Abstract
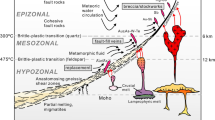
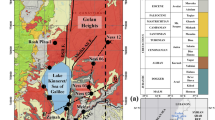
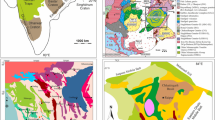
A submersible study of a fast spreading (12 cm yr-1) Mid-Ocean ridge segment (East Pacific Rise near 12°50′ N) led to the discovery of intense hydrothermal activity. Twenty four sites with active vents and sixty inactive hydrothermal deposits were found within a narrow graben averaging about 300 m in width along a 20 km long segment of the ridge crest. The graben is floored with fresh basaltic sheet flows including collapsed pits or lava lake structures. From both deep towed camera stations and manned submersible observations, it is estimated that the average spacing between the ridge axis hydrothermal deposits averaging in size 10–50 m in diameter lies between 100 to 200 m.
The hydrothermal deposits found in the central graben are believed to have formed rapidly (on the order of a few decades). Detailed investigations of one active site have enabled us to witness the growth of an active chimney which increased its height by 40 cm in 5 days i.e. 8 cm per day.
Extensive hydrothermal deposits were discovered on an off-axis seamount located 6 km East of the ridge axis. The hydrothermal deposits found on both the ridge axis and on the seamount are similar in composition and consist essentially of zinc, copper and iron mineral phases.
Chemical studies conducted on the venting fluids (320°C) showed that the concentration of the dissolved major metal ions (Fe, Mn, and Zn) is about 0.10–0.13 gl-1. If we accept an average flow rate of 10ls-1 based on visual observations the mass of metallic products spewing out from an active chimney must be about 100 kg per day.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BallardR. D., HolcombR. T., and VanAndelT. H.: 1979, ‘The Galapagos Rift at 86°W: Sheet Flows, Collapsed Pits and Lava Lakes of the Rift Valley’, J. Geophys. Res. 84, 5407–5422.
BallardR. D., FrancheteauJ., JuteauT., RanginC., and NormarkW.: 1981, ‘East Pacific Rise at 21° N: The Volcanic, Tectonic and Hydrothermal Processes of the Central Axis’, Earth. Planet. Sci. Lett. 55, 1–10.
BallardR. D. and FrancheteauJ.: 1982, ‘The Relationship between Active Sulfide Deposition and the Axial Processes of the Mid-Ocean Ridge’, Marine Technol. Soc. Jour. 16, (2), 8–22.
BoulèqueJ., MichardG., BougaultH., and CharlouJ. L.: 1980, ‘Hydrothermal Activity on the East Pacific Rise between 15° N and 7° S′ (abstract) AGU Fall Meeting EOS 61, 992.
ChoukrouneP., FrancheteauJ., and LePichonX.: 1978, ‘In situ Structural Observations along Transform Fault “A” in the FAMOUS Area, Mid-Atlantic Ridge’, Bull. Geol. Soc. Amer. 89, 1013–1029.
CYAMEX: 1978, ‘Découverte par submersible de sulfures polymétalliques massifs sur la dorsale du Pacifique oriental par 21° N (projet RITA)’, C. R. Ac. Sc. Paris, Ser. D. 287, 1365–1368.
CYAMEX Scientific Team and BougaultH., CambonP., and HekinianR.: 1979, ‘Massive Deep-Sea Sulfide Ore Deposits Discovered on the East Pacific Rise’, Nature 277 (5601), 523–528.
CYAMEX Scientific Team: 1981, ‘First Manned Submersible Dives on the East Pacific Rise at 21° N (projet RITA): General Results’, Marine Geophys. Res. 4, 345–379.
Fevrier, M.: 1981, Hydrothermalisme et minéralisations sur la dorsale Est Pacifique à 21° N, Thèse, Université de Bretagne Occidentale et C.O.B. Brest, France, 270 p.
