Summary
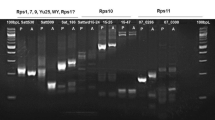
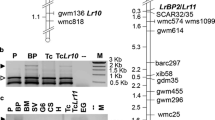
The Rp1 locus of maize is a complex rust resistance locus where multiple resistance genes are clustered. Rare recombination events between Rp1 genes or alleles can produce two or more detectable genes linked in coupling phase. Such ‘compound’ genes can then be manipulated as a single gene in breeding programs. Several compound Rp1 genes, each carrying two or three tightly linked resistance genes, were constructed to test their utility in controlling common rust. While none of the lines carrying single Rp1 genes were resistant to all of the characterized North American P. sorghi biotypes, most of the two component and all of the three component Rp1 complexes were resistant. The potential for utilization of compound resistance genes in other crop species is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brodory U., R.Nelson & L.Gregory, 1986. The residual and interactive expressions of ‘defeated’ wheat stem rust resistance genes. Phytopathology 76: 546–549.
Day P.R., J.A.Barrett & M.S.Wolfe, 1983. The evolution of host-parasite interaction. In: T.Kosuge & C.P.Meredith (Eds), Genetic Engineering of Plants. Plenum Press, New York.
Dickinson M., D.A.Jones & J.D.G.Jones, 1993. Close linkage between the Cf-2/Cf-5 and Mi resistance loci in tomato. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 6: 341–347.
Ellis J.G., G.J.Lawrence, E.J.Finnegan & P.A.Anderson, 1995. Contrasting complexity of two rust resistance loci in flax. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92: 4185–4188.
Farrara B.F., T.W.Ilott & R.W.Michelmore, 1987. Genetic analysis of factors for resistance to downy mildew (Bremia lactucae) in species of lettuce (Lactucae sativa and L. serriola). Plant Pathol. 36: 499–514.
Flor H.H., 1965. Tests for allelism of rust-resistance genes in flax. Crop Sci. 5: 415–418.
Flor H.H., 1971. Current status of the gene-for-gene concept. Adv. Genet. 8: 29–54.
Giese H., 1981. Powdery mildew resistance genes in the M1-a and M1-k regions on barley chromosome 5. Hereditas 95: 51–62.
Groth J.V., D.V.Davis, R.J.Zeyen & B.D.Mogen, 1983a. Ranking of partial resistance to common rust (Puccinia sorghi Schw) in 30 sweet corn (Zea mays) hybrids. Crop Prot. 2: 219–223.
Groth J.V., R.J.Zeyen, D.W.Davis & B.J.Christ, 1983b. Yield and quality losses caused by common rust (Puccinia sorghi Schw) in sweet corn (Zea mays) hybrids. Crop Prot. 2: 105–111.
Hagan W.L. & A.L.Hooker, 1965. Genetics of reaction to Puccinia sorghi in eleven corn inbreds from Central and South America. Phytopathology 55: 193–197.
Hooker A.L., 1985. Corn and sorghum rust. In: A.P.Roelfs & W.R.Bushnell (Eds). The Cereal Rusts. Vol. 2. Disease Distribution, Epidemiology and Control. pp. 207–236. Academic Press, New York.
Hooker A.L. & W.A.Russell, 1962. Inheritance of resistance to Puccinia sorghi in six corn inbred lines. Phytopathology 52: 122–128.
Hu G. & S.H.Hulbert, 1994. Evidence for involvement of gene conversion in meiotic instability of the Rp1 rust resistance genes of maize. Genome 37: 742–746.
Hulbert S.H. & J.L.Bennetzen, 1991. Recombination at the Rp1 locus of maize. Mol. Gen. Genet. 226: 377–382.
Hulbert S.H. & R.W.Michelmore, 1985. Linkage analysis of genes for resistance to downy mildew (Bremia lactucae) in lettuce (Lactuca sativa). Theor. Appl. Genet. 70: 520–528.
Hulbert S.H., P.C.Lyons & J.L.Bennetzen, 1991. Reactions of maize lines carrying resistance to isolates of the common rust pathogen, Puccinia sorghi. Plant Dis. 75: 1130–1133.
Hulbert S.H., M.A.Sudupak & K.S.Hong, 1993. Genetic relationships between alleles of the Rp1 rust resistance locus of maize. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 6: 387–392.
Jensen J., 1981. Coordinator's report: chromosome 5. Barley Genet. Newslett. 11: 87–88.
Kim S.K. & J.L.Brewbaker, 1977. Inheritance of general resistance in maize to Puccinia sorghi Schw. Crop Sci. 17: 456–461.
Koch M. & J.E.Parlevliet, 1991. Residual effects of the Xa-4 resistance gene in three rice cultivars when exposed to a virulent isolate of Xanthomonas campestris pv. oryzae. Euphytica 55: 187–193.
Martin T. & A.Ellingboe, 1976. Differences between compatible parasite/host genotypes involving the Pm4 locus of wheat and the corresponding genes in Erysiphe graminis f. sp. tritici. Phytopathology 66: 1435–1438.
Mayo G.M.E. & K.W.Shepherd, 1980. Studies of genes controlling specific host-parasite interactions in flax and its rust. 1. Fine structure analysis of the M group in the host. Heredity 44: 211–227.
Nelson R.R., 1972. Stabilizing racial populations of plant pathogens by use of resistance genes. J. Environ. Quality 1: 220–227.
Pataky J.K., 1986. Partial rust resistance in sweet corn hybrid seedlings. Phytopathology 76: 702–707.
Pataky J.K. & J.M.Headrick, 1989. Management of common rust on sweet corn with resistance and fungicides. J. Prod. Agric. 2: 362–369.
Pederson W. & S.Leath, 1988. Pyramiding major genes for resistance to maintain residual effects. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 26: 369–378.
Randle W.M., D.W.Davis & J.V.Groth, 1984. Improvement and genetic control of partial resistance in sweet corn to corn leaf rust. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 109: 777–781.
Saxena K.M.S. & A.L.Hooker, 1968. On the structure of a gene for disease resistance in maize. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 68: 1300–1305.
Shepherd K.W. & G.M.E.Mayo, 1972. Genes conferring specific plant disease resistance. Science 175: 375–380.
Sudupak M.A., J.L.Bennetzen & S.H.Hulbert, 1993. Unequal exchange and meiotic instability of Rp1 region disease resistance genes in maize. Genetics 133: 119–125.
Watson I.A., 1970. Changes in virulence and population shifts in plant pathogens. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 8: 209–230.
Wilkinson D.R. & A.L.Hooker, 1968. Genetics of reaction to Puccinia sorghi in ten corn inbreds from Africa and Europe. Phytopathology 58: 605–608.
Wise R.P. & A.H.Ellingboe, 1985. Fine structure and instability of the ML-a locus in barley. Genetics 111: 113–130.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, G., Hulbert, S. Construction of ‘compound’ rust resistance genes in maize. Euphytica 87, 45–51 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00022963
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00022963