Abstract
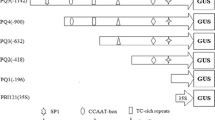
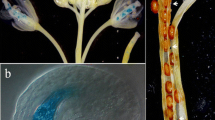
A genomic DNA fragment containing the 5′-upstream sequence and part of the open reading frame corresponding to Triticum aestivum puroindoline-b cDNA, was isolated by inverse PCR. Promoter fragments extending to −1068, −388, −210 or −124 upstream of the translation initiation ATG codon and the sequence coding for the first 13 amino acids of the puroindoline-b, were translationally fused to the uidA reporter gene encoding β-glucuronidase and transferred to rice calli via particle bombardment-mediated transformation. The 1068 bp and 124 bp promoters were also transcriptionally fused to the uidA reporter gene. Out of the 196 plants regenerated from transformed rice calli, 118 plants set seeds. No GUS activity was detectable in the stems, roots, leaves or pollen of the transgenic rice which had integrated the puroindoline-b promoter or its deletions; GUS activity was detected only in seeds, except in those having integrated the 124 bp promoter. Within seeds, histological localisation showed GUS activity as being restricted to the endosperm, aleurone cells and pericarp cell layers; no GUS activity was detected in the embryonic axis. Analysis of 5′ promoter deletions identified the region between −388 and −210 as essential for endosperm expression, and the region between −210 and −124 as essential for expression in the epithelium of the scutellum. No difference of expression was observed between the translational and transcriptional fusion genes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen RD, Bernier F, Lessard P, Beachy RN: Nuclear factors interact with a soybean β-conglycinin enhancer. Plant Cell 1: 623–631 (1989).
Ayres NM, Park WD: Genetic transformation of rice. Cri Rev Plant Sci 13: 219–239 (1994).
Barcelo P, Hagel C, Becker D, Martin A, Lörz H: Transgenic cereal (Tritordeum) plants obtained at high efficiency of microprojectile bombardment of inflorescence tissue. Plant J 5: 583–592 (1994).
Bettge AD, Morris CF, Greenblatt GA: Assessing genotypic softness in single wheat kernels using starch granuleassociated friabilin as a biochemical marker. Euphytica 86: 65–72 (1995).
Blackwell T, Weintraub H: Differences and similarities in DNA-binding preferences of MyoD and E2A protein complexes revealed by binding site selection. Science 250: 1104–1110 (1990).
Blochet JE, Chevalier C, Forest E, Pebay-Peyroula E, Gautier MF, Joudrier P, Pézolet M, Marion D: Complete amino acid sequence of puroindoline, a new basic and cystine-rich protein with a unique tryptophan-rich domain, isolated from wheat endosperm by Triton X114 phase partitioning. FEBS Lett 329: 336–340 (1993).
Brethnach R, Chambon P: Organization and expression of eukaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem 50: 349–384 (1981).
Christou P: Transformation technology. Trends Plant Sci 12: 423–431 (1996).
Clark DC, Wilde PJ, Marion D: The protection of beer foam from against lipid-induced destabilization. J Inst Brew 100: 23–25 (1994).
Dubreil L, Quillien L, Legoux MA, Compoint JP, Marion D: Variability and localization of wheat kernel indolines and lipid transfer proteins. In: Proceedings of the International Meeting on 'Wheat Kernel Proteins Molecular and Functional Aspects', (Viterbo, Italy), pp. 331–333 (1994).
Dubreil L, Compoint JP, Marion D: Interaction of puroindolines with wheat flour polar lipids determines their foaming properties. J Agric Food Chem 45: 108–116 (1997).
Dynan WS, Tjian R: Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence specific DNA-binding proteins. Nature 316: 774–778 (1985).
Ellerström M, Stalberg K, Ezcurra I, Rask L: Functional dissection of a napin gene promoter: identification of promoter elements required for embryo and endosperm-specific transcription. Plant Mol Biol 32: 1019–1027 (1996).
Fauquet CM, Zhang S, Chen L, Marmey P, de Kochko A, Beachy RN: Biolistic transformation of rice: now efficient and routine for japonica and indica rices. In: Khush GS (ed) Proceedings of the Third International Rice Genetics Symposium, pp. 153–165 (1996).
Finnegan J, McElroy D: Transgene inactivation: plants fight back! Bio/technology 12: 883–888 (1994).
Foster R, Izawa T, Chua NH: Plant bZIP proteins gather at ACGT elements. FASEB J 8: 192–200 (1994).
Gallusci P, Salamini F, Thompson RD: Differences in cell type-specific expression of the gene Opaque 2 in maize and transgenic tobacco. Mol Gen Genet 244: 391–400 (1994).
Gautier MF, Aleman ME, Guirao A, Marion D, Joudrier P: Triticum aestivum puroindolines two cDNA sequence analysis and developmental gene expression. Plant Mol Biol 25: 43–57 (1994).
Goldberg RB: Regulation of plant gene expression. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 314: 343–353 (1986).
Greenblatt GA, Bettge AD, Morris CF: Relationship between endosperm texture and the occurence of friabilin and bound polar lipids on wheat starch. Cereal Chem 72: 172–176 (1995).
Greenwell P, Schofield JD: A starch granule protein associated with endosperm softness in wheat. Cereal Chem 63: 379–380 (1986).
Grosset J, Alary R, Gautier MF, Menossi M, Martinez-Izquierdo JA, Joudrier P: Characterization of barley genes coding for an α-amylase inhibitor subunit (CMd protein) and analysis of promoter in transgenic tobacco plants and in maize kernels by microprojectile bombardment. Plant Mol Biol 34: 331–338 (1997).
