Abstract
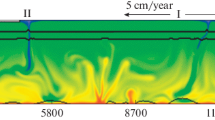
This study presents the results of numerical simulations of a model for lithospheremantle coupling in a terrestrial type planet. To first order, a geologically active terrestrial type planet may consist of a metallic core, silicate mantle and lithosphere, with the lithosphere being rheologically different from the mantle. Therefore we have developed a numerical model consisting of a thin non-Newtonian fluid hoop that is dynamically coupled to a thick Newtonian fluid cylindrical annulus. Thus the rheological dichotomy between mantle and lithosphere is built into the model. Time-dependent calculations show the existence of at least two regimes of behaviors. In one regime, the behavior of the hoop switches between periods characterized by low or high speeds, in response to changes in convective vigor and planform. This regime may apply to the planet Venus where the available evidence indicates that prior to 500 myr ago, the planet was resurfaced on a time scale of <100 myr. Since that time, large-scale tectonic activity on Venus has been sharply curtailed. In the other regime, which is more like plate tectonics on Earth, the hoop speeds rise and fall on short time scales.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bercovici, D., Schubert, G., andGlatzmeir, G. A. (1992),Three-dimensional Convection of an Infinite-Prandtl Number Compressible Fluid in a Basally Heated Spherical Shell, J. Fluid Mech.239, 683–719.
Bercovici, D. (1993),A Simple Model of Plate Generation from Mantle Flow, Geophys. J. Int.114, 635–650.
Bercovici, D. (1995),A Source-sink Model of the Generation of Plate Tectonics from non-Newtonian Mantle Flow, J. Geophys. Res.100, 2013–2030.
Cathles, L. M.,Viscosity of the Earth's Mantle (Princeton University Press, Princeton 1975).
Christensen, U. R. (1983),Convection in a Variable Viscosity Fluid: Newtonian Versus Power-law, Earth. Planet. Sci. Lett.64, 153–162.
Christensen, U. R. (1984),Convection with Pressure- and Temperature-dependent non-Newtonian Rheology, Geophys. J. R. Astr. Soc.77, 343–384.
Christensen, U. R., andHarder, H. (1991),3-D Convection with Variable Viscosity, Geophys. J. Int.104, 213–226.
Cserepes, L. (1982),Numerical Simulations of non-Newtonian Mantle Convection. Phys. Earth. Planet. Inter.30, 49–61.
Davies, G. F. (1988),Role of the Lithosphere in Mantle Convection, J. Geophys. Res.93, 10,451–10,466.
DeMets, C., Gordon, R. G., Argus, D. F., andStein, S. (1990),Current Plate Motions, Geophys. J. Int.101, 425–478.
Elsasser, W. M.,Convection and stress propagation in the upper mantle. InThe Application of Modern Physics to the Earth and Planetary Interiors (ed. Runcorn, S. K.) (Wiley Interscience, New York 1969) pp. 223–246.
Hager, B. H., andO'Connell, R. J. (1981),A Simple Model of Plate Dynamics and Mantle Convection, J. Geophys. Res.86, 4843–4867.
Jacoby, W. R., andSchmeling, H. (1982),On the Effects of the Lithosphere on Mantle Convection and Evolution, Phys. Earth Planet. Int.29, 305–319.
King, S. D., andHager, B. H. (1990),The Relationship between Plate Velocity and Trench Viscosity in Newtonian and Power-law Subduction Calculations. Geophys. Res. Lett.12, 2409–2412.
Minster, J. B., andJordan, J. H. (1978),Present-day Plate Motions, J. Geophys. Res.83, 5331–5354.
Peltier, W. R.,Mantle convection and viscosity. InProceedings of the Enrico Fermi International School of Physics, Course LXXVIII (eds. Dziewonski, A. M., and Boschi, E.) (North Holland, Amsterdam 1980) pp. 362–431.
Phillips, R. J., Raubertas, R. F., Arvidson, R. E., Sarkar, I. C., Herrick, R. R., Izenberg, N., andGrimm, R. E. (1992),Impact Craters and Venus Resurfacing History, J. Geophys. Res.97, 15,923–15,948.
Solomon, S. C., Smrekar, S. E., Bindschadler, D. L., Grimm, R. E., Kaula, W. M., McGill, G. E., Phillips, R. J., Saunders, S., Schubert, G., Squyers, S. W., andStofan, E. (1992),Venus Tectonics: An Overview of Magellan Observations, J. Geophys. Res.97, 13,199–13,255.
Solomon, S. C. (1993),The Geophysics of Venus, Phys. Today47, 48–55.
Strom, R. G., Schaber, G. G., andDawson, D. D. (1994), The Global Resurfacing of Venus. J. Geophys. Res.99, 10,899–10,926.
Surkov, Y. A., Kirnozov, F. F., Glazov, V. N., Dunchenko, A. G., Tasty, L. P., andSobornov, O. P. (1987),Uranium, Thorium and Potassium in the Venusian Rocks at the Landing Site of Vega 1 and 2, Proc. Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. 17th, Part 2, J. Geophys. Res.92 Suppl., E537-E540.
Turcotte, D. L. (1993),An Episodic Hypothesis for Venusian Tectonics, J. Geophys. Res.98, 17,061–17,068.
Weinstein, S. A., andOlson, P. L. (1992),Thermal Convection with non-Newtonian Plates, Geophys. J. Int.109, 481–487.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weinstein, S.A. Thermal convection in a cylindrical annulus with a non-Newtonian outer surface. PAGEOPH 146, 551–572 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00874733
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00874733