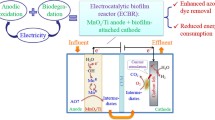
Abstract
A novel bioelectrochemical system (BES) operated with polarity reversion was explored for simultaneous anaerobic/aerobic treatment of azo dye and production of bioelectricity under extremely low buffer. The Congo red was first decolorized in anode, with completed color removal in 35 h. The resultant decolorization intermediates were then mineralized after the anode reversed to aerobic biocathode, evidenced by 55 % chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal in 200 h. The mineralization efficiency was further increased to 70 % when the period of the half-cycle was prolonged to 375 h. Meanwhile, the BES produced a continuous stable positive/negative alternate voltage output under 5 mM phosphate buffer because of the self-neutralization of the accumulated protons and hydroxyl ions in electrolyte. The electrode performance was significantly improved, which was indicated by alleviated electrode polarization, due to in situ use of accumulated protons and hydroxyl ions and enhanced electron transfer in the presence of Congo red and its degradation intermediates, which resulted in 1.05-fold increases in maximum power density (67.5 vs. 32.9 mW/m2). An analysis of the microbial diversity in the biofilm revealed that the biofilm was dominated by facultative bacteria with functional roles in contaminant degradation and electricity generation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 19th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215(3):403–10
Cai P, Xiao X, He Y, Li W, Chu J, Wu C, He M, Zhang Z, Sheng G, Lam MH, Xu F, Yu H (2012) Anaerobic biodecolorization mechanism of methyl orange by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93(4):1769–1776
Chen B, Hsueh C, Liu S, Ng I, Wang Y (2013) Deciphering mediating characteristics of decolorized intermediates for reductive decolorization and bioelectricity generation. Bioresour Technol 145:321–325
Chen BY, Zhang MM, Chang CT, Ding Y, Lin KL, Chiou CS, Hsueh CC, Xu H (2010) Assessment upon azo dye decolorization and bioelectricity generation by Proteus hauseri. Bioresour Technol 101:4737–4741
Cheng KY, Ho G, Cord-Ruwisch RA (2010) Anodophilic biofilm catalyzes cathodic oxygen reduction. Environ Sci Technol 44(1):518–525
El-Chakhtoura J, El-Fadel M, Ananda Rao H, Li D, Ghanimeh S, Saikaly PE (2014) Electricity generation and microbial community structure of air-cathode microbial fuel cells powered with the organic fraction of municipal solid waste and inoculated with different seeds. Biomass Bioenerg 67:24–31
Fernando E, Keshavarz T, Kyazze G (2013) Simultaneous co-metabolic decolourisation of azo dye mixtures and bio-electricity generation under thermophilic (50 °C) and saline conditions by an adapted anaerobic mixed culture in microbial fuel cells. Bioresour Technol 127:1–8
Gil GC, Chang IS, Kim BH, Kim M, Jang JK, Park HS, Kim HJ (2003) Operational parameters affecting the performance of a mediator-less microbial fuel cell. Biosens Bioelectron 18:327–334
Grabowski A, Tindall BJ, Bardin V, Blanchet D, Jeanthon C (2005) Petrimonas sulfuriphila gen. nov., sp. nov., a mesophilic fermentative bacterium isolated from a biodegraded oil reservoir. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55(3):1113–1121
Gupta RS, Lorenzini E (2007) Phylogeny and molecular signatures (conserved proteins and indels) that are specific for the Bacteroidetes and Chlorobi species. BMC Evol Biol 7(1):71
Harnisch F, Schroder U, Scholz F (2008) The suitability of monopolar and bipolar ion exchange membranes as separators for biological fuel cells. Environ Sci Technol 42:1740–1746
He Z, Mansfeld F (2009) Exploring the use of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) in microbial fuel cell studies. Energy Environ Sci 2:215–219
Iino T, Mori K, Uchino Y, Nakagawa T, Harayama S, Suzuki K (2010) Ignavibacterium album gen. nov., sp. nov., a moderately thermophilic anaerobic bacterium isolated from microbial mats at a terrestrial hot spring and proposal of Ignavibacteria classis nov., for a novel lineage at the periphery of green sulfur bacteria. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60(6):1376–1382
Jung J, Yeom J, Kim J, Han J, Lim H, Park H, Hyun S, Park W (2011) Change in gene abundance in the nitrogen biogeochemical cycle with temperature and nitrogen addition in Antarctic soils. Res Microbiol 162:1018–1026
Kiely PD, Regan JM, Logan BE (2011) The electric picnic: synergistic requirements for exoelectrogenic microbial communities. Curr Opin Biotechnol 22(3):378–385
Kragelund C, Levantesi C, Borger A, Thelen K, Eikelboom D, Tandoi V, Kong K, Waarde J, Krooneman J, Rossetti S, Thomsen TR, Nielsen PH (2007) Identity, abundance and ecophysiology of filamentous Chloroflexi species present inactivated sludge treatment plants. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 59(3):671–682
Liang B, Cheng H, Van Nostrand JD, Ma J, Yu H, Kong D, Liu W, Ren N, Wu L, Wang A, Lee D, Zhou J (2014) Microbial community structure and function of nitrobenzene reduction biocathode in response to carbon source switchover. Water Res 54(1):137–148
Liu R, Sheng G, Sun M, Zang G, Li W, Tong Z, Dong F, Lam MH, Yu H (2011) Enhanced reductive degradation of methyl orange in a microbial fuel cell through cathode modification with redox mediators. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89(1):201–208
