Abstract
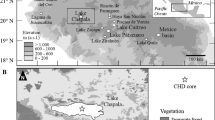
Yuanyang Lake (24°35′N, 121°24′E), located at an altitude of 1,670 m within a nature preserve in northern Taiwan, is an acidic lake. Remains of diatoms and pollen from a 3.72-m sediment core were used to elucidate the relationships between the vegetation of the watershed and the paleolimnological environment. Past pH, saprobity level, and total P of the lake were inferred from the diatom assemblages and were analyzed with respect to changes in the terrestrial vegetation. The inferred pH values fluctuated only slightly, whereas the inferred saprobity level increased markedly towards the sediment surface. In the topmost sediment, a slight drop in the inferred pH was associated with a lowering in the saprobity index. This was interpreted as a possible result of recent anthropogenic acidification and changes in productivity related to changes in acidity. Based on pollen analyses, we conclude that Chamaecyparis persisted over at least the last four thousand years in the watershed. The vegetation in the watershed changed little during this period of time, which is consistent with the constancy of inferred pH values. A positive correlation between the inferred pH and δ13C values of the sediments was found.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agbeti, M. & M. Dickman, 1989. Use of lake fossil diatom assemblages to determine historical changes in trophic status. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 46: 1013–1021.
American Public Health Associations (APHA), American Water Works Association & Water Pollution Control Federation. 1992. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. 18th ed. APHA, Washington, D.C.
Battarbee, R. W., iJ. P. Smol & J. Meriläinen, 1986. Diatoms as indicators of pH: A historical review. In: Smol, J. P., R. W. Battarbee, R. B. Davis & J. Meriläinen (eds), Diatoms and Lake Acidity: The Use of Siliceous Algal Microfossils in Reconstructing pH. Junk, Dordrecht. pp. 5–14.
Beug, H.-J., 1957. Untersuchungen zur spätglazialen und frühpostglazialen Floren-und Vegetationsgeschichte einiger Mittelgebirge (Fichtelgebirge, Harz und Rhon). Flora 145: 167–211.
Charles, D. F., 1985. Relationships between surface diatom assemblages and lakewater characteristics in Adirondack lakes. Ecology 66: 994–1011.
Chen, C. T. A., J. Y. Lou & J. K. Wann, 1993. Preliminary paleoclimatological records from high mountain lakes in Taiwan. TAO 4: 321–329.
Cleve-Euler, A., 1951–1955. Die Diatomeen von Schweden und Finnland. Almqvist & Wiksells Boktryckeri AB, Stockholm.
Davis, R. B. & D. S. Anderson, 1985. Methods of pH calibration of sedimentary diatom remains for reconstructing history of pH in lakes. Hydrobiologia 120: 69–87.
Erdtman, G., 1952. Pollen Morphology and Plant Taxonomy, Angiosperms. Almqvist & Wiksell, Stockholm.
Friedli, H., H. Lötscher, H. Oeschger, U. Siegenthaler & B. Stauffer, 1986. Ice core record of the 13C/12C ratio of atmospheric CO2 in the past two centuries. Nature 324: 237–238.
Fritz, S. C., A. C. Stevenson, S. T. Patrick, P. G. Appleby, F. Oldfield, B. Rippey, J. Natkanski & R. W. Battarbee, 1989. Paleolimnological evidence for the recent acidification of Llyn, Hir, Dyfed, Wales. J. Paleolim. 2: 245–262.
Gerloff, J. & B. J. Cholnoky, 1970. Diatomaceae II. J. Cramer Verlag, Berlin, Stuttgart. 835 pp.
Halfman, J. D., D. F. Jacobson, C. M. Cannella, K. A. Haberyan & B. P. Finney, 1992. Fossil diatoms and the mid to late Holocene paleolimnology of Lake Turkana, Kenya: a reconnaissance study. J. Paleolim. 7: 23–35.
Hall, R. I. & J. P. Smol, 1992. A weighted-averaging regression and calibration model for inferring total phosphorus concentration from diatoms in British Columbia (Canada) lakes. Freshwat. Biol. 27: 4117–4434.
