Abstract
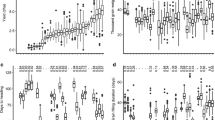
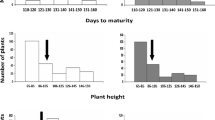
Three previously identified grain yield quantitative trait loci (QTL) on chromosomes 2S(2HS), 3C(3HC) and 5L(1HL), designated QTL-2S, QTL-3 and QTL-5L, respectively, were evaluated for their potential to increase yields of high-quality malting barley without disturbing their favorable malting quality profile. QTL mapping of yield related traits was performed and near-isogenic lines (NILs) were developed. QTL for plant height, head shattering, seed weight and number of rachis nodes/spike were detected in the QTL-3 region. NILs developed by introgressing QTL-3 from the high-yielding cv. Steptoe to the superior malting quality, moderate-yielding cv. Morex acquired reduced height, lodging and head shattering features of Steptoe without major changes in malting quality. The yield of NILs, measured by minimizing the losses due to lodging and head shattering, did not exceed that of Morex. Steptoe NILs, with the Morex QTL-2S region, flowered 10 days later than Steptoe but the grain yield was not changed. None of the 3 QTL studied altered the measured yield of the recipient genotype, per se, although QTL 2S and QTL-3 affected yield-related traits. We conclude that these yield QTL must interact with other genes for full expression. Alternatively, they affect the harvestable yield through reduced lodging, head shattering, and/or altered flowering time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Society of Brewing Chemists: Methods of Analysis, 8th ed (Kneen E, ed.). American Society of Brewing Chemists, St. Paul, MN (1992).
Anderson MK, Reinbergs E: Barley breeding. In: Rasmusson DC (Ed.) Barley, Agronomy Series Monograph 26, pp. 231-268. ASA-CSSA-SSSA Publishers, Madison, WI (1985).
Backes G, Graner A, Horoughi-Wehr G, Fishbeck G, Wenzel G, Jahoor A: Localization of quantitative trait loci for agronomic important characters by the use of a RFLP map in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor Appl Genet 90: 294-302 (1995).
Bezant J, Laurie D, Prachett N, Chojecki J, Kearsey M: Marker regression mapping of QTL controlling flowering time and plant height in a spring barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) cross. Heredity 77: 64-73 (1996).
Bezant J, Laurie D, Prachett N, Chojecki J, Kearsey M: Mapping QTL controlling yield and yield components in a spring barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) cross using marker regression. Mol Breed 3: 29-38 (1997).
Churchill GA, Doerge RW: Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 138: 963-971 (1994).
Haley CS, Knott SA: A simple regression method for mapping quantitative trait loci in line crosses using flanking markers. Heredity 69: 315-324 (1992).
Han F, Ullrich SE: Mapping of quantitative trait loci associated with malting quality in barley. Barley Genet Newsl 23: 84-97 (1993).
Hayes PM, Iyamabo O, North American Barley Genome Mapping Project: Summary of QTL effects in the Steptoe × Morex population. Barley Genet Newsl 23: 98-143 (1993).
Hayes PM, Liu BH, Knapp SJ, Chen F, Jones BL, Blake T, Franckowiak J, Rasmusson D, Sorrells M, Ullrich SE, Wesenberg DM, Kleinhofs A: Quantitative trait locus effects and environmental interaction in a sample of North American barley germplasm. Theor Appl Genet 87: 392-401 (1993).
Hayes PM, Chen FQ, Kleinhofs A, Kilian A, Mather DE: Barley genome mapping and its applications. In: Jahuar PP (Ed.) Methods of Genome Analysis, pp. 229-249. CRC press, Fargo, ND (1996).
Karsai I, Mezsaros K, Hayes PM, Bedo Z: Effects of loci on chromosomes 2(2H) and 7(5H) on developmental patterns in barley under different photoperiod regimes. Theor Appl Genet 94: 612-618 (1997).
Kjaer B, Haahr V, Jensen J: Associations between 23 quantitative traits and 10 genetics markers in a barley cross. Plant Breeding 106: 261-274 (1991).
Kjaer B, Jensen J, Giese H: Quantitative trait loci for heading date and straw characters in barley. Genome 38: 1098-1104 (1995).
Kleinhofs A, Kilian A, Saghai-Maroof MA, Biyashev RM, Hayes P, Chen FQ, Lapitan N, Fenwick A, Blake TK, Kanazin V, Ananiev E, Dahleen L, Kudrna DA, Bollinger J, Knapp SJ, Liu B, Sorrells M, Heun M, Franckowiak JD, Hoffman D, Skadsen R, Steffenson BJ: A molecular, isozyme and morphological map of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) genome. Theor Appl Genet 86: 705-712 (1993).
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newburg L: MAPMAKER: An interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1: 174-181 (1987).
