cell 89: 951–961.
Merrick, W.C. and Hershey, J.W.B. 1996. The pathway and mechanism of proteins synthesis. In: J.W.B. Hershey, M.B. Mathews and N. Sonenberg (Eds.) Translational Control, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Plainview, NY, pp. 31–70.
Metz, A.M. and Browning, K.S. 1996. Mutational analysis of the functional domains of the large subunit of the isozyme form of wheat initiation factor eIF4F. J. Biol. Chem. 271: 31033–31036.
Mould R. and Robinson C. 1991. A proton gradient is required for the transport of two lumenal oxygen-evolving proteins across the thylakoid membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 266: 12189–12193.
Morley, S.J., Curtis, P.S. and Pain, V.M. 1997. eIF4G: translation's mystery factor begins to yield its secrets. RNA 3: 1085–1104.
Pain, V.M. 1996. Initiation of protein synthesis in eukaryotic cells. Eur. J. Biochem 236: 747–771.
Pause, A., Belsham, G.J., Gringas, A.-C., Donze, O., Lin, T.A., Lawrence, J.C. Jr. and Sonenberg, N. 1994. Insulin-dependent stimulation of protein synthesis by phosphorylation of a regulator of 5'-cap function. Nature 371: 762–767.
Poulin, F., Gringas, A.-C., Olsen, H., Chevalier, S. and Sonenberg, N. 1998. 4E-BP3, a new member of the eukaryotic initiation factor 4E-binding protein family. J. Biol. Chem. 273: 14002–14007.
Provost, P., Samuelson, B. and Radmark, O. 1999. Interaction of 5-lipoxygenase with cellular proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96: 1881–1885.
Ptushkina, M., van der Haar, T., Vasilescu, S., Frank, R., Birkenhager, R. and McCarthy, J.E.G. 1998. Cooperative modulation by eIF4G of eIF4E-binding to the mRNA 5' cap in yeast involves a site partially shared by p20. EMBO J. 17: 4798–4808.
Reinbothe, S., Reinbothe, C., Heintzen, C., Seidenbecher, C. and Parthier, B. 1993a. A methyl jasmonate-induced shift in the length of the 5' untranslated region impairs translation of the plastid rbcL transcript in barley. EMBO J. 12: 1505–1512.
Reinbothe, S., Reinbothe, C. and Parthier, B. 1993b. Methyl jasmonate represses translation initiation of a specific set of mRNAs in barley. Plant J. 4: 459–467.
Reinbothe, S., Reinbothe, C. and Parthier, B. 1993c. Methyl jasmonate-regulated translation of nuclear-encoded chloroplast proteins in barley (Hordeum vulgare L. cv. Salome). J. Biol. Chem. 268: 10606–10611.
Reinbothe, S., Reinbothe, C., Lehmann, J., Becker, W., Apel, K. and Parthier, B. 1994a. JIP60, amethyl jasmonate-induced ribosomeinactivating protein involved in plant stress reactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 7012–7016.
Reinbothe, S., Mollenhauer, B. and Reinbothe, C. 1994b. JIPs and RIPs: the regulation of plant gene expression by jasmonates in response to environmental cues and pathogens. Plant Cell 6: 1197–1209.
Rodriguez, C., Freire, M.A., Camilleri, C. and Robaglia, C. 1998. The Arabidopsis thaliana cDNAs coding for eIF4E and eIF4(iso)4E are not functionally equivalent for yeast complementation and are differentally expressed during plant development. Plant J. 13: 465–473.
Rosenwald, I.B. 1996. Deregulation of protein synthesis as a mechanism of neoplastic transformation. Bioessays 18: 243–250.
Ruud, K.A., Kulhow, C., Goss, D.J. and Browning, K.S. 1998. Identification and characterization of a novel cap-binding protein from Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Biol. Chem 273: 10325–10330.
Sachs, A.B., Sarnow, P. and Hentze, M.W. 1997. Starting at the beginning, middle, and end: translation initiation in eukaryotes. Cell 89: 831–838.
Sembdner, G. and Parthier, B. 1993. The biochemistry and the physiological and molecular actions of jasmonates. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 44: 569–589.
Siedow, J. 1991. Plant lipoxygenase: structure and function. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 42: 145–188.
Sonenberg, N. 1996. mRNA 5' cap-binding protein eIF4E and control of the cell growth. In: J.W.B. Hershey, M.B. Mathew and N. Sonenberg (Eds.) Translational Control, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Plainview, NY, pp. 245–270.
Sonenberg, N. and Gringas, A. 1998. The mRNA 5' cap-binding protein eIF4E and control of cell growth. Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol. 10: 268–275.
Tirode, F., Malaguti, C., Romero, F., Attar, R., Camonis, J. and Egly, J.M. 1997. A conditionally expressed third partner stabilizes or prevents the formation of a transcriptional activator in a threehybrid system. J. Biol. Chem. 272: 22995–22999.
Vojtek, A.B., Hollenberg, S.M. and Cooper, J.A. 1993. Mammalian Ras interacts directly with the serine/threonine kinase Raf. Cell 74: 205–214.
Wittmann, S., Chatel, H., Fortin, M.G. and Laliberté, J.F. 1997. Interaction of the viral protein genome linked of turnip mosaic potyvirus with the translational eukaryotic initiation factor (iso) 4E of Arabidopsis thaliana using the yeast two-hybrid system. Virology 234: 84–92.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Freire, M.A., Tourneur, C., Granier, F. et al. Plant lipoxygenase 2 is a translation initiation factor-4E-binding protein. Plant Mol Biol 44, 129–140 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006494628892
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006494628892