Summary
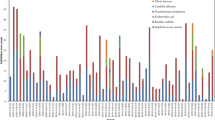
Bioactive actinomycetes were isolated from marine sediments using rifampicin. Plating the sediments on starch-casein agar, supplemented with rifampicin, eliminated the occurrence of contaminating microorganisms. Total counts, however, were reduced in the presence of rifampicin. Most of the isolates contained ll-2,6-diaminopimelic acid (DAP), whereas 37% contained meso-DAP. The use of increasing concentrations of rifampicin tended to yield a higher proportion of strains with cell extracts positive for meso-DAP. Streptomyces and Micromonospora represented the major genera identified. Antimicrobial activity was exhibited by 46% of the isolates, primarily against Gram-positive bacteria. Inhibition of Gram-negative bacteria was minimal, but antimycotic activity was displayed by 28% of the actinomycetes. Most of the latter activity was attributable to polyenes, particularly hexanenes. The results obtained indicate that rifampicin, added to starch-casein agar, is effective for the isolation of bioactive actinomycetes from marine sediments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Athalye M, Lacey J, Goodfellow M (1981) Selective isolation and enumeration of actinomycetes using rifampicin. J Appl Bacteriol 51:289–297
Becker B, Lechevalier MP, Gordon RE, Lechevalier HA (1964) Rapid differentiation between Nocardia and Streptomyces by paper chromatography of whole cell hydrolysates. Appl Microbiol 12:421–423
Chromonova NT (1978) Isolation of Actinomadura from soil samples on selective media with kanamycin and rifampicin. Antibiotiki 23:22–26
Cross T (1982) Actinomycetes: a continuing source of new metabolites. Dev Ind Microbiol 23:1–18
Goodfellow M, Haynes JA (1984) Actinomycetes in marine sedeiments. In: Ortiz-Ortiz L, Bojalil LF, Yakoleff V (eds) Biological, biochemical and biomedial aspects of actinomycetes. Academic Press, New York, pp 453–472
Okami Y (1984) Marine microorganisms as a source of bioactive substances. In: Klug MJ, Reddy CA (eds) Current perspectives in microbial ecology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 651–655
Okami Y (1986) Marine microorganisms as a source of bioactive agents. Microb Ecol 12:65–78
Okazaki T, Okami Y (1972) Studies on marine microorganisms. II. Actinomycetes in Sagami Bay and their antibiotic substances. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 25:461–466
Pisano MA, Sommer MJ, Lopez MM (1986) Application of pretreatments for the isolation of bioactive actinomycetes from marine sediments. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 25:285–288
Pisano MA, Sommer MJ, Brett BP (1987) Hudson River sediments as a source of actinomycetes exhibiting antifungal activity. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 27:214–217
Tunac JB, Graham BD, Dobson WE, Lenzini MD (1985) Fermentation by a new daunomycin-producing organism, Streptomyces insignis ATCC 31913. Appl Environ Microbiol 49:265–268
Vickers JC, Williams ST, Ross GW (1984) A taxonomic approach to selective isolation of streptomycetes from soil. In: Ortiz-Ortiz L, Bojalil LF, Yakoleff V (eds) Biological, biochemical, and biomedical aspects of actinomycetes. Academic Press, New York, pp 553–561
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pisano, M.A., Sommer, M.J. & Brancaccio, L. Isolation of bioactive actinomycetes from marine sediments using rifampicin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 31, 609–612 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00270804
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00270804