Abstract
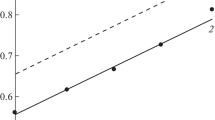
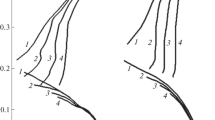
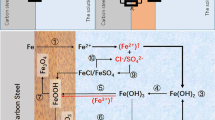
Complementary electrochemical, spectrophotometric and electron microsopic investigations were made in addition to the conversion electron Mössbauer spectroscopic (CEMS) measurements to learn more about the mechanism of corrosion of low carbon steel samples in aqueous sulfate and sulfite containing sulfate solutions (pH 3.5, 6.5 and 8.5). Passivation of iron in pure sulfate solution was studied in detail in earlier papers. In the present work, we used a solution containing both sulfate and sulfite anions to obtain more information about the effect of acid rain on low carbon steel samples. The compositions and thicknesses of the passive films formed due to the electrochemical treatments were determined from the CEM spectra. γ-FeOOH was found in each case on the surface of the samples; nevertheless, at pH 3.5 the sextet belonging to Fe3C appears in the CEM spectra, and also FeSO4 · H2O was detected in low concentration after the shortest polarization time (90 min). The results of the applied methods proved that the sulfite ions induce pitting corrosion at pH 3.5 and 6.5, while the measurements referred to suppressed pitting at pH 8.5.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.C. Marco, J. Davalos, J.R. Gancedo and M. Gracia, Hyp. Int. 46(1989)453.
E. Kuzmann, M.L. Varsányi, A. Vértes and W. Meisel, Electrochim. Acta 36(1991)911.
M.L. Varsányi, Cs. Vértes, A. Vértes, W. Meisel, P. Griesbach, L. Kiss and P. Gütlich, J. Electochem. Soc. 139(1992)1301.
F. Salvat and J. Parellada, Nucl. Instr. Meth. B1(1984)70.
Cs. Vértes, M.L. Varsányi, A. Vértes, E. Kuzmann, W. Meisel and P. Gütlich, Hyp. Int. 69(1991)731.
T. Shinjo, F. Hoh, H. Takaki, Y. Nakamura and N. Shikazono, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 19(1964)1252.
W. Meisel, U. Stumm and P. Gütlich, Fresenius Z. Anal. Chem. 333(1989)555.
W. Meisel, Hyp. Int. 45(1989)73.
Cs. Vértes, M.L. Varsányi, W. Meisel, A. Vértes and P. Gütlich, Nucl. Inst. Meth. B76(1993)20.
Cs. Vértes, M.L. Varsányi, W. Meisel, A. Vértes, P. Gütlich and L. Kiss, Electrochim. Acta 38(1993)253.
J.F. Marco, J.R. Gancedo, W. Meisel, P. Griesbach and P. Gütlich, Corros. (NACE) 47(1991)498.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vértes, C., Lakatos-Varsányi, M., Vértes, A. et al. A study of electrochemically-induced corrosion of low carbon steel in a medium modelling acid rain. Hyperfine Interact 93, 1817–1822 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02072952
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02072952