Hirano HY, Tabayashi N, Matsumura T, Tanida M, Komeda Y, Sano Y: Tissue-dependent expression of the rice wx+ gene promoter in transgenic rice and petunia. Plant Cell Physiol 36: 37–44 (1995).
Jefferson RA: Assaying chimeric genes in plants the GUS gene fusion system. Plant Mol Biol Rep 5: 387–405 (1987).
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW: GUS fusions: β-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6: 3901–3907 (1987).
Jolly CJ, Rahman S, Kortt AA, Higgins TJV: Characterization of grain-softness protein a marker of endosperm texture in wheat. In: Procedings of 40th Australian Cereal Chemistry Conference (Albury, Australia), pp. 92–95 (1990).
Jolly C, Rahman S, Kortt AA, Higgins TJV: Characterization of the wheat Mr 15 000 'grain-softness-protein' and analysis of the relationship between its accumulation in the whole seed and grain softness. Theor Appl Genet 86: 589–597 (1993).
Kawagoe Y, Murai N: Four distinct nuclear proteins recognize in vitro the proximal promoter of the bean storage protein β-phaseolin gene conferring spatial and temporal control. Plant J 2: 927–936 (1992).
Kim SY, Wu R: Multiple protein factors bind to a rice glutelin promoter region. Nucl Acids Res 8: 6845–6852 (1990).
Klimyuk VI, Caroll BJ, Thomas CM, Jones DG: Alkali treatment for rapid preparation of plant material for reliable PCR analysis. Plant J 3: 493–494 (1993).
Law CN, Young CF, Brown JWS, Snape JW, Worland AJ: The study of grain-protein control in wheat using whole chromosome substitution lines. In: Seed Protein Improvement by Nuclear Techniques, pp. 483–502. International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna (1978).
Leisy DJ, Hnilo J, Zhao Y, Okita TW: Expression of a rice glutelin promoter in transgenic tobacco. Plant Mol Biol 14: 41–50 (1989).
Marion D, Gautier MF, Joudrier P, Ptak M, Pézolet M, Forest E, Clark DC, Broekaert W: Structure and function of wheat lipid binding proteins. In: Proceedings of International Meeting on 'Wheat Kernel Proteins Molecular and Functional Aspects' (Viterbo, Italy), pp. 175–180 (1994).
Martoja R, Martoja M: Initiation aux Techniques de l'Histologie Animale. Masson et Cie, Paris (1967).
Mattern PJ, Morris R, Schmidt JW, Johnson VA: Locations of genes for kernel properties in the wheat variety 'Cheyenne' using chromosome substitution lines. In: Proceedings of 4th International Wheat Genetic Symposium (Columbus, MO), pp. 703–707 (1973).
Morton RL, Quiggin D, Higgins TJV: Regulation of seed storage protein gene expression. In: Kigel J, Galili G (eds) Seed Development and Germination, pp. 103–136. Marcel Dekker, New York/Basel/Hong Kong (1995).
Motto M, Di Fonzo N, Hartings H, Maddaloni M, Salamini F, Soave C, Thompson RD: Regulatory genes affecting maize storage protein synthesis. Oxford Surv Plant Mol Cell Biol 6: 87–114 (1989).
Murre C, McCaw PS, Baltimore D: A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding daughterless MyoD and myc proteins. Cell 56: 777–783 (1989).
Ochman H, Gerber AS, Hartl DL: Genetic application of an inverse polymerase chain reaction. Genetics 120: 621–625 (1988).
Oda S, Schofield JD: Characterization of friabilin polypeptides. J Cereal Sci 26: 29–36 (1997).
Rahman S, Jolly CJ, Skerritt JH, Wallosheck A: Cloning of a wheat 15 kDa grain softness protein (GSP) GSP is a mixture of different puroindoline-like polypeptides. Eur J Biochem 223: 917–925 (1994).
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR: DNA sequencing with chain terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74: 5463–5467 (1977).
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T: Molecular Cloning a LaboratoryManual, 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor NY (1989).
Sourdille P, Perretant MR, Charmet G, Leroy P, Gautier MF, Joudrier P, Nelson JC, Sorrells ME, Bernard M: Linkage between RFLP markers and genes affecting kernel hardness in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 93: 580–586 (1996).
Takaiwa F, Oono K: Interaction of an immature seed-specific trans-acting factor with the 5′ upstream region of a rice glutelin gene. Mol Gen Genet 224: 289–293 (1990).
Takaiwa F, Oono K, Kato A: Analysis of the 5′ flanking region responsible for the endosperm-specific expression of a rice glutelin chimeric gene in transgenic tobacco. Plant Mol Biol 16: 49–58 (1991).
Thomas MS, Flavell RB: Identification of an enhancer element for the endosperm-specific expression of high molecular weight glutenin. Plant Cell 2: 1171–1180 (1990).
Thompson RD, Bartels D, Harberd NP, Flavell RB: Characterization of the multigene family coding for HMWglutenin subunits in wheat using cDNA clones. Theor Appl Genet 67: 87–96 (1983).
Wan Y, Lemaux PG: Generation of large numbers of independently transformed fertile barley plants. Plant Physiol 104: 37–48 (1994).
Wilde PJ, Clarck DC, Marion D: Influence of competitive adsorption of a lysopalmitoylphosphatidylcholine on the functional properties of puroindoline a lipid-binding protein isolated from wheat flour. J Agric Food Chem 41: 1570–1576 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Digeon, Jf., Guiderdoni, E., Alary, R. et al. Cloning of a wheat puroindoline gene promoter by IPCR and analysis of promoter regions required for tissue-specific expression in transgenic rice seeds. Plant Mol Biol 39, 1101–1112 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006194326804
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006194326804