Francheteau, J.: 1981, Characteristics of the Axial Region of the East Pacific Rise, (abstract), in AGU Chapman Conference. The creation of the Oceanic Lithosphere, April 6–10, Warrenton, Virginia.
FrancheteauJ., JuteauT., and RanginC.: 1979, ‘Balaltic Pillars in Collapsed Lava Pools on the Deep Ocean Floor’, Nature 281 (5728), 209–211.
Francheteau, J. and Ballard, R. D.: ‘The East Pacific Rise near 21° N, 13° N and 20° S. Inference for a long Strike Variability of Axial Proceses of the Mid-Oceanic Ridge’, Earth. Plan. Sci. Lett. (in press).
HekinianR., FevrierM., NeedhamH. D., AvedikF., and CambonP.: 1981, ‘Sulfide Deposits: East Pacific Rise near 13° N’ (abstract), EOS 62 (45), 913.
HekinianR., FevrierM., AvedikF., CambonP., CharlouJ. L., RaillardJ., NeedhamH. D., BoulégueJ., MoinetA., MerlivatL., ManganiniS., and LangeJ.: 1983, ‘East Pacific Rise near 11–13° N: Geology of New Hydrothermal Fields’, Science 219, 1321–1324.
LalouC. and BrichetE.: 1981, ‘Possibilité de datation des dépôts de sulfures métalliques hydrothermaux sous-marins par les descendants à vie courte de l'uranium et du thorium’, C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris t. 293 (2), 821–826.
LalouC. and BrichetE.: 1982, ‘Ages and Implications of East Pacific Rise Sulfide Deposits at 21° N’, Nature 300, 169–171.
LonsdaleP. F., BishoffJ. L., BurnsV. M., KastnerM., and SweeneyR. E.: 1980, ‘A High Temperature Hydrothermal Deposit on the Seabed at the Gulf of California Spreading Center’, Earth. Planet. Sci. Lett. 49, 8–20.
LonsdaleP. F., BatizaR., and SimkinT.: 1982, ‘Metallogenesis at Seamounts on the East Pacific Rise’, Marine Technol. Soc. 6 (3), 54–61.
MacdonaldK. C., BeckerK., SpiessF. N., and BallardR. D.: 1980, ‘Hydrothermal Heat Flux of the “Black Smoker” Vents on the East Pacific Rise’, Earth. Plant. Sci. Lett. 48, 1–7.
MerlivatL., BoulégueJ., and DimonB.: 1981, ‘Helium Isotopes and Manganese Distribution in the Water Column at 13° N on the East Pacific Rise’, (abstract) in AGU Fall Meeting, EOS 62 (45), 913.
MichardA., MichardG., AlbaredeF., MinsterJ. F., and CharlouJ. L.: 1982, ‘The Chemistry and 87Sr/Sr86 Ratio of the Hydrothermal Vent Waters at 13° N (East Pacific Rise)’, EOS 63 (45), 1014 (abstract).
SimoneitB. R. T. and LonsdaleP. F.: 1982, ‘Hydrothermal Petroleum in Mineralized Mounds at the Seabed of Guaymas Basin’, Nature 295, 198–202.
SpiessF. N., MacdonaldK., AtwaterT., BallardR. D., CarranzaA., CordobaD., CoxC., Diaz GarciaV. M., FrancheteauJ., GuerreroJ., HawkinsJ., HaymonR., HesslerR., JuteauT., KastnerM., LarsonR., LuyendykB., MacdougallJ. D., MillerS., NozmarkW., OrcuttJ., and RanginC.: 1980, ’East Pacific Rise: Hot Springs and Geophysical Experiments’, Science 207, 1421–1433.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Contribution N° 801 du Centre Océanologique de Bretagne.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hekinian, R., Francheteau, J., Renard, V. et al. Intense hydrothermal activity at the axis of the east pacific rise near 13°N: Sumbersible witnesses the growth of sulfide chimney. Mar Geophys Res 6, 1–14 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00300395
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00300395