Abstract
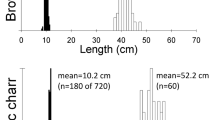
Predation could be one force determining which contemporary species occupy a certain habitat. Aeshna viridis is an endangered dragonfly species with a larval distribution strongly associated with lakes where the water plant, water soldier, Stratiotes aloides, occurs. In this study, the larvae were almost exclusively found in patches of S. aloides. To study larval association with S. aloides further, we conducted a series of laboratory experiments. Behavioural experiments indicated that larvae preferred S. aloides. Aeshna viridis larvae were nocturnal and rather inactive. Larvae on S. aloides were less susceptible to predation by the perch, Perca fluviatilis, than larvae on another water plant, Myriophyllum alterniflorum. According to our study it seems that occurrence of S. aloides may limit the distribution of A. viridis, and the protection of refuges may be essential in planning the conservation of this endangered species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Askew R.R. 1988. The Dragonflies of Europe. Harley Books, Colchester, USA, 291 pp.
Corbet P.S. 1999. Dragonflies: Behavior and Ecology of Odonata. Harley, Colchester, USA, 829 pp.
Crooks K.R. and Soulé M.E. 1999. Mesopredator release and avifaunal extictions in a fragmented system. Nature 400: 563–566.
Crowder L.B. and Cooper W.E. 1982. Habitat structural complexity and the interaction between bluegills and their prey. Ecology 63: 1802–1813.
Diehl S. 1993. Effects of habitat structure on resource availability, diet and growth of benthivorous perch, Perca fluviatilis. Oikos 67: 403–414.
Guti G. 1993. Mortality, growth and diet of perch Perca fluviatilis L. in the Cikola branch system of the Szigetköz area, River Danube. Arch. Hydrobiol. 128: 317–327.
Hämet-Ahti L., Suominen J., Ulvinen T., Uotila P. and Vuokko S. 1984. Retkeilykasvio. Suomen Luonnonsuojelun Tuki Oy, Helsinki, 544 pp.
Higler L.W.G. 1977. Macrofauna canoes on Stratiotes plants in Dutch broads. Verh. Res. Inst. Nat. Manag. 11: 1–86.
Hopper K.R. 2001. Flexible antipredator behaviour in a dragonfly species that coexists with different predator types. Oikos 93: 470–476.
Johnson D.M. 1991. Behavioral ecology of larval dragonflies and damselflies. TREE 6: 8–13.
de Jong T.H. 2000. DeSoortenbeschermingsplan voor Krabbescheer en Groene Glazenmaker. Provincie Utrecht, Drukkerij Anraad b.v., Nieuwegein, The Netherlands.
de Jong T.H. 2001. DeBeschermingsplan groene glazenmaker 2002-2006. Rapport Directie Natuurbeheer, Ministerie van Landbouw, Natuurbeheer en Visserij 2001/015: 1–72.
Lessels C.M. and Boag P.T. 1987. Unrepeatable repeatabilities: a common mistake. Auk 104: 116–121.
Martin T.H., Johnson D.M. and Moore R.D. 1991. Fish mediated alternative life-history strategies in the dragonfly Epitheca cynosura. J. N. Am. Benth. Soc. 10: 271–279.
McPeek M.A. 1998. The consequences of changing the top predator in a food web: a comparative experimental approach. Ecol. Monogr. 68: 1–23.
Morin P.J. 1984. Odonate guild composition: experiments with colonization history and fish predation. Ecology 65: 1866–1873.
Norling U. 1971. The life history and seasonal regulation of Aeshna viridis Eversm. in southern Sweden (Odonata). Ent. Scand. 2: 170–190.
Norling U. and Sahlen G. 1997. Odonata, dragonflies and damselflies.. In: Nilsson A. (ed.), Aquatic Insects of North Europe. Vol. 2. Apollo Books, pp. 13–65.
Persson L. 1983. Effects of intra-and interspecific competition on dynamics and size structure of a perch Perca fluviatilis and a roach Rutilus rutilus population. Oikos 41: 126–132.
Prejs A. 1973. Experimentally increased fish stock in the pond type Lake Warniak 4. Feeding of introduced and autochthonous nonpredatory fish. Ekol. Pol. 21: 465–504.
Prejs A., Koperski P. and Prejs K. 1997. Food-web manipulation in a small, eutrophic Lake Wirbel, Poland: The effect of replacement of key predators on epiphytic fauna. Hydrobiologia 342/ 343: 377–381.
Rantalainen E. and Kanervo E. 1928. DeAeshna viridiksen esiintymisestä ja elintavoista Suomessa. Luonnon Ystävä 32: 161–170.
Rask M. 1986. The diet and diel feeding activity of perch, Perca fluviatilis L., in small lake in southern Finland. Ann. Zool. Fenn. 23: 49–56.
Roelofs J.G.M. 1991. Inlet of alkaline river water into peaty lowlands: effects on water quality and Stratiotes aloides L. stands. Aquat. Bot. 39: 267–293.
Schoener T.W. and Spiller D.A. 1995. Effect of predators and area on invasion: An experiment with island spiders. Science 267: 1811–1813.
Sih A. 1987. Predator and Prey Lifestyles: An Evolutionary and Ecological Overview.. In: Kerfoot W.C. and Sih A. (eds), Predation: Direct and Indirect Impacts on Aquatic Communities. University Press of New England, Hanover, New Hampshier, USA, pp. 203–224.
Smolders A.J.P, Roelofs J.G.M. and Den Hartog C. 1996. Possible causes for the decline of the water soldier (Stratiotes aloides L.) in Netherlands. Arch. Hydrobiol. 136: 327–342.
Valle K. 1952. DeSuomen eläimet 7. Sudenkorennot. WSOY, Porvoo and Helsinki, 159 pp.
Valtonen P. 1997. DeSuku Aeshna Suomessa ja Pirkanmaalla 1. Osa. Diamina 6: 6–12.
Wellborn G.A. and Robinson J.V. 1987. Microhabitat selection as an antipredator strategy in the aquatic insect Pachydiplax longipennis Burmeister (Odonata: Libellulidae). Oecologia 71: 185–189.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rantala, M.J., Ilmonen, J., Koskimäki, J. et al. The macrophyte, Stratiotes aloides, protects larvae of dragonfly Aeshna viridis against fish predation. Aquatic Ecology 38, 77–82 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:AECO.0000021005.22624.16
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:AECO.0000021005.22624.16