Abstract
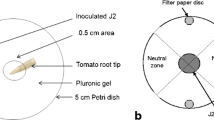
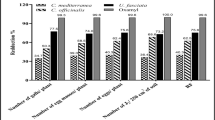
Treatment of Arabidopsis thaliana plants with a commercially-available, alkaline extract of the marine brown alga, Ascophyllum nodosum, resulted in a significant decrease in the number of females of the root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne javanica, which developed in the roots compared to those of plants grown in a water control medium. Significant reductions in egg recovery were also achieved from plants treated with the seaweed extract. Similar effects were produced when betaine components of the seaweed extract (γ-aminobutyric acid betaine, δ-aminovaleric acid betaine and glycinebetaine) were used in quantities equivalent to those applied in the seaweed extract treatment. As the experiments were conducted under monoxenic conditions, it can be concluded that the results obtained with the application of either the seaweed extract or betaines are indicative of their effects on the plants and are not dependent on microorganisms associated with the rhizosphere.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker JO, Zavaleta-Mejia E, Colbert SF, Schroth MN, Weinhold AR, Hancock JG, van Gundy SD (1988) Effects of rhizobacteria on root-knot nematodes and gall formation. Phytopathology 78: 1466–1469.
Blunden G, Cripps AL, Gordon SM, Mason TG, Turner CH (1986) The characterisation and quantitative estimation of betaines in commercial seaweed extracts. Bot. mar. 29: 155–160.
Crouch IJ, van Staden J (1993) Effect of seaweed concentrate from Ecklonia maxima (Osbeck) Papenfuss on Meloidogyne incognita infection on tomato J. appl. Phycol. 5: 37–43.
Featonby-Smith BC, van Staden J (1983) The effect of seaweed concentrate on the growth of tomato plants in nematode infested soil. Scientia Hortic. 20: 137–146.
Godoy G, Rodriguez-Kabana R, Shelby RA, Morgan-Jones G (1983) Chitin amendments for control of Meloidogyne arenaria in infested soil. II – Effects on microbial population. Nematropica 13: 63–74.
Kraska T, Schönbeck F (1992) Resistance induction in plants by trigonelline and possible mechanisms. In Tyihák E (ed.), Proceedings of 3rd International Conference on Role of Formaldehyde in Biological Systems. Methylation and Demethylation Processes. Hungarian Biochemical Society, 163–168.
Manninger K, Csösz M, Tyihák E (1992) Biochemical immunization of wheat plants to biotrophic fungi by endogenous, fully N-methylated compounds. In Tyihák E (ed), Proceedings of 3rd International Conference on Role of Formaldehyde in Biological Systems. Methylation and Demethylation Processes. Hungarian Biochemical Society, 157–162.
Miller PM (1977) Reducing field populations of several plant parasitic nematodes by leaf would compost and some other additives. Pl. Dis. Reptr. 61: 328–331.
Sijmons PC, Grundler FMW, von Mende N, Burrows PR, Wyss U (1991). Arabidopsis thaliana as a new model host for plant-parasitic nematodes. The Plant J. 1: 245–254.
Southey JF (1986) Laboratory Methods for Work with Plant and Soil Nematodes. Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food, London, UK, 202 pp.
Tyihák E, Sarhan ART, Cong NT, Barna B, Kiraly Z (1988) The level of trigonelline and other quaternary ammonium compounds in tomato leaves in ratio to the changing nitrogen supply. Plant and Soil 109: 285–287.
Whapham CA, Jenkins T, Blunden G, Hankins SD (1994) The role of seaweed extracts, Ascophyllum nodosum, in the reduction in fecundity of Meloidogyne javanica. Fundam. appl. Nematol. 17: 181–183.
Wu Y (1996) Biologically active compounds in seaweed extracts. Ph D Thesis, University of Portsmouth.
Wu Y, Jenkins T, Blunden G, Whapham C, Hankins SD (1997) The role of betaines in alkaline extracts of Ascophyllum nodosum in the reduction of Meloidogyne javanica and M. incognita infestations of tomato plants. Fundam. appl. Nematol. 20: 99–102.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Jenkins, T., Blunden, G. et al. Suppression of fecundity of the root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne javanica, in monoxenic cultures of Arabidopsis thaliana treated with an alkaline extract of Ascophyllum nodosum. Journal of Applied Phycology 10, 91–94 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008067420092
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008067420092