Abstract
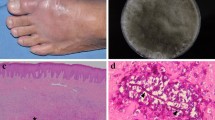
Cutaneous phaeohyphomycosis due to E. jeanselmei developed on the sole of a 61 years old Japanese female who was receiving the corticoids therapy for nephrotic syndrome. Although the causative fungus was resistant to 5-fluorocytosine, amphotericin B and ketoconazole, the lesion was successfully treated by surgical excision.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carmichael, J. W., 1966. Cerebral mycetoma of trout due to a Phialophora-like fungus. Sabouraudia 5: 120–123.
Fukushiro, R., 1977. Some consideration on infections by dematiaceous fungi, with special regard to chromomycosis. Japan. J. Med. Mycol. 18: 398–421.
Hoog, G. S. de & Hermanides-Nijhof, E. J., 1977. The black yeasts and allied hyphomycetes. Stud. Mycol. 15, Centraalbureau voor Schimmercultures, Barrn.
Katz, B. & McGinnis, M. R., 1980. A new species of Exophiala recovered from loblolly pine litter. Mycotaxon 11: 182–184.
McGinnis, M. R., 1978. Human pathogenic species of Exophiala, Phialophora, and Wangiella. PAHO Sci. Pub. No. 356, p. 37–59.
McGinnis, M. R., 1979. Taxonomy of Exophiala werneckii and its relationship to Microsporum mansonii. Sabouraudia 17: 145–154.
McGinnis, M. R. & Ajello, L., 1974. A new species of Exophiala isolated from channel catfish. Mycologia 66: 518–520.
McGinnis, M. R. & Padhye, A. A., 1977. Exophiala jeanselmei, a new combination for Phialophora jeanselmei. Mycotaxon 5: 341–352.
McGinnis, M. R., Sorrell, D. F., Miller, R. L. & Kaminski, G. W., 1981. Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by Exophiala moniliae. Mycopathologia 73: 69–72.
Nielsen, H. S. & Conant, N. F., 1968. A new human pathogenic Phialophora. Sabouraudia 6: 228–231.
Nishimura, K. & Miyaji, M., 1981. Annellated conidiogenous cells in Exophiala dermatitidis, agent of phaeohyphomycosis. Mycologia 73: 1181–1183.
Shadomy, S. & Espinel-Ingroff, A., 1974. Susceptibility testing of antifungal agents, p. 569–574. In: E. H. Lennette, E. H. Spaulding and J. P. Truant (eds.). Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 2nd ed., American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D.C.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hironaga, M., Mochizuki, T. & Watanabe, S. Cutaneous phaeohyphomycosis of the sole caused by Exophiala jeanselmei and its susceptibility to amphotericin B, 5-FC and ketaoconazole. Mycopathologia 79, 101–104 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00468086
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00468086