Abstract
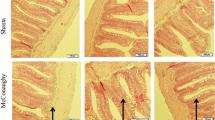
Four growth studies were conducted to determine the signs, biochemical indices and histopathology of a thiamin deficiency and the thiamin requirement of young rainbow trout reared at 15°C on a semi-purified test diet. The major overt signs of a thiamin deficiency in rainbow trout are predominantly neurological: irritability and instability. Other signs include convulsions, feed refusal, dark pigmentation and finally mortalities. Growth reduction in the thiamin deficient trout appear to result from anorexia or feed refusal and not specifically to a thiamin deficiency. Although there were prominant neurological signs in the thiamin deficient trout, there were no histopathological signs in any tissues of the trout, including the brain and central nervous system, examined by light microscopic techniques. The tissue transketolase activity would appear to be a sensitive and specific indicator of the thiamin status in the trout. In addition, the levels of plasma lactate and serum pyruvate are also elevated in thiamin deficient trout. On the basis of the growth parameters, absence of deficiency signs and kidney and liver transketolase activity, the thiamin requirement of rainbow trout reared at 15°C on a semi-purified test diet is 1 mg/kg feed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoe, H., Masuda, I., Mimura, T., Salto, T., Komo, A. and Kitamura, S. 1969. Water-soluable vitamin requirements of carp-VI. Requirement for thiamine and effects of antithiamines. Bull. Jap. Soc. Sci. Fish. 35: 459–465.
Bligh, E.G. and W.G. Dyer. 1959. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 37: 911–917.
Brin, M. 1962a. Erythrocyte transketolase in early thiamine deficiency. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 98: 528.
Brin, M. 1962b. Effects of thiamine deficiency and of oxythiamine on rat tissue transketolase. J. Nutr. 78: 179–183.
Brin, M. 1964. Erythrocyte as biopsy tissue for the functional evaluation of thiamin adequacy. J. Amer. Med. Assoc. 187: 762–766.
Brin, M. 1966. Transketolase: Clinical aspects.In Methods in Enzymology. Vol. 9. pp. 506–514. Edited by W.A. Wood. Academic Press, New York.
Brin, M., Tai, M., Ostashever, A.S. and Kalinsky, H. 1960. The effect of thiamine deficiency on the activity of erythrocyte hemolysate transketolase. J. Nutr. 71: 273–281.
Collins, G.H. 1967. Celial cell changes in the brain stem of thiamin-deficient rats. Am. J. Path. 50: 791–814.
Cowey, C.B., Adron, J.W. and Knox, D. 1975. Studies on the nutrition of marine flatfish. The thiamin requirement of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Br. J. Nutr. 34: 383–390.
Edwin, E.E., Markson, L.M. and Jackman, R. 1982. The aetiology of cerebrocortical necrosis: the role of thiamin deficiency and of deltapyrrolinium. Br. Vet. J. 138: 337–349.
Ensminger, A.H., Ensminger, M.E., Konlande, J.E. and Robson, J.R.K. 1983. Foods and Nutrition Encyclopedia. Vol. 2, I-Z. Pegus Press, California.
Gries, C.L. and Scott, M.L. 1972. The pathology of thiamin, riboflavin, panthothenic acid, and niacin deficiencies in the chick. J. Nutr. 102: 1269–1286.
Gubler, C.J. 1961. Studies on the physiological functions of thiamine. I. The effects of thiamine deficiency and thiamine antagonists on the oxidation of α-ketoacids by rat tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 236: 3112–3120.
Guyton, A.C. 1981. Textbook of Medical Physiology. Sixth edition. W.B. Saunders Company, Toronto.
Halver, J.E. 1972. The vitamins.In Fish Nutrition. pp. 29–103. Edited by J.E. Halver. Academic Press, New York.
Hilton, J.W. and Slinger, S.J. 1981. Nutrition and feeding of rainbow trout. Can. Special Public. Fish. Aqua. Sci. 55, Ottawa.
Hilton, J.W. and Atkinson, J.L. 1982. Responses of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) to increased levels of available carbohydrate in practical trout diets. Br. J. Nutr. 47: 597–607.
Hilton, J.W., Cho, C.Y. and Slinger, S.J. 1978. Effect of graded levels of supplemental ascorbic acid in practical trout diets fed to rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 35: 431–436.
Horwitz, W., Chichilo, P. and Reynolds, H. (eds.) 1970. AOAC Methods, Official Method of Analysis of the Official Analytical Chemists. Eleventh edition. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington, D.C.
