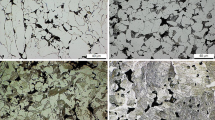
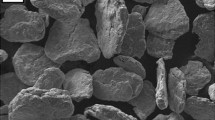
Abstract
High-energy disintegration of powder charges (the method of mechanical alloying) in which the initial components interact at a higher substructural level than in conventional mixing provides qualitatively new powder materials with a high degree of homogeneity and dispersity of the structure. The possibilities of the given method for a radical improvement of the quality of low-alloy heat-treatable steels virtually have not been studied because of the absence of data on the special features of polymorphic transformations in mechanically alloyed powder materials based on iron. This hampers realization of the advantages of powder metallurgy over other less efficient technologies in the field of manufacturing high-strength structural parts. In order to substantiate the choice of heat-treatment regimes of mechanically alloyed materials, the authors of the present paper studied the special features of the isothermal γ→α transformation and the structure and properties of low-alloy steels after sintering and heat treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. N. Antsiferov, N. N. Maslennikov, S. N. Peshcherenko, and A. I. Rabinovich, “Determination of chemical nonuniformity of the distribution of alloying elements in powder materials,”Poroshk. Metall., No. 2, 63–66 (1982).
E. A. Apaev,Phase Magnetic Analysis of Alloys [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1973).
L. I. Mirkin,X-Ray Diffraction Control of Machine Materials, A Reference Book [in Russian], Mashinostroenie, Moscow (1979).
L. E. Popova and A. A. Popov,Diagrams of Austenite Transformation in Steels and β-Solutions in Titanium Alloys, A Reference Book [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1991).
G. V. Kurdyumov, L. M. Utevskii, and R. I. Éntin,Transformations in Iron and Steel [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1977).
A. P. Gulyaev,Physical Metallurgy [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1977).
S. S. D'yachenko,Formation of Austenite in Iron-Carbon Steels [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1982).
I. P. Kholodny, N. A. Sidorov, and V. F. Astrakhantsev, “A study of properties of powder low-alloy steels,” in:Powder Structural Materials, Coll. Works [in Russian], IPM AN UkrSSR, Kiev (1980), pp. 42–45.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 8, pp. 20–22, August, 1997.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maslennikov, N.N., Bobrova, S.N., Grevnov, L.M. et al. Effect of the manufacturing technology on the structure and properties of heat-treatable powder steels. Met Sci Heat Treat 39, 343–346 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02467633
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02467633