Conclusions
-
1.
Iron and steel may be impregnated by vaporization of tin or antimony in a vacuum. Tin impregnation turns the diffusion layer into a substitutional solid solution of tin in iron. Antimony impregnation causes the formation of a defect solid solution with a composition that approximately equals the FeSb phase.
-
2.
Impregnation of iron and steel with tin or antimony gives rise to an increase in volume which is rather insignificant in impregnating with tin and considerable with antimony.
-
3.
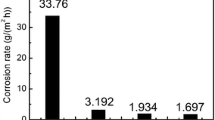
The impregnation with tin or antimony increases the corrosion resistance of steel and iron in aqueous solutions of certain acids and salts by several times.
-
4.
Impregnation with tin should be conducted at 1050 to 1150° C for two hours; the optimal temperature for the impregnation with antimony lies around 550° C with a holding time of about three hours. In both cases a 1 mm Hg vacuum is sufficient.
Similar content being viewed by others
Bibliography
M. I. Parfenov, N. A. Izgaryshev, Zhurnal prikladnoy khimii, Vol. 25, No. 7, 1952.
N. S. Gorbunov, Diffusion Layers on Steel and Iron, Izd. AN SSSR, 1958.
E. Gudremon, Special Steels, Metallurgizdat, Vol. II, 1960.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Titov, V.K., Makarov, Y.F. Diffusive impregnation of iron and steel with tin and antimony. Met Sci Heat Treat 3, 353–355 (1961). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00810402
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00810402