Abstract
Mining of a highly-stressed remnant in a deep South African gold mine was accompanied by considerable seismic activity and some significant rockbursts. The larger seismic events were registered some 60 km away at a WSSN station and several shear ruptures corresponding to these events were encountered during mining operations.
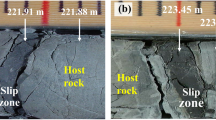
A careful study based on detailed exploration of two of these ruptures proved them to be the source of two of the larger rockbursts.
Certain striking features revealed by a scanning electron microscopic study of some of the fresh cataclastic ‘rock-flour’ forming part of the comminuted filling of these ruptures provide strong evidence of violent ’shock rebound’ phenomena in the faulting process. This interpretation could provide useful insight into earthquake source mechanisms and also has practical significance in the understanding of mine rockbursts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gay, N. C., andOrtlepp, W. D. (1979),Anatomy of a Mining-induced Fault Zone, Geol. Soc. of Am. Bull., Part 1,90, 47–58.
Gibowicz, S. J.,The mechanism of large mining tremors in Poland. InProc. 1st Int. Symp. on Rockbursts and Seismicity in Mines (SAIMM Symp. Series No. 6, Johannesburg, South Africa 1984) pp. 17–28.
Hanks, T. C.,A rms and seismic source studies. InProc. 1st Int. Symp. on Rockbursts and Seismicity in Mines (SAIMM Symp. Series No. 6, Johannesburg, South Africa 1984) pp. 39–44.
Lomnitz-Adler, J. (1991),Model for Steady-state Friction, J. Geophys. Rev.96, No. B4, 6121–6131.
Lurie, J. (1991),Private communication, Dr. J. Lurie of Technikon, Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa (Fax) (011) 402–0475.
McGarr, A., Pollard, D. D., Gay, N. C., andOrtlepp, W. D. (1979),Observations and analysis of structures in exhumed mine-induced faults. InProceedings of Conference VIII: Analysis of Actual Fault Zones in Bedrock (U. S. Geol. Survey, Menlo Park. Open file Rep. 79-1239) pp. 101–120.
McGarr, A., Spottiswoode, S. M., andGay, N. C. (1975),Relationship of Mine Tremors to Induced Stresses and to Rock Properties in the Focal Region, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am.65, 981–993.
Morris, R. C. (1986),Private communication, CSIRO Division of Minerals and Geochemistry, Underwood Ave., Floreat Park, WA, Australia.
Olgaard, D. L., andBrace, W. F. (1983),The Microstructure of Gouge from a Mining-induced Seismic Shear Zone, Int. J. Rock Mech. and Min. Sci.,20, 11–19.
Ortlepp, W. D. (1978),The Mechanism of a Rockburst, Proc. 19th U.S. Rock Mechanics Symp. Stateline, Nevada, pp. 476–483.
Ortlepp, W. D. (1992),The Design of Support for the Containment of Rockburst Damage in Tunnels—An Engineering Approach, Int. Symp. on Rock Support, Laurentian Univ, Sudbury, Ontario, Canada, 606 pp.
Segall, P., andPollard, D. D. (1980),Mechanics of Discontinuous Faults, J. Geophys. Res.85, B8, 4337–4350.
Spottiswoode, S. M.,Source mechanism of mine tremors at Blyvooruitzucht Gold Mine. InProc. 1st Int. Symp. on Rockbursts and Seismicity in Mines (SAIMM Symp. Series No 6, 1984) pp. 29–37.
Van Aswegen, G.,Fault stability in S. A. gold mines. InProc. Int. Conf. on Mechanics of Joint and Faulted Rock (Tech. Univ. of Vienna, Vienna, Austria, April 1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ortlepp, W.D. Note on fault-slip motion inferred from a study of micro-cataclastic particles from an underground shear rupture. PAGEOPH 139, 677–695 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00879958
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00879958