Abstract
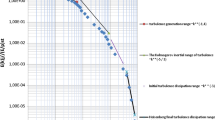
The whole paper consists of two parts (Part I and Part II). In part I, we shall analyze the relation between the two theories of turbulence involving large Reynolds number: the Markov process theory from the Lagrangian point of view and Kolmogoroff's theory from the Eulerian point of view. It will be pointed out that the Reynolds number needed for the Markovian description of turbulence should be as large as that needed for Kolmogoroff's second hypothesis, that the eddies of the period of order T1 (the self-correlation time scale of the random velocity u) and the eddies of the period of order T1 (the self-correlation time scale of the random force f) correspond to the energy-containing eddies and the eddies in the dissipation range respectively, and that T*⩽t≪β−1, the time interval for the applicability of Richardson's law during twoparticle's dispersion, corresponds to the inertial subrange in Kolmogoroff's theory. Thus, these two theories reflect the property of the turbulence involving very large Reynolds number arguing from different aspects.
In Part II, by using physical analysis in Part I, we shall establish in a certain way the quantitative relation between these two theories. In terms of this relation and the results of the study of two-particle's dispersion motion, we shall obtain the structure functions, the correlation functions and the energy spectrum, which are appliciable not only to the inertial subrange, but also to the whole range with the wave number less than that in the inertial subrange. Kolmogoroff's “2/3 law” and ”−5/3 law” are the asymptotic solutions with respect to the present result in the inertial subrange. Thus, the present result is an extension of Kolmogoroff's laws.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yueh, T. Y., et al., Scientia Sinica, 17, (1974), 181–192.
Kolmogoroff, A.,The local structure of turbulence in an incompressible viscous fluid for very large Reynolds number (1941), in: Turbulence, Classic Papers on Statistical Theory, Ed. S. K. Friedlander and Leonard Topper, (1961).
Kolmogoroff, A.,On degeneration of isotropic turbulence in an incompressible viscous liquid, ibid, in: Turbulence, Classic Papers on Statistical Theory, Ed. S. K. Friedlander and Leonard Topper, (1941).
Kolmogoroff, A.,Dissipation of energy in the locally isotropic turbulence ibid., in: Turbulence, Classic Papers on Statistical Theory, Ed. S. K. Friedlander and Leonard Topper, 1941).
Krassnoff, E. and R. L. Peskin,Geophysical Fluid Dynamics 2 (1971), 123–146.
Wang Z. K.,The basis and the applications of the theory of probability, Science Press, (1976). (in Chinese)
Hinze, J. O.? Turbulence, McGraw-Hill, Inc. (1975).
Obukhov, A. M., Advances in Geophysics, 6, (1959), 113.
Stewart, R. W. and A. A. Townsend, Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. London, 243A, (1951), 359.
Chandrasekhar, S., Review of Modern Physics, 15, (1943), 1–89.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by Dai Shi-giang.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng-yuan, Y., Bin, Z. The relation between Markov process theory and Kolmogoroff's theory of turbulence and the extension of Kolmogoroff's laws. Appl Math Mech 3, 845–851 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01895339
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01895339