Abstract
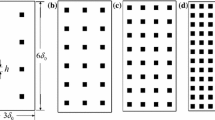
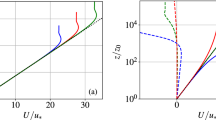
We develop a parameterisation for the effective roughness length of terrain that consists of a repeating sequence of patches, in which each patch is composed of strips of two roughness types. A numerical model with second-order closure in the turbulent stress is developed and used to show that: (i) the normalised Reynolds stress develops as a self-similar profile; (ii) the mixing-length parameterisation is a good first-order approximation to the Reynolds stress. These findings are used to characterise the blending layer, where the stress adjusts smoothly from its local surface value to its ‘effective’ value aloft. Previous studies have assumed that this adjustment occurs abruptly at a single level, often called the blending height. The blending layer is shown to be characterised by height scales that arise naturally in linear models of surface layer flow over roughness changes, and calculations with the numerical model show that these height scales remain appropriate in the nonlinear regime. This concept of the blending layer allows the development of a new parameterisation of the effective roughness length, which gives values for the effective roughness length that are shown to compare well with both atmospheric measurements and values determined from the second-order model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belcher, S. E., Xu, D. P., and Hunt, J. C. R.: 1990, ‘The Response of a Turbulent Boundary Layer to Arbitrarily Distributed Two-Dimensional Roughness Changes’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 116, 611-635.
Belcher, S. E., Newley, T. M. J., and Hunt, J. C. R.: 1993, ‘The Drag on an Undulating Surface Induced by the Flow of a Turbulent Boundary Layer’, J. Fluid Mech. 249, 557-596.
Bradley, E. F.: 1968, ‘A Micrometeorological Study of Velocity Profiles and Surface Drag in the Region Modified by a Change in Surface Roughness’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 94, 361-379.
Brutsaert, W. H.: 1982, Evaporation into the Atmosphere — Theory, History and Applications, Reidel, Dordrecht, 299 pp.
Claussen, M.: 1987, ‘The Flow in a Turbulent Boundary Layer Upstream of a Change in Surface Roughness’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 40, 31-86.
Claussen, M.: 1990, ‘Area-Averaging of Surface Fluxes in a Neutrally Stratified, Horizontally Inhomogeneous Atmospheric Boundary Layer’, Atmos. Environ. 24A, 1349-1360.
Dufort, E. C. and Frankel, S. P.: 1953, Math. Tables Aid Comput. 7, 135-152.
Fiedler, F. and Panofsky, H. A.: 1972, ‘The Geostrophic Drag Coefficient and the “Effective” Roughness Length’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 98, 213-221.
Garratt, J. R.: 1994, The Atmospheric Boundary Layer, Cambridge University Press, U.K., 316 pp.
Goode, K.: 1997, Modelling Surface-Layer Flow over Heterogeneous Terrain, Ph.D. Thesis, University of Reading.
Hobson, J. M, Wood, N., and Brown, A. R.: 1999, ‘Large-Eddy Simulations of Neutrally-Stratified Flow over Surfaces with Spatially Varying Roughness Length’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc., in press.
Hogstrom, U.: 1988, ‘Non-Dimensional Wind and Temperature Profiles in the Atmospheric Surface Layer: A Re-Evaluation’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 42, 55-78.
Hopwood, W. P.: 1995, ‘Surface Transfer of Heat and Momentum over an Inhomogeneous Vegetated Land Surface’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 121, 1549-1574.
Huang, C. H. and Nickerson, E. C.: 1974, ‘Stratified Flow over Non-Uniform Surface Conditions: Mixing Length Model’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 5, 395-417.
Kaimal, J. C. and Finnigan, J. J.: 1994, Atmospheric Boundary Layer Flows: Their Structure and Measurement, Oxford University Press, U.K., 289 pp.
Lewellen, W. S. and Teske, M.: 1973, ‘Prediction of the Monin-Obukov Similarity Functions from an Invariant Model of Turbulence’, J. Atmos. Sci. 30, 1340-1345.
Mahrt, L.: 1996, ‘The Bulk Aerodynamic Formulation over Heterogeneous Surfaces’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 78, 87-119.
Mason, P. J.: 1988, ‘The Formation of Areally-Averaged Roughness Lengths’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 114, 399-420.
Panofsky, H. A. and Townsend, A. A: 1964, ‘Change of Terrain Roughness and the Wind Profile’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 98, 845-854.
Rao, K. S., Wyngaard, J. C., and Cote, O. R.: 1974, ‘The Structure of the Two-Dimensional Internal Boundary Layer over a Sudden Change of Surface Roughness’, J. Atmos. Sci. 31, 738-746.
Raupach, M. R., Coppin, P. A., and Legg, B. J.: 1986, ‘Experiments on Scalar Dispersion within a Model Plant Canopy Part I. The Turbulence Structure’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 35, 21-52.
Rotta, J. C.: 1951, ‘Statistische Theorie Nichthomogener Turbulenz’, Z. Phys. 129, 547-572; 131, 51–77.
Schmid, H. P. and Bunzli, B.: 1995, ‘The Influence of Surface Texture on the Effective Roughness Length’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 121, 1-21.
Smith, F. B. and Carson, D. J.: 1977, ‘Some Thoughts on the Specification of the Boundary Layer Relevant to Numerical Modelling’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 12, 307-330.
Taylor, P. A.: 1969, ‘On Wind and Shear Stress Profiles above a Change in Surface Roughness’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 95, 77-91.
Taylor, P. A.: 1987, ‘Comments and Further Analysis on the Effective Roughness Length for Use in Numerical Three Dimensional Models’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 39, 403-419.
Weiringa, J.: 1986, ‘Roughness-Dependent Geographical Interpolation of Surface Wind Speed Averages’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 112, 867-889.
Wood, D. H.: 1982, ‘Internal Boundary Layer Growth Following a Step Change in Surface Roughness’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 22, 241-244.
Wood, N. and Mason, P.: 1991, ‘The Influence of Static Stability on the Effective Roughness Lengths for Momentum and Heat Transfer’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 117, 1025-1056.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goode, K., Belcher, S.E. On the Parameterisation of the Effective Roughness Length for Momentum Transfer over Heterogeneous Terrain. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 93, 133–154 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002035509882
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002035509882