Jones, J.H. and Deangeli, E. 1960. Thiamine deficiency and thein vivo oxidation of lactate and pyruvate labelled with carbon-14. J. Nutr. 70: 537–546.
Lehmitz, R. and Spannhof, L. 1977. Transketolase Aktivitat bei Thiaminmangel in der Niere von Regenbogenforellen,Salmo gairdneri, Nach kontinuierliche Futterung mit rohen Hering.). Arch. Tierenaehrung. 27: 287–295.
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A., and Randall, R.J. 1951. Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193: 265–275.
McLaren, B.A., Keller, E., O'Donnell, D.J. and Elvehjem, C.A. 1947a. The nutrition of rainbow trout. I. Studies of vitamin requirements. Arch. Biochem. 15: 169–178.
McLaren, B.A., Keller, E., O'Donnell, D.J. and Elvehjem, C.A. 1947b. The nutrition of rainbow trout. II. Further studies with purified diets. Arch. Biochem. 15: 179–185.
Morgan, K.T. 1973. An ultrastructural study of ovine polioencephalomalacia. J. Path. 110: 123–130.
Murai, T. and Andrews, J.W. 1978. Thiamine requirement of channel catfish fingerlings. J. Nutr. 108: 176–180.
National Research Council (NRC). 1981. Nutrient Requirements of Coldwater Fishes. No. 16 National Academy Press, Washington, D.C.
Phillips, A.M., Jr., Tunison, A.V., Shaffer, H.B., White, G.K., Sullivan, M.W., Vincent, C., Brockway, D.R. and McCay, C.M. 1945. The nutrition of the trout. Fish. Res. Bull. No. 7, N.Y. State Conservation Dept., Albany, New York.
Rucker, R.R., Johnson, H.E. and Kaydas, G.M. 1952. An interim report on gill disease. Prog. Fish Cult. 14: 10–14.
Platt, B.S. and Lu, G.D. 1939. Studies on the metabolism of pyruvic acid in normal and vitamin B1 deficiency states. IV. The accumulation of pyruvic acid and other carbonyl compounds in beriberi and the effect of vitamin B1. Biochem. J. 33: 1525–1537.
Rogers, L.E., Porter, F.S. and Jr. Didbury, J.B. 1969. Thiamine-responsive megaloblastic anemia. J. Pediat. 74: 494–504.
Sato, M., Yoshinaka, K. and Ikeda, S. 1978. Dietary ascorbic acid requirement for growth and collagen formation. Bull. Jap. Soc. Sci. Fish. 44: 1029–1035.
Sauberlich, H.E. 1967. Biochemical alterations in thiamine deficiency — their interpretation. Amer. J. Clin. Nutr. 20: 528–542.
Schneberger, E. 1941. Fisheries research in Wisconsin. Prog. Fish Cult. 56: 14. U.S. Dept. Interior, Fish and Wildl. Serv. Memo 1–131.
Smeets, E.H.J., Muller, H. and DeWael, J. 1971. A NADH-dependent transketolase assay in erythrocyte hemolysates. Clin. Chim. Acta 33: 379–386.
Steele, R.G.D. and Torrie, J.H. 1980. Principles and Procedures of Statistics. Second edition. McGraw-Hill Book Company, Toronto.
Tiemann, U. and Jurss, K. 1978. Biochemische untersuchungen zum Thiaminmangel der Regenbogenforelle (Salmo gairdneri). Wissensch. Schrift. 16: 31–33.
Tunison, A.V., Brockway, D.R., Maxwell, J.M., Dou, A.L. and McCay, C.M. 1942. The nutrition of the trout. Fish. Res. Bull. No. 4, N.Y. State Conservation Dept., Albany, New York.
Vo-Khactu, K.P., Clayburgh, R.H. and Sandstead, H.H. 1974. An improved NADH-dependent transketolase assay for assessing thiamine nutrition. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 83: 983–989.
Woodbury, LA. 1942. Vitamin B1 deficiency in hatchery reared rainbow trout. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 72: 30–32.
Wright, R.C. and Scott, E.M. 1953. Pyruvate and α-ketoglutarate metabolism in thiamine deficiency. J. Biol. Chem. 206: 725–733.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morito, C.L.H., Conrad, D.H. & Hilton, J.W. The thiamin deficiency signs and requirement of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri, Richardson). Fish Physiol Biochem 1, 93–104 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02290209
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02290209