Summary
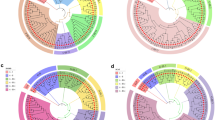
Thirty-five rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties, including 18 japonica, 5 javanica and 12 indica subspecies and 12 lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) varieties were identified taxonomically, using PCR with originally designed 21 RAPD (Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA) primers and 8 sequence-specific primers, used for amplifying four specific DNA fragments. Use of these primers revealed polymorphisms among varieties in rice and lettuce and facilitates DNA fingerprinting. Dendrograms of both species based on polymorphisms were constructed and genetical relationships were established. In rice, half the number of amplified bands were polymorphic and almost all varieties differentiated. However, differentiation of minor genetic alterations among somaclonal variants or mutants and their mother varieties was not feasible. In L. sativa, 47% of the amplified fragments were polymorphic and all 12 varieties were differentiated. Some of the PCR fragments were variety or type specific, which could be used for indicators for type-selection. The dendrogram obtained showed differentiated clusters of crisphead, leaf and butterhead type, findings in good accord with the classification based on the genetic background.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fukuoka S., K.Hosaka & O.Kamijima, 1992. Use of random amplified polymorphic DNAs (RAPDs) for identification of rice accessions. Jpn. J. Genet. 67: 243–252.
Glaszmann J.C., 1988. Geographic pattern of variation among Asian native rice cultivars (Oryza sativa L.) based on fifteen isozyme loci. Genome 30: 782–794.
Kesseli R.V. & R.W.Michelmore, 1986. Genetic variation and phylogenies detected from isozyme markers in species of Lactuca. J. Hered. 77: 324–331.
Kesseli R., O.Ochoa & R.Michelmore, 1991. Variation at RFLP loci in Lactuca spp. and origin of cultivated lettuce (L. sativa). Genome 24: 430–436.
Matsuo T., 1952. Genecological studies on cultivated rice. Bull. Nat. Inst. Agric. Sci. Jpn. D3: 1–111.
Minami E., Y.Ozeki, M.Matsuoka, N.Koizuka & Y.Tanaka, 1989. Structure and some characterization of the gene for phenylalanine ammonia-lyase from rice plants. Eur. J. Biochem. 185: 19–25.
Murray M.G. & W.F.Thompson, 1980. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Research 8: 4321–4325.
Oka H.I., 1953. Variations of various characters and character combinations among rice varieties. Jpn. J. Breed. 3 (2): 33–43.
O'Neill S.D., M.H.Kumagai, A.Majumdar, N.Hung, T.D.Sutliff & R.L.rodriguez, 1990. The α-amylase genes in Oryza sativa: Characterization of cDNA clones and mRNA expression during seed germination. Mol. Gen. Genet. 221: 235–244.
Saiki R.S., S.Scharf, F.Faloona, K.B.Mullis, G.T.Horn, H.A.Erlich & N.Arnheim, 1985. Enzymatic amplification of β-globulin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science 230: 1350–1354.
Sneath P.H.A. & R.R.Sokal, 1973. Numerical taxonomy. W.H. Freeman, San Francisco, CA.
Sokal R.R. & C.D.Michener, 1958. A statistical method for evaluating systematic relationships. Univ. Kansas Sci. Bull. 38: 1409–1438.
Song K., T.C.Osborn & P.H.Williams, 1990. Brassica taxonomy based on nuclear restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs). Theor. Appl. Genet. 79: 497–506.
Takaiwa F., H.Ebinuma, S.Kikuchi & K.Oono, 1987. Nucleotide sequence of a rice glutelin gene. FEBS Lett. 221: 43–47.
Takaiwa F., S.Kikuchi & K.Oono, 1990. The complete nucleotide sequence of the intergenic spacer between 25s and 17s rDNAs in rice. Plant Molecular Biology 15: 933–935.
Tanksley S.D., S.D.Young, A.H.Paterson & M.W.Bonierbale, 1989. RFLP mapping in plant breeding—new tools for an old science. Bio/Technology 7: 257–264.
Wang Z.Y. & S.D.Tanksley, 1989. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms in Oryza sativa L. Genome 32: 1113–1118.
Watari M. & M.Kishi, 1981. Programs for multivariate analysis. Kougaku Tosho, Tokyo.
Welsh J. & M.McClelland, 1991. Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Research 18: 7213–7218.
Williams J.G.K., A.R.Kubelik, K.J.Livak, J.A.Rafalski & S.V.Tingey, 1991. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Research 18: 6531–6535.
Xie Y. & R.Wu, 1988. Nucleotide sequence of a ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase small subunit gene (rbcS) in rice. Nucleic Acids Research 15: 7749.
Zheng K.L., B.Shen & H.R.Qian, 1991. DNA polymorphisms generated by arbitrary primed PCR in rice. Rice Genetic Newsletter 8: 134–136.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamamoto, T., Nishikawa, A. & Oeda, K. DNA polymorphisms in Oryza sativa L. and Lactuca sativa L. amplified by arbitrary primed PCR. Euphytica 78, 143–148 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00021410
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00021410