Larson SR, Kadyrzhanova D, McDonald C, Sorrells M, Blake TK: Evaluation of barley chromosome-3 yield QTLs in a backcross of F2 population using STS-PCR. Theor Appl Genet 93: 618-625 (1996).
Larson SR, Habernicht DK, Blake TK: Backcross gains for six-rowed grain and malt qualities with introgression of a feed barley yield QTL. J Am Soc Brew Chem 55: 52-57 (1997).
Laurie DA, Prachett N, Romero C, Simpson E, Snape JW: Assignment of the denso dwarfing gene to the long arm of chromosome 3(3H) of barley by use of RFLP markers. Plant Breed 111: 198-203 (1993).
Laurie DA, Prachett N, Bezant JH, Snape JW: Genetic analysis of a photoperiod response gene on the short arm of chromosome 2(2H) of Hordeum vulgare (barley). Heredity 72: 619-627 (1994).
Laurie DA, Prachett N, Bezant JH, Snape JW: RFLP mapping of five major genes and eight QTL controlling flowering time in a winter × spring Hordeum vulgare L. cross. Genome 38: 575-585 (1995).
Mather DE, Tinker NA, LaBerge DE, Edney M, Jones BL, Rossnagel GG, Legge WG, Briggs KG, Irvine RB, Kasha KJ: Regions of the genome that affects grain and malt quality in a North American two-row barley cross. Crop Sci 37: 544-554 (1997).
Nedel JL, Ullrich SE, Clancy JA, Pan WL: Barley semidwarf and standard isotype yield and malting quality response to nitrogen. Crop Sci 33: 258-263 (1993).
Oziel A: Mapping of quantitative trait loci for malting quality in a winter x spring barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) cross. M.Sc. thesis. Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR (1993).
Peterson GA, Foster AE: Malting barley in the United States. Adv Agron 25: 327-378 (1973).
Powell W, Caligari PDS, Thomas WTB, Jinks JL: The effects of major genes on quantitatively varying characters in barley. 2. The denso and deylength response loci. Heredity 54: 349-352 (1985).
Powell W, Thomas WTB, Baird E, Lawrance P, Booth A, Harrower B, McNicol JW, Waugh R: Analysis of quantitative traits in barley by the use of amplified fragment length polymorphism. Heredity 79: 48-59 (1997).
Romagosa I, Han F, Ullrich SE, Hayes PM, Wesenberg DM: Verification of yield QTL through realized molecular marker assisted selection responses in a barley cross. Mol Breed 5: 143-152 (1999).
SAS Institute: SAS user's guide. Statistics, Version 6.10. SAS Inst., Cary, NC (1991).
Steel RGD, Torrie JH, Dickey DA: Principles and Procedures of Statistics: A Biometrical Approach. 3rd ed. McGraw-Hill, New York (1997).
Stracke S, Borner A: Molecular mapping of the photoperiod response geneea7 in barley. Theor Appl Genet 97: 797-800 (1998).
Thomas WTB, Powell W, Waugh R, Chalmers KJ, Barua UM, Jack P, Lea V, Forster BF, Swanston JS, Ellis RP, Hanson PR, Lance RCM: Detection of quantitative trait loci for agronomic, yield, grain and disease characters in spring barley. Theor Appl Genet 91: 1037-1047 (1995).
Tinker NA, Mather DE, Rossnagel BG, Kasha KJ, Kleinhofs A, Hayes PM, Falk DE, Ferguson T, Shugar LP, Legge WG, Irvine RB, Choo TM, Briggs KG, Ullrich SE, Franckowiak JD, Blake TK, Graf RJ, Dofing SM, Saghai Maroof MA, Scoles GJ, Hoffman D, Dahleen LS, Kilian A, Chen F, Biyashev RM, Kudrna DA, Steffenson BJ: Regions of the genome that affect agronomic performance in two row barley. Crop Sci 36: 1053-1062 (1996).
Tinker NA, Mather DE: Methods for QTL analysis with progeny replicated in multiple environments. J Quant Trait Loci (http://probe.nalusda.gov:8000/otherdocs/-jqtl/1995-01/jqtl15.html) (1995).
Tinker NA, Mather DE: MQTL software for simplified composite interval mapping of QTL in multiple environments. J Quant Trait Loci (http://probe.nalusda.gov:8000/otherdocs/-jqtl/1995-02/jqtl16r2.html) (1995).
Traore A: Quantitative trait locus mapping of yield and yield components in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). M.Sc. thesis, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR (1993).
Zhu H, Briceno G, Dovel R, Hayes PM, Liu BH, Liu CT, Ullrich SE: Molecular breeding for grain yield in barley: an evaluation of QTL effects in a spring barley cross. Theor Appl Genet 98: 772-779 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kandemir, N., Jones, B.L., Wesenberg, D.M. et al. Marker-assisted analysis of three grain yield QTL in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) using near isogenic lines. Molecular Breeding 6, 157–167 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009602514106
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009602514106