Abstract
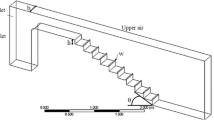
From 1970s, studies have been conducted on the hydraulic design of stepped spillways and many empirical formulas were developed. Despite the simple geometry of these spillways, their hydraulic behavior is complicated. As a result, for many cases, the physical models are studied to verify the design. Numerical simulation is considered as a tool to reduce the laboratory tests, in order to save time and money. Furthermore, the parameters which are not investigated or measured in physical models could be evaluated. In this paper, the results of numerical simulations are compared with the results of physical models and empirical formulas for the spillway of Renwick dam studied in a 1/8 scale model by Hunt and Kadavy (World Environmental and Water Resources Congress. ASCE, Great Rivers, pp. 3061–3071, 2009). Numerical simulation of flow is achieved by a mixture multi-phase flow model and a realizable k-\({\varepsilon}\) turbulence model proposed by Qian et al. (Sci China Ser E-Tech Sci 52(7), 1958–1965, 2009). Grid sensitivity is accomplished and the size of mesh is reduced in locations where a high gradient of certain parameters exists or a higher precision is required. The numerical simulation results conform to the physical model tests. The velocity profile, energy dissipation, and the location of inception point where air entrainment in the flow is guaranteed, are investigated and compared to the scale model results. Also, thanks to this satisfaction, we could obtain the parameters such as pressure field which are not measured in the physical model.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hunt, S.L.; Kadavy, K.C.: The effect of step height on energy dissipation in stepped spillways. World Environmental and Water Resources Congress. ASCE, Great Rivers, pp. 3061–3071 (2009)
Qian Z., XiaoQing H., WenXin H., AMADOR A.: Numerical simulation and analysis of water flow over stepped spillways. Sci China Ser. E-Tech. Sci. 52(7), 1958–1965 (2009)
Boes R.M., Hager W.H.: Hydr aulic design of stepped spillways. J. Hydrol. Eng. ASCE 129(9), 671–679 (2003)
Tongkratoke A., Chinnarasri C., Pornprommin A., Dechaumphai P., Juntasaro V.: Non-linear turbulence models for multiphase recirculating free-surface flow over stepped spillways. Int. J. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 23(5), 401–409 (2009)
Chanson, H.: The Hydraulics of Stepped Chutes and Spillways. Bulkema Publ., The Netherlands, pp. 140–180 (2002)
Hunt, S.L.; Kadavy, K.C.: Velocities and energy dissipation on a flatsloped stepped spillway. In: Proceedings of American Society of Agriculutral and Biological Engineers (ASABE) Annual International Meeting, Paper No. 084151. ASABE, St. Joesph (2008)
Takahashi M., Gonzalez C.A., Chanson H.: Self-aeration and turbulence in a stepped channel: influence of cavity surface roughness. Int. J. Multiphase Flow 32, 1370–1385 (2006)
Boes R.M., Hager W.H.: Two-phase flow characteristics of stepped spillways. J. Hydrol. Eng. ASCE 129(9), 661–670 (2003)
Motamedi Zoka H., Omidian A., Kholghi H.: A comparative assessment of compressible Reynolds Stress model and some variant k-\({\varepsilon}\) for engine flow applications. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 37(6), 1737–1749 (2012)
Karimi, M.; Jahromi, H.: Turbulence models in skimming flow simulation. 9th Iranian Conference of Hydraulics, Tarbiat Modarres University, Tehran (2010)
Kavianpoor, M.; Moshtaghian, A.; Shamloo, H.; Najafi, M.: Air entrainment mechanism in stepped spillways. 7th Iranian Conference of Hydraulics, Power and Water University of Technology, Tehran (2008)
Hosseini, M.; Kavianpoor, M.: Characteristics of two-phase flow over stepped spillways. 9th Iranian Conference of Hydraulics, Tarbiat Modarres University, Tehran (2010)
Mirzaeian, A.; Javan, M.: Comparison VOF and Mixture models in skimming flow simulation. 9th Iranian Conference of Hydraulics, Tarbiat Modarres University, Tehran (2010)
Ohtsu, I.; Yasuda, Y.: Characteristics of flow conditions on stepped channels. In: Proceedings of 27th IAHR Biennal Congress, Theme D, San Francisco, pp. 583–588 (1997)
Amador, A.; Sanchez-Juny, M.; Dolz, J.; Sanchez-Tembleque, F.; Puertas, J.: Velocity and pressure measurements in skimming flow in stepped spillways. In: Yazdandoost, F.; Attari, J. (eds.) Proceedings of the International Conference on Hydraulics of Dams and River Structures. Balkema Publ., Tehran, pp. 279–285 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Attarian, A., Hosseini, K., Abdi, H. et al. The Effect of the Step Height on Energy Dissipation in Stepped Spillways Using Numerical Simulation. Arab J Sci Eng 39, 2587–2594 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-013-0900-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-013-0900-y