Abstract
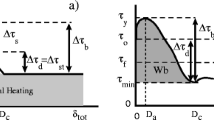
Source parameter scaling relations are examined for microseismic events (−2.4≤M≤−0.3) occurring within higyly and moderately stressed and fractured rock masses at Strathcona mine, Sudbury, Canada. Insight into scaling is provided by waveform complexities, calculated rupture velocities, and maximum shear stresses based onin situ and numerical modelling data. The importance of normal stress on the failure process is also considered. Our results show that a strong dependence exists between stress release and seismic moment. An observed positive scaling in excess stress release (Δσ/2−σ a ) is consistent with the concept of overshoot. Rupture velocities ranging from 0.2 to 0.5β and waveform complexities less than 1.5 suggested that overshoot was related to healing behind a slowly advancing rupture front. Scaling in seismic efficiency paralleled that in apparent stress, implying that seismic stress release estimates are quasi-independent of the maximum shear stress. High levels of normal stress further supported the importance of high resisting stress in the observed overshoot behaviour and its role in the failure process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aki, K. (1984),Asperities, Barriers, Characteristic Earthquakes and Strong Motion Prediction, J. Geophys. Res.89, 5867–5872.
Barton, N., andBandis, S. C.,Review of predictive capabilities of JRC-JCS model in engineering practice. InRock Joint (eds. Barton, N., and Bandis, S. C.) (A. A. Balkema, Rotterdam 1990) pp. 603–610.
Bird, S. (1993),Link of Structural Mapping, Numerical Modelling, and Microseismic Source Parameters with Application to Mine Design, M.Sc. Thesis, Department of Mining Engineering, Queen's University, Kingston, Canada.
Boatwright, J. (1980),A Spectral Theory for Circular Seismic Sources; Simple Estimates of Source Dimension, Dynamic Stress-drop, and Radiated Seismic Energy, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am.70, 1–27.
Boatwright, J. (1984),The Effect of Rupture Complexity on Estimates of Source Size, J. Geophys. Res.89, 1132–1146.
Boore, D. M., andBoatwright, J. (1984),Average Body-wave Radiation Coefficients, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am.74, 1615–1621.
Brune, J. N. (1970),Tectonic Stress and the Spectra of Seismic Shear Waves from Earthquakes, J. Geophys. Res.75, 4997–5009, Correction in J. Geophys. Res.76, 5002 (1971).
Cichowicz, A., Green, R. W. E., Brink, A. V. Z., Grobler, P., andMontfort, P. I.,The space and time variation of microevents occurring in front of an active slope. InRokbursts and Seismicity in Mines (ed. Fairhurst, C.) (A. A. Balkema, Rotterdam 1990) pp. 171–175.
Cochrane, L. B. (1991),Analysis of the Structural and the Tectonic Environments Associated with Rock Mass Failures in the Mines of the Sudbury District, Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Geological Sciences, Queen's University, Kingston, Canada.
Feustel, A., Urbancic, T. I., andYoung, R. P.,Estimates of Q using the spectral decay technique for seismic events with M<−1. InRockbursts and Seismicity in Mines (ed. Young, R. P.) (A. A. Balkema Rotterdam 1993) pp. 337–342.
Fletcher, J. B., Haar, L. C., Vernon, F. L., Brune, J. N., Hanks, T. C., andBerger, J.,The effect of attenuation on the scaling of source parameters for earthquakes at Anza, California. InEarthquake Source Mechanics (eds. Das, S., Boatwright, J., and Scholz, C. H.) Am. Geophys. Union, Washington, D.C. (1986) pp. 331–338.
Gephart, J. W., andForsyth, D. W. (1984),An Improved Method for Determining the Original Stress Tensor Using Earthquake Focal Mechanism Data: Application to the San Fernando Earthquake Sequence, J. Geophys. Res.89, 9305–9320.
Gibowicz, S. J., Young, R. P., Talebi, S., andRawlence, D. J. (1991),Source Parameters of Seismic Events at the Underground Research Laboratory in Manitoba, Canada: Scaling Relations for Events with Moment Magnitude Smaller than-2, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am.81, 1157–1182.
Hanks, T. C. (1977),Earthquake Stress Drops, Ambient Tectonic Stress and Stresses that Drive Plate Motions, Pure and Appl. Geophys.115, 441–448.
Hanks, T. C., andKanamori, H. (1979),A Moment Magnitude Scale, J. Geophys. Res.84, 2348–2350.
Hanks, T. C., andMcGuire (1981),The Character of High Frequency Strong Ground Motion, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am.71, 2071–2096.
Kagan, Y. Y. (1994),Incremental Stress and Earthquakes, Geophys. J. Int.117, 345–364.
Madariaga, R. (1976),Dynamics of an Expanding Circular Fault, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am.66, 639–666.
McGarr, A. (1981),Analysis of Peak Ground Motion in Terms of a Model of Inhomogeneous Faulting. J. Geophys. Res.86, 3901–3912.
McGarr, A. (1984),Scaling of Ground Motion Parameters, State of Stress, and Focal Depth, J. Geophys. Res.89, 6969–6979.
McGarr, A. (1994),Some Comparisons between Mining Induced and Laboratory Earthquakes, Pure and Appl. Geophys.142, 467–489.
Naldrett, A. L., andKullerud, G. (1967),A Study of the Strathcona Mine and its Bearing on the Origin of the Nickel-copper Ores of the Sudbury District, Ontario, J. Petrology8, 453–531.
Snoke, J. A. (1987),Stable Determination of (Brune) Stress Drops, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am.77, 530–538.
Rudnicki, J. W., andKanamori, H. (1981),Effects of Fault Interaction on Moment, Stress Drop, and Strain Energy Release, J. Geophys. Res.86, 1785–1793.
Urbancic, T. I., Feignier, B., andYoung, R. P. (1992),Influence of Source Region Properties on Scaling Relations for M<O Events, Pure and Appl. Geophys.139, 721–739.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Urbancic, T.I., Trifu, CI. Effects of rupture complexity and stress regime on scaling relations of induced microseismic events. PAGEOPH 147, 319–343 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00877486
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00877486