Abstract
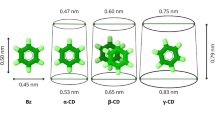
The association constant values, Ka, for the inclusion of α- and β-CD with monosubstituted benzene derivatives were determined by means of UV-vis and fluorescence spectroscopy. The stability of the complexes is influenced by the properties of the substituents of the guest compounds. Regression analysis was used to create a set of inclusion models with the experimental association constant ln Ka and the corresponding substituent molar refraction Rm, hydrophobic constant π and Hammett σ constant of the benzene derivatives. The ln Ka value mainly correlated with Rm for α-CD and with both Rm and π for β-CD complexes. The association constants predicted by the models are in good agreement with the experimentally determined data. This suggests that the inclusion complexation of benzene derivatives with α-CD is predominantly driven by van der Waals force and with β-CD mainly by van der Waals force and hydrophobic interactions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.L. Bender and M. Komiyama: Cyclodextrin Chemistry, Springer Verlag, Berlin (1978).
J. Szejtli: Cyclodextrin Technology, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (1988).
H. Dugas: Bioorganic Chemistry: A Chemical Approach to Enzyme Action (3rd Ed.), Springer Verlag, New York (1995).
D. Sybilska and E. Smolkova-Keulemansova: in J.L. Atwood, J.E.D. Davies, and D.D. MacNicol (Eds.), Inclusion Compounds, Academic Press, London, Vol. 3, Ch. 6 (1984).
V. Schurig and H.-P. Nowotny: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 29, 939 (1990).
T. Cserhati and G. Oros: J. Incl. Phenom. 18, 265 (1994).
F. Hirayama, M. Yamanaka, T. Horikawa, and K. Uekema: Chem. Pharm. Bull. 43, 130 (1985).
(a) R. Breslow, S.D. Dong, Y. Webb, and R. Xu: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118, 118, 6588 (1996). (b) R. Breslow and C. Schmuck: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118, 6601 (1996).
O. Tee, C. Mazza, and X. Du: J. Org. Chem. 55, 3603 (1990).
(a) I. Tabushi: Acc. Chem. Res. 15, 66 (1982); Tetrahedron 40, 269 (1984). (b) I. Tabushi and Y. Kuroba: J. Am. Chem Soc. 106, 4580 (1984).
(a) V.T. D'Souza, X.L. Lu, R.D. Ginger, and M.L. Bender: Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84, 673 (1987). (b) V.T. D'Souza, and M.L. Bender: Acc. Chem. Res. 20, 146 (1987).
E.V. Akkaya and A.W. Czarnik: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 110, 8553 (1988).
(a) T. Ikeda, R. Kojin, C.-J, Yoon, H. Ikeda, M. Iijima, K. Hottori, and F. Toda: J. Incl. Phenom. 2, 669 (1984). (b) T. Ikeda, T. Kojin, C.-J. Yoon, K. Ikeda, M. Iijima, and F. Toda: ibid. 5, 93 (1987). (c) H. Ikeda, R. Kojin, C.-J. Yoon, T. Ikeda, and F. Toda: ibid. 7, 117 (1989).
(a) Y. Inoue: Annual Reports on NMR Spectroscopy 59 (1993). (b) K. Kano, Y. Tawiya, and S. Hashimoto: J. Incl. Phenom. 3, 287 (1992).
D.M. Davies and J.R. Savage: J. Chem. Res. (M), 0663 (1993); J. Chem. Res. (S), 94 (1993). D.M. Davies and M.E. Deary: J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans 2, 1287 (1995).
K.A. Connors, S.-F. Lin, and A.B. Wong: J. Pharm. Sci. 71, 217 (1982). K.A. Connors and D.D. Peadergast: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 106, 7607 (1984).
J.H. Park and T.W. Nah: J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans 2, 1359 (1994).
Q.-X. Guo, Z.-Z. Li, T. Ren, X.-Q. Zhu, and Y.-C. Liu: J. Incl. Phenom. 17, 149 (1994).
(a) Q.-X. Guo, S.-H. Luo, H. Wang, M.-S. Zhang, and Y.-C. Liu: J. Chem. Res. (S) 38 (1996). (b) Q.-X. Guo, S.-H. Luo, H. Wang, M.-S. Zhang, and Y.-C. Liu: Chin. Chem. Lett. 7, 285 (1996). (c) Q.-X. Guo, S.-H. Luo, X.-Q. Zheng, and Y.-C. Liu: Chin. Chem. Lett. 7, 767 (1996).
E.E. Tucker and S.D. Cristian: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 106, 1942 (1984).
I. Sanema and Y. Akamine: Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 60, 2059 (1987).
M. Hoshino and M. Imamura: J. Phys. Chem. 85, 1820 (1981).
G.L. Bertrand: J. Phys. Chem. 93, 6863 (1989).
A.B. Wang: J. Pharm. Sci. 72, 388 (1983).
Y.-C. Jean and H.J. Ache: J. Phys. Chem. 81, 2093 (1977).
T. Takuma, T. Deguchi, and I. Sanemasa: Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 63, 1246 (1990).
R.L. van Etten, J.F. Sebastian, G.A. Clowes, and M.L. Bender: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 89, 3242 (1967).
S. Li and W.C. Purdy: Chem. Rev. 92, 1457 (1992).
A.D. Buckingham: Quart. Rev. Chem. Soc. 13, 183 (1959).
F. London: Z. Phys. 63, 245 (1930).
A. Bondi: J. Phys. Chem. 68, 441 (1964).
Y. Matsui and K. Mochida: Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 52, 2808 (1979).
M. Delaage in M. Delaage (ed.), Molecular Recognition Mechanisms, Ch. 1, VCH Publishers, New York (1991).
G. Nemethy: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 6, 195 (1967).
K. Kiehs, C. Hansch, and L. Moore: Biochemistry 5, 2602 (1966).
F. Helmer, K. Kiehs, and C. Hansch: Biochemistry 7, 2858 (1968).
A. Leo, C. Hansch, and D. Elkins: Chem. Rev. 71, 525 (1971).
C. Hansch, A. Leo, and D. Nikaitani: J. Org. Chem. 37, 3090 (1972).
C. Hansch, A. Leo, S.H. Unger, K.H. Kim, D. Nikaitani, and E.J. Lien: J. Med. Chem. 16, 1207 (1973).
R.N. Smith, C. Hansch, and M.M. Ames: J. Pharm. Sci. 64, 599 (1975).
C. Silipo and C. Hansch: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 97, 6849 (1975).
J.T. Chou and P.C. Jurs: J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 19, 172 (1979).
N. Yoshida, A. Seiyama, and M. Fujimoto: J. Incl. Phenom. 2, 573 (1984).
G. Wenz: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 33, 803 (1994).
M. Kitagawa, H. Hoshi, M. Sakurai, Y. Inoue, and R. Chujo: Carbohydr. Res. 163, c1 (1987).
M. Sakurai, M. Kitagawa, Y. Inoue, and R. Chujo: Carbohydr. Res. 198, 181 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, QX., Luo, SH. & Liu, YC. Substituent Effects on the Driving Force for Inclusion Complexation of α- and β-Cyclodextrin with Monosubstituted Benzene Derivatives. Journal of Inclusion Phenomena 30, 173–182 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007985107256
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007985107256