Abstract
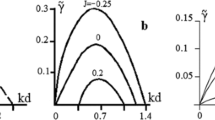
A Simple slab model of the planetary boundary layer is extended to include vertical shear of the geostrophic wind. The layer depth is assumed to be determined by a Richardson number criterion. The cross-isobar angle for the surface wind is given in terms of the drag coefficient, the Froude number of the layer, and the angle between the thermal wind and the surface isobars. The theoretical results resemble the observations rather well.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernstein, A. B.: 1973, ‘Some Observations of the Influence of Geostrophic Shear on the Cross-Isobar Angle of the Surface Wind’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 3, 381–384.
Lettau, H. H.: 1950, ‘A Re-Examination of the Leipzig Wind Profile’,Tellus 2, 125.
MacKay, K. P.: 1971, ‘Steady State Hodographs in a Baroclinic Boundary Layer’,Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 2, 161–168.
Pollard, R. T., Rhines, P. B., and Thompson, R. O. R. Y.: 1973, ‘The Deepening of the Wind-Mixed Layer’,Geophys. Fluid Dynamics 3, 381–404.
Thompson, R. O. R. Y.: 1973, ‘Stratifid Ekman Layer Models’,Geophys. Fluid Dynamics, (in press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thompson, R.O.R.Y. The influence of geostrophic shear on the cross-isobar angle of the surface wind. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 6, 515–518 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02137684
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02137684