Summary
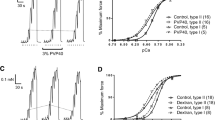
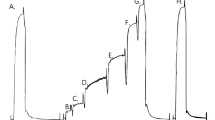
The effect of temperature (5–35° C) on maximum force production was examined in intact and chemically skinned muscle fibre bundles (10–25 fibres) from the anterior byssus retractor muscle of Mytilus edulis. In intact fibre bundles, 10 μm acetylcholine induced a tonic contraction which had a magnitude of 65.4±4.0 N cm-2 (n=30) at 23° C. Activation by caffeine (20 mm) produced a force response which was 157.1±7.9% (n=16) of the acetylcholine response at 23° C and acetylcholine and caffeine together produced force which was not significantly different from the response to caffeine alone. At 5° C the acetylcholine and caffeine responses were decreased by 9.6±3.4% (n=6) and 14.6±2.8% (n=8) compared with the respective responses at 23° C. However, there was no significant reduction of the response induced by the combined action of acetylcholine and caffeine when the temperature was decreased from 23° C to 5° C. The 20–80% of peak force activation time increased by about one order of magnitude for all acetylcholine, caffeine and combined acetylcholine-caffeine-induced responses when the temperature was decreased from 23–5° C. Repeated exposure of the intact preparation to caffeine caused a marked decrease in the caffeine-induced response (complete abolition of force after the third exposure to caffeine), but the response to caffeine could be fully restored following one acetylcholine-induced activation. The maximum Ca2+-activated force after skinning the preparation with saponin was not significantly different from the caffeine or combined acetylcholine-caffeine-induced responses before skinning. In the saponin skinned fibre preparation a drop in temperature from 23° C to 15° C or 5° C decreased the maximum Ca2+-activated force by 13.2±1.4% (n=8) and 41.4±3.1% (n=5) respectively. The activation time between 20–80% of the peak Ca2+-activated force increased at 15° C and 5° C by a factor of 1.5±0.1 (n=5) and 6.8±1.1 (n=5) respectively when compared to corresponding values at 23° C. The relaxation half-time decreased by a factor of 1.7±0.2 (n=5) and 3.0±0.2 (n=5) at 15° C and 5° C respectively compared with that at 23° C. It was possible to distinguish between the temperature effects on the contractile apparatus per se and the Ca2+ regulatory system with the results indicating that the contractile apparatus was more sensitive to a change in temperature than the Ca2+-regulatory system. Increasing the temperature to 35° C irreversibly affected the ability to develop and maintain force in both intact and skinned muscle preparations. These results indicate that: (1) acetylcholine does not fully activate the intact ‘catch’ muscle at 23° C; (2) acetylcholine is able to replenish the internal stores after depletion by caffeine; (3) compensatory mechanisms which oppose the inhibitory effect of lower temperatures on the contractile apparatus and the Ca2+-regulatory system must be operating in the intact fibre preparations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashley, C. C. & Moisescu, D. G. (1977) Effect of changing the composition of the bathing solutions upon the isometric tensions-pCa relationship in bundles of crustacean myofibrils. J. Physiol. 270, 627–52.
Atsumi, S. & Sugi, H. (1976) Localization of calcium accumulating structures in the anterior byssus retractor muscle of Mytilus edulis and their role in the regulation of active and catch contractions. J. Physiol. 257, 549–60.
Bennett, A. F. (1984) Thermal dependence of muscle function. Am. J. Physiol. 247, R217–29.
Butcher, R. W. & Sutherland, E. W. (1962) Adenosine 3′5′-phosphate in biological materials. I. Purification and properties of cyclic 3′,5′-nucleotide phophodiesterase and use of this enzyme to characterize adenosine 3′,5′-phosphate in human urine. J. Biol. Chem. 237, 1244–50.
Cole, R. A. & Twarog, B. M. (1972) Relaxation of catch in a molluscan smooth muscle. I. Effects of drugs which act on the adenyl cyclase system. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 43A, 321–30.
