Summary
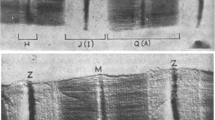
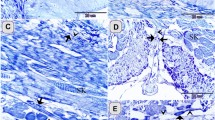
Using Golgi infiltration we have studied the structure and disposition of tranverse tubules in muscle fibres from the sand dab fin musculature. Three types of fibres differ significantly from each other in the extent and disposition of junctions between transverse tubules and the sarcoplasmic reticulum. These correlate with the three groups of fibres having different relaxation times shown in the accompanying paper (Gilly & Aladjem, 1987). Fibres with very slow relaxation (tonic fibres) correspond to those which have an unusual disposition of T tubules and very rare T-SR junctions. In the fast twitch fibres the peripheral T tubules segments converge into tangentially arranged tubules before joining the plasmalemma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altringam, J. D. &Johnston, I. A. (1979) Forcevelocity relationship of skinned fibres isolated from dogfish myotomal muscle.J. Physiol 319, 85.
Akster, H. A. (1985) Morphometry of muscle fibre types in the carp (Cyprinus carpio, L.).Cell Tissue Res. 241, 193–201.
Akster, H. A., Granzier, H. L. M. &Keurs, H. E. D. J. (1985) A comparison of quantitative ultrastructural and contractile characteristics of muscle fibre types of the perch.Perca fluviatilis. J. Comp. Physiol. 155, 685–91.
Bone, Q. (1964) Patterns of muscular innervation.Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 6, 99–147.
Bone, Q., Kiceniuk, J. &Jones, D. R. (1978) On the role of the different fibre types in fish myotomes at intermediate swimming speeds.Fish Bull. 76(2), 691–9.
Bone, Q., Johnstone, I. A., Pulsford, A. &Ryan, R. P. (1986) Contractile properties and ultrastructure of three types of muscle fibres in the dogfish myotome.J. Musc. Res. Cell Motility 7, 547–61.
Dulhunty, A. F. (1984) Heterogeneity of T-tubule geometry in vertebrate skeletal muscle fibres.J. Musc. Res. Cell Motility 5, 333–48.
Dulhunty, A. F. &Dlutowsky, M. (1979) Fibre types in red and white segments of rat sternomastoid muscle.Am. J. Anat. 156, 51–9.
Eisenberg, B. R. (1983) Quantitative ultrastructure of mammalian skeletal muscle. InHandbook of Physiology, Section 10,Skeletal Muscle (edited byPeachey, L. D. andAdrian, R. H.), pp. 73–112. American Physiological Society Baltimore, Maryland.
Eisenberg, B. &Kuda, A. M. (1976) Discrimination between fibre populations in mammalian skeletal muscle by using ultrastructural parameters.J. Ultrastructure Res. 54, 776–88.
Eisenberg, B., Kuda, A. M. &Peter, J. B. (1974) Stereological analysis of mammalian skeletal muscle. I Soleus muscle of the adult guinea pig.J. Cell Biol. 60, 732–54.
Egginton, S. &Johnston, I. A. (1982) A morphometric analysis of regional differences in myotonal muscle ultrastructure in the juvenile eel (Anguilla anguilla, L.).Cell Tissue Res 222, 579–96.
Flitney, F. W. &Johnston, I. A. (1979) Mechanical properties of isolated fish red and white muscle fibres,J. Physiol. 295, 49.
Flood, P. R. (1979) The vascular supply of the three fibre types in the parietal trunk muscle of the atlantic hagfish (Myxine glutinosa, L.).Microvasc. Res. 17, 55–70.
Flood, P. R. &Storm Mathisen, J. (1962) A third type of muscle fibre in the parietal muscle of the atlantic hagfishMyxine glutinosa L.Z. Zellforsch u mikroskop Anat. 58, 638–40.
Franzini-Armstrong, C. (1973) Studies of the triad. IV Structure of the junction in frog slow fibresJ. Cell Biol. 56, 120–8.
Franzini-Armstrong, C. (1986) The sarcoplasmic reticulum and the transverse tubules. InMyology (edited byEngel, A. G. andBanker, B. Q.), pp. 125–54 New York, McGraw-Hill.
Franzini-Armstrong, C. &Peachey, L. D. (1982). A modified Golgi black reaction method for light and electron microscopy.J. Histochem. and Cytochem. 30, 99–105.
Franzini-Armstrong, C. &Porter, K. R. (1964) Sarcolemmal invaginations constituting the T system in fish muscle fibres.J. Cell Biol. 22, 675–96.
Franzini-Armstrong, C., Landmesser, L. &Pilar, G. (1975) Size and shape of transverse tubule openings in frog twitch muscle fibres.J. Cell. Biol. 64, 493–7.
