Abstract
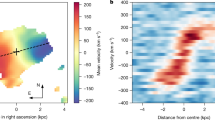
We present first results from the Near-infrared Integral Field Spectrograph (NIFS) located at Gemini North. For the active galaxies Cygnus A and Perseus A we observe rotationally-supported accretion disks and adduce the existence of massive central black holes and estimate their masses. In Cygnus A we also see remarkable high-excitation ionization cones dominated by photoionization from the central engine. In the T-Tauri stars HV Tau C and DG Tau we see highly-collimated bipolar outflows in the [Fe II] λ 1.644 micron line, surrounded by a slower molecular bipolar outflow seen in the H2 lines, in accordance with the model advocated by Pyo, T.-S., et al., Astrophys. J. 570, 724 (2002).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appenzeller, I., Bertout, C., Stahl, O.: Astron. Astrophys. 434, 1005 (2005)
Bicknell, G.V., Dopita, M.A., O’Dea, C.P.: Astrophys. J. 485, 112 (1997)
Bicknell, G.V., Sutherland, R.S., van Breugel, W.J.M., Dopita, M.A., Dey, A., Miley, G.K.: Astrophys. J. 540, 678 (2000)
Canalizo, G., Max, C., Whysong, D., Antonucci, R., Dahm, S.E.: Astrophys. J. 597, 823 (2003)
Conselice, C.J., Gallagher, J.S. III, Wyse, R.F.G.: Astron. J. 122, 2281 (2001)
Dopita, M.A., et al.: Astrophys. J. 490, 202 (1997)
Dopita, M., McGregor, P., Beasley, A., Freeman, K., Wilson, A., Storch-Bergmann, T., Blum, R.D.: (2007, in preparation)
Fabian, A.C.: Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 32, 277 (1994)
Fabian, A.C.: Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 344, L65 (2003)
Fabian, A.C., et al.: Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 318, L65 (2000)
Fabian, A.C., et al.: Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 344, L43 (2003)
Garcia, P.J.V., Ferreira, J., Cabrit, S., Binette, L.: Astron. Astrophys. 377, 589 (2001)
Gómez de Castro, A.I.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 292, 561 (2004)
Groves, B.A., Dopita, M.A., Sutherland, R.S.: Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 153, 9 (2004a)
Groves, B.A., Dopita, M.A., Sutherland, R.S.: Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 153, 75 (2004b)
Güdel, M., Skinner, S.L., Briggs, K.R., Audard, M., Arzner, K., Telleschi, A.: Astrophys. J. 626, 53 (2004)
Kino, M., Kawakatu, N.: Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 364, 659 (2005)
Krabbe, A., et al.: Astron. Astrophys. 354, 439 (2000)
Küker, M., Henning, Th., Rüdiger, G.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 292, 599 (2004)
Lavalley-Fouquet, C., Cabrit, S., Dougados, C.: Astron. Astrophys. 356, 41 (2000)
Magazzu, A., Martin, E.L.: Astron. Astrophys. 287, 571 (1994)
McGregor, P.J., Conroy, P., Bloxham, G., van Harmelen, J.: Proc. Astron. Soc. Aust. 16, 273 (1999)
McGregor, P.J., Dopita, M., Wood, P., Burton, M.G.: Proc. Astron. Soc. Aust. 18, 41–57 (2001)
Minkowski, R.: In: Van de Hulst, H.C. (ed.) Proc. IAU Symp. 4, p. 107. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1957)
Monin, J.-L., Bouvier, J.: Astron. Astrophys. 356, 75 (2000)
Lynds, R.: Astrophys. J. 159, L151 (1970)
Padgett, D.L., et al.: Astron. J. 117, 1490 (1999)
Pyo, T.-S., et al.: Astrophys. J. 570, 724 (2002)
Pyo, T.-S., et al.: In: Brandner, W., Kasper, M.E. (eds.) Proceedings of the ESO Workshop Science with Adaptive Optics, p. 242. Springer, Berlin (2005)
Rudy, R.J., et al.: Astrophys. J. 414, 527 (1993)
Shu, F., Najita, J., Ostriker, E., Wilkin, F., Ruden, S., Lizano, S.: Astrophys. J. 429, 781 (1994)
Simon, M., Chen, W.P., Howell, R.R., Benson, J.A., Slowik, D.: Astrophys. J. 384, 212 (1992)
Stapelfeldt, K.R., et al.: Astrophys. J. 589, 410 (2003)
Tadhunter, C.N., et al.: Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 313, 52 (2000)
Takami, M., et al.: Astron. Astrophys. 416, 213 (2004)
Terada, H.: Poster presented at the Conference “Protostars & planets V” (2005)
Wilman, R.J., Fabian, A.C., Ghandi, P.: Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 318, 1232 (2000)
Wilman, R.J., Edge, A.C., Johnstone, R.M.: Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 359, 755 (2005)
Wilson, A.S., Smith, D.A., Young, A.J.: Astrophys. J. 644, 9 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McGregor, P., Dopita, M., Sutherland, R. et al. Gemini observations of disks and jets in young stellar objects and in active galaxies. Astrophys Space Sci 311, 223–230 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-007-9537-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-007-9537-1