Huber-Pestalozzi, G., 1942. Das Phytoplankton des Süsswassers. Part 2. Die Binnen-gewässer. Band XVI. E. Schweizerbart'sche Verlagsbuchhandlung, Stuttgart. 549 pp.
Hustedt, F., 1927–1966. Die Kieselalgen Deutschlands, Östereichs und der Schweiz I, II, III. In L. Rabenhorst (ed), Kryptogamen-Flora von Deutschland. Östereich und der Schweiz. Band 7, Teil 1, 2, 3. Goest & Portzig, Leipzig. Reprint 1977. Koeltz, Koenigstein.
Hustedt, F., 1937–1939. Ökologische und systematische Untersuchungen uber die Diatomeenflora von Java, Bali und Sumatra. Arch. Hydrobiol. suppl. 15: 131–177, 187–295, 292–506; suppl. 16: 1–155.
Krammer, K. & H. Lange-Bertalot, 1986–1991. Bacillariophyceae. Teile 1–4. Gustav Fisher Verlag, Stuttgart.
Liew, P. M., C. M. Kuo, C. T. A. Chen & J. Y. Lou, 1995. Climatic fluctuations during the last several millennia indicated by lake sediments of Taiwan. Proc. Nagoya IGBT-PAGES/PET/II Symp. pp. 103–108.
Lin, H. S., 1994. Paleogeomagnetic study of the sediments from Yuanyang Lake. Mass thesis, Dept of Geology, National Taiwan University, 108 pp.
Liu, G. & G. S. Hsu, 1973. Ecological studies of Yuanyang Lake nature preserve. Rep. Taiwan Prov. Forest Res. 237: 1–32.
Rabenhorst, L., 1971. Die Kieselalgen Deutschlands. Part III. Johnson Reprint Co., New York.
Schmidt, R. & H. Simola, 1991. Diatomeen, pollen und sedimentmikrostratigraphische Untersuchungen zur anthropogenen Beeinflussung des Hoellerer Sees. Aquat. Sci. 53: 74–89.
Simonsen, R., 1987. Atlas and catalogue of the diatom types of Friedrich Hustedt. Vol. I-III. J. Cramer, Berlin.
Sádček, H., 1973. System of water quality from the biological point of view. Arch. Hydrobiol. (Beih.) 7: 1–218.
Steinberg, C., H. Hartmann, K. Arzet & D. Krause-Dellin, 1988. Paleoindication of acidification in Kleiner Arbersee (FRG) by chydorids, chrysophytes, and diatoms. J. Paleolim. 1: 149–157.
Steinberg, C. & B. Lenhart, 1985. Wenn Gewässer sauer werden. BLV Verlags-gesellschaft, Munich. p. 127.
Whitehead, D. R., D. F. Charles, S. T. Jackson, J. P. Smol & D. R. Engstrom, 1989. The development history of Adirondack (N.Y.) Lakes. J. Paleolim. 2: 185–206.
Wu, J. T. & S. C. Chang, 1996. Relation of the diatom assemblages in the surface sediments to the pH values of an alpine lake in Taiwan. Arch. Hydrobiol. 137: 551–563.
Wu, J. T., P. P. Chuang, L. Z. Wu & C. T. A. Chen, 1997. Diatoms as indicators of environmental changes: a case study in Great Ghost Lake. Proc. Natl. Sci. Counc. (ROC) 21: 112–119.
Wu, J. T., Y. S. Wang, S. C. Chang & M. K. Hsu, 1998. Causal factors for acidification in a subtropical alpine lake of Taiwan. (under review)
Yeh, H. W., S. H. Chen, W. C. Chang & W. Y. Kao, 1995. Paleolimnology of Yuen-yang Lake based on isotopic composition of organic carbon. J. Geol. Soc. China 38: 125–139.
Zelinka, M. & P. Marvan, 1961. Zur Präzisierung der biologischen Klassifikation der Reinheit fliessender Gewässer. Arch. Hydrobiol. 57: 387–497.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, SH., Wu, JT. Paleolimnological environment indicated by the diatom and pollen assemblages in an alpine lake in Taiwan. Journal of Paleolimnology 22, 149–158 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008067928365
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008067928365