Logan B, Regan JM (2006) Electricity-producing bacterial communities in microbial fuel cells. Trends Microbiol 14(12):512–518
Lovley DR, Phillips EJP (1988) Novel mode of microbial energy metabolism: organism carbon oxidation coupled to dissimilatory reduction of iron and manganese. Appl Environ Microbiol 54(6):1472–1480
Pandey A, Singh P, Iyengar L (2007) Bacterial decolorization and degradation of azo dyes. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 59:73–84
Pankratov TA, Ivanova AO, Dedysh SN, Liesack W (2014) Bacterial populations and environmental factors controlling cellulose degradation in an acidic Sphagnum peat. Appl Environ Microbiol 13(7):1800–1814
Pant D, Bogaert GV, Diels L, Vanbroekhoven K (2010) A review of the substrates used in microbial fuel cells (MFCs) for sustainable energy production. Bioresour Technol 101(6):1533–1543
Pant D, Singh A, Van Bogaert G, Irving Olsen S, Singh Nigam P, Diels L, Vanbroekhoven K (2012) Bioelectrochemical systems (BES) for sustainable energy production and product recovery from organic wastes and industrial wastewaters. RSC Adv 2(4):1248–1263
Qiu G, Song Y, Zeng P, Duan L, Xiao P (2013) Characterization of bacterial communities in hybrid upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB)–membrane bioreactor (MBR) process for berberine antibiotic wastewater treatment. Bioresour Technol 142:52–62
Rosenbaum MA, Frank AE (2014) Microbial catalysis in bioelectrochemical technologies: status quo, challenges and perspectives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(2):509–518
Shinoda Y, Sakai Y, Uenishi H, Uchihashi Y, Hiraishi A, Yukawa H, Yurimoto H, Kato N (2004) Aerobic and anaerobic toluene degradation by a newly isolated denitrifying bacterium, Thauera sp. strain DNT-1. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(3):1385–1392
Solanki K, Subramanian S, Basu S (2013) Microbial fuel cells for azo dye treatment with electricity generation: a review. Bioresour Technol 131:564–571
Strik DPBTB, Hamelers HVM, Buisman CJN (2010) Solar energy powered microbial fuel cell with a reversible bioelectrode. Environ Sci Technol 44(1):532–537
Štursová M, Žifčáková L, Leigh MB, Burgess R, Baldrian P (2012) Cellulose utilization in forest litter and soil: identification of bacterial and fungal decomposers. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 80(3):735–746
Sui WJ, Asuming-Brempong S, Wang Q, Tourlousse DM, Penton CR, Deng Y, Rodrigues JLM, Adiku SGK, Jones JW, Zhou J, Cole JR, Tiedjea JM (2013) Tropical agricultural land management influences on soil microbial communities through its effect on soil organic carbon. Soil Biol Biochem 65:33–38
Sun J, Bi Z, Hou B, Cao Y, Hu Y (2011) Further treatment of decolorization liquid of azo dye coupled with increased power production using microbial fuel cell equipped with an aerobic biocathode. Water Res 45(1):283–291
Sun J, Li Y, Hu Y, Hou B, Zhang Y, Li S (2013) Understanding the degradation of Congo red and bacterial diversity in an air–cathode microbial fuel cell being evaluated for simultaneous azo dye removal from wastewater and bioelectricity generation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(8):3711–3719
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5261–5267
Wang Z, Zheng Y, Xiao Y, Wu S, Wu Y, Yang Z, Zhao F (2013) Analysis of oxygen reduction and microbial community of air-diffusion biocathode in microbial fuel cells. Bioresour Technol 144:74–79
Wu J, Jiang C, Wang B, Ma Y, Liu Z, Liu S (2006) Novel partial reductive pathway for 4-chloronitrobenzene and nitrobenzene degradation in Comamonas sp. strain CNB-1. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(3):1759–1765
Yamada T, Imachi H, Ohashi A, Harada H, Hanada S, Kamagata Y, Sekiguchi Y (2007) Bellilinea caldifistulae gen. nov., sp. nov. and Longilinea arvoryzae gen. nov., sp. nov., strictly anaerobic, filamentous bacteria of the phylum Chloroflexi isolated from methanogenic propionate-degrading consortia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57(10):2299–2306
Yang Q, Wang J, Wang H, Chen X, Ren S, Li X, Xu Y, Zhang H, Li X (2012) Evolution of the microbial community in a full-scale printing and dyeing wastewater treatment system. Bioresour Technol 117:155–163
Zanaroli G, Balloi A, Negroni A, Borruso L, Daffonchio D, Fava FA (2012) Chloroflexi bacterium dechlorinates polychlorinated biphenyls in marine sediments under in situ-like biogeochemical conditions. J Hazard Mater 209–210:449–457
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the financial support provided by the National Natural Science Fund of China (No. 51108186) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2014ZZ0018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary
UV-visible spectra data for the decolorization liuquid in the bicathode reversed from previous anode, membrane transport of main cations in the BES during polarity reversion, and electrochemical impedance spectra and cyclic voltammograms of the bioelectrodes before and after polarity reversion are shown in Figure S1-4. (PDF 279 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, J., Zhang, Y., Liu, G. et al. Unveiling characteristics of a bioelectrochemical system with polarity reversion for simultaneous azo dye treatment and bioelectricity generation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 7295–7305 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6614-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6614-1