Cornelius, F. (1980) The regulation of tension in a chemically skinned molluscan smooth muscle. J. Gen. Physiol. 75, 709–25.
Crichton, C. A., Taggart, M. J., Wray, S. & Smith, G. L. (1993) Effects of pH and inorganic phsophate on force production in α-toxin-permeabilized isolated rat uterine smooth muscle. J. Physiol. 465, 629–45.
Fabris, G. J., Harris, J. E. & Tawfik, F. A. (1978) Heavy metals in the mussel Mytilus edulis planulatus from Port Phillip and Corio Bays. Marine Studies Group, Ministry for Conservation, Victoria, Australia.
Ishii, N., Simpson, A. W. M. & Ashley, C. C. (1988) Carbachol and KCl-induced changes in intracellular free calcium concentrations in isolated, fura-2 loaded smooth-muscle cells from the anterior byssus retractor muscle of Mytilus edulis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Com. 153, 683–9.
Ishii, N., Simpson, A. W. M. & Ashley, C. C. (1989) Free calcium at rest during ‘catch’ in single smooth muscle cells. Science 243, 1367–8.
Köhler, G. & Lindl, T. (1980) Effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine, dopamine and acetylcholine on accumulation of cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP in the anterior byssus retractor muscle of Mytilus edulis L. (Mollusca). Pflügers Archiv 383, 257–62.
Lineham, C. M. (1982) The effect of temperature on the tension response of the anterior byssus retractor muscle (ABRM) of Mytilus edulis. J. Exper. Biol. 97, 375–84.
Moisescu, D. G. & Thieleczek, R. (1978) Calcium and strontium concentration changes within skinned muscle preparations following a change in the external bathing solution. J. Physiol. 275, 241–62.
Oyamada, H., Iino, M. & Endo, M. (1993) Effects of ryanodine on the properties of Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in skinned skeletal muscle fibres of the frog. J. Physiol. 470, 335–48.
Pfitzer, G. & Rüegg, J. C. (1982) Molluscan catch muscle: regulation and mechanisms in living and skinned anterior byssus retractor muscle of Mytilus edulis. J. Comp. Physiol. 147, 137–42.
Rees, B. B. & Stephenson, D. G. (1987) Thermal dependence of maximum Ca2+ activated force in skinned muscle fibres of the toad Bufo marinus acclimated at different temperatures. J. Exper. Biol. 129, 309–27.
Sunano, S. & Miyazaki, E. (1981) A comparison of the effects of temperature and metabolic inhibition on the contraction of smooth muscle. Jap. J. Physiol. 31, 445–56.
Tameyasu, T. (1990) Regulation of cross-bridge detachment by Ca2+ ions at high ionic strengths in molluscan catch muscle. Experientia 46, 677–9.
Twarog, B. M. (1967) Factors influencing contraction and catch in Mytilus smooth muscle. J. Physiol. 192, 847–56.
Twarog, B. M. (1976) Aspects of smooth muscle function in molluscan catch muscle. Physiol. Rev. 56, 829–38.
Twarog, B. M. & Muneoka, Y. (1972) Calcium and the control of contraction and relaxation in a molluscan catch muscle. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 37, 489–503.
Yamada, A., Ishii, N., Shimmen, T. & Takahashi, K. (1989) Mg-ATPase activity and motility of native thick filaments isolated from the anterior byssus retractor muscle of Mytilus edulis. J. Muscle. Res. Cell Motil. 10, 124–34.
Zange, J., Pörtner, H. O., Jans, A. W. H. & Grieshaber, M. K. (1990) The intracellular pH of a molluscan smooth muscle during a contraction-catch-relaxation cycle estimated by the distribution of [14C] DMO and by 31P-NMR spectroscopy. J. Exper. Biol. 150, 81–93.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chick, J.J., Stephenson, D.G. The effect of temperature on contractile activation of intact and chemically skinned ‘catch’ muscle fibre bundles of Mytilus edulis . J Muscle Res Cell Motil 16, 285–294 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00121137
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00121137