Abstract
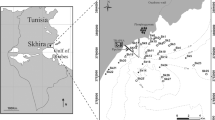
Within the Gulf of Riga Project, phytobenthic and associated animal communities were sampled in 1995 and 1996 using SCUBA techniques. The aim was to quantitatively describe the phytobenthic communities and their distribution and to evaluate the present status of the phytobenthos in comparison to earlier investigations, as well as its contribution to the ecosystem of the Gulf as a whole. Classification and ordination analysis showed differences among the different areas of the Gulf of Riga, where Saaremaa, the Pärnu area and the middle and the inner part of the Gulf formed distinctive groups. The inner part and the Pärnu Bay area are influenced by the nutrient and pollution load of mainly the rivers Pärnu and Daugava. The intermediate western and eastern coasts of the Gulf of Riga, as well as the northern coasts along the island of Saaremaa seem to hold phytobenthic communities of comparable composition and biomass found elsewhere in clean areas of the Baltic Sea.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonsdorff, 1992. Drifting algae and zoobenthos - effects on settling and community structure. Neth. J. Sea Res. 30: 57–62.
Clarke, K. R., 1993. Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Austr. J. Ecol. 18: 117–143.
Clarke, K. R. & R. M. Warwick, 1994. Changes in marine communities: an approach to statistical analysis and interpretation. Plymouth.
Eichwald, E., 1847. Erster Nachtrag zur Infusorienkunde Russlands. Bull. Soc. Imp. Nat. Moscou 20: 27–28.
Jansson, A.-M. & N. Kautsky, 1977. Quantitative survey of hard bottom communities in a Baltic archipelago. In: O'Ceidigh, P., B. F. Keegan, P. J. S. Boaden (eds), Biology of Benthic Organisms. Pergamon Press, Oxford, New York: 359–366.
Kautsky, H., 1989. Quantitative distribution of plant and animal communities of the phytobenthic zone in the Baltic Sea. Askö Contribution no 35. Stockholm University: 1–80.
Kautsky, H., 1992. The impact of pulp mill effluents on phytobenthic communities of the Baltic Sea. Ambio 21: 308–313.
Kautsky, H., 1995. Quantitative distribution of sublittoral plant and animal communities in the Baltic Sea gradient. In Elefteriou, A., A. Ansell & C. Smith Jr. (eds), Biology and Ecology of Shallow Coastal Waters. Olsen & Olsen, Fredensborg: 23–31.
Kautsky, H. & E. Van der Maarel, 1990. Multivariate approaches to the variation in benthic communities and environmental vectors in the Baltic Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog.Ser. 60: 169–184.
Kautsky, U. & H. Kautsky, 1995. Production and nutrient dynamics of coastal vegetation covered bottoms of the Baltic Sea. In Elefteriou, A., A. Ansell & C. Smith, Jr. (eds). Biology and Ecology of Shallow Coastal Waters. Olsen & Olsen, Fredensborg: 31–38.
Kukk, H., 1995. Phytobenthos. In Ojaveer, J. (ed.), Ecosystem of the Gulf of Riga between 1920 and 1990. Estonia Academy Publishers, Tallinn: 131–138.
Kukk, H. & G. Martin, 1992. Long-term dynamics of the phytobenthos in Pärnu Bay, the Baltic Sea. Proc. Acad. Sci. of Estonia Ecol. 2: 110–118.
Martin, G., 1999. Distribution of phytobenthos biomass in the Gulf of Riga (1984–1991). Hydrobiologia 393 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 135): 181–190.
Mäkinen, A. & K. Autio, 1986. Cladophora glomerata (Chlorophyta) as an indicator of coastal eutrophication. Proceedings of the third Finnish-Swedish seminar of the Gulf of Bothnia. Vesihallituksem Julkaisuja-Water Res. Inst. Finland 68: 160–163.
Norkko, A. & E. Bonsdorff, 1996. Rapid zoobenthos community responses to accumulations of drifting algae. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 131: 143–157.
Pullisaar, T., 1961. Bottom vegetation of Pärnu Bay - (in Estonian). Pärnu lahe pöhjataimestikust. Proc. Estonian Acad. Sci. Biol. 10: 340–345.
Schramm, W. & P. H. Nienhuis, 1996. Marine Benthic Vegetation. Recent Changes and the Effect of Eutrophication. Ecological Studies 123, Springer, Berlin: 470 pp.
Trei, T., 1986. Floristic composition of the phytobentos in Pärnu Bay and around Kihnu Island. (in Russian). Proc. Estonian Acad. Sci. Biol. 35: 56–60.
Warwick, R. M., 1993. Environmental impact studies on marine communities: pragmatic al considerations. Austr. J. Ecol. 18: 63–80.
Yurkovskis, A., F. Wulff, L. Rahm, A. Andruzaitis & M. Rodriguez-Medina (1993). A nutrient budget of the Gulf of Riga; Baltic Sea. Estuar. coast. Shelf Sci. 37: 113–127.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kautsky, H., Martin, G., Mäkinen, A. et al. Structure of phytobenthic and associated animal communities in the Gulf of Riga. Hydrobiologia 393, 191–200 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003510105274
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003510105274