Franzini-Armstrong, C., Eastwood, A. E. &Peachey, L. D. (1986) Shape and disposition of clefts, tubules, and sarcoplasmic reticulum in long and short sarcomere fibres of crab and crayfish.Cell Tissue Res. 244, 9–19.
Gilly, W. F. &Aladjem, E. (1987). Physiological properties of three muscle fibre types controlling dorsal fin movements in a flatfish,Citharichtus sordidus.J. Musc. Res. and Cell Motility 8, 407–17.
Gilly, W. F. &Hui, C. S. (1980) Mechanical activation in slow and twitch skeletal muscle fibres of the frog.J. Physiol. 301, 137–56.
Ginsborg, B. L. (1960) Some properties of avian skeletal muscle fibres with multiple neuromuscular junctions.J. Physiol. 154, 581–98.
Huxley, A. F. (1971) The activation of striated muscle and its mechanical response.Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. B 178, 1–27.
Johnston, I. A. (1982) Biochemistry of myosin and contractile properties of fish skeletal muscle.Molec. Physiol. 2, 15–29.
Kilarski, W. (1967) The fine structure of striated muscle in teleosts.Z. Zellforsch. 79, 562–80.
Kilarski, W. (1973) Cytomorphometry of sarcoplasmic reticulum in extrinsic eye muscles of the teleost (Tinca tinca, L.).Z. Zellforsch. 136, 535–44.
Kilarski, W. &Bigaj, J. (1969) Organization and fine structure of extraocular muscles in Carassius and RanaZ. Zellforsch. 94, 194–204.
Kilarski, W. &Kozlowska, M. (1983) Ultrastructural characteristics of the teleostean muscle fibres and their endings. The stickleback (Gastosteus aculeatus, L.).Z. Mikroskop. Anat. Forsch. 97, 1022–36.
Korneliussen, H. &Nicolaysen, K. (1973) Ultrastructure of four types of striated muscle fibres in the Atlantic hagfish (Myxine glutinosa).Z. Zellforsch. 143, 273–90.
Kryvi, H., Flood, P. &Guljaeu, D. (1980) The ultrastructure and vascular supply of the different types in the axial muscle of the sturgeonAcipenser stellatus.Cell Tissue Res. 212, 117–26.
Nag, A. C. (1972) Ultrastructure and adenosinetriphosphatase activity of red and white muscle fibres of the caudal region of a fish,Salmo gairdneri.J. Cell Biol. 55, 42–57.
Nakajima, Y. (1969) Fine structure of red and white muscle fibres and their neuromuscular junctions in the snake fish (Ophiocephalus argus).Tissue and cell 1, 229–46.
Page, S. G. (1965) A comparison of the fine structure of frog slow and twitch muscle fibresJ. Cell Biol. 26, 477–97.
Page, S. G. (1968) Fine structure of tortoise muscle.J. Physiol (Lond.) 197, 709–15.
Page, S. G. (1969) Structure and some contractile properties of fast and slow muscles of chicken.J. Physiol. 205, 131–42.
Peachey, L. D. (1982) A simple digital morphometry system for electron microscopy.Ultramicroscopy 8, 253–62.
Peachey, L. D. &Huxley, A. F. (1962) Structural identification of twitch and slow striated muscle fibres of the frog.J. Cell Biol. 13, 177–180.
Rowlerson, A., Scapolo, P. A., Mascarello, F., Carpene, E. &Veggetti, A. (1985) Comparative study of myosins present in the lateral muscle of some fish: species variations in myosin isoforms and their distribution in red, pink and white muscle.J. Musc. Res. Cell Motility 6, 601–41.
Smith, D. S. (1961) The structure of insect fibrillar flight muscle. A study made with special reference to the membrane systems of the fiber.J. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol. 10 (4, part 2), 123–58.
Takeuchi, A. (1959) Neuromuscular transmission of fish skeletal muscles investigated with intracellular microelectrodes.J. cell. comp. Physiol. 54, 211–20.
Veratti, E. (1902) Ricerche sulla fine struttura della fibre muscolare striata.Mem. Ist. Lombardo Cl. Sci. Mat. Nat. 19, 87–133. Translated in (1961)J. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol.10, No. 4, suppl., 3–59.
Willeuse, J. J. &De Ruiter, A. (1979) A quantitative identification of four types of fibres in the lateral musculature of immature European eelAnguilla anguilla L.Aquaculture 17, 105–11.
Zampighi, E. G., Vergara, J. &Ramon, F. (1975) The conection between the T tubules and the plasma membrane in frog skeletal muscle.J. Cell Biol. 64, 734–40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Franzini-Armstrong, C., Gilly, W.F., Aladjem, E. et al. Golgi stain identifies three types of fibres in fish muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 8, 418–427 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01578431
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01578431