Abstract
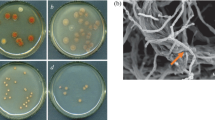
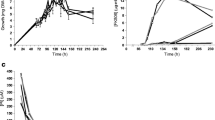
‘Streptomyces tsukubaensis’ was the first tacrolimus producer strain identified. Although it has been included in the Streptomyces genus, its taxonomic position has not been rigorously determined. By using a polyphasic approach, we have established that the tacrolimus producer strain ‘S. tsukubaensis’ NRRL 18488 represents a unique species in the Streptomyces genus, which is phylogenetically distant from other subsequently described producers. This fact means a horizontal transference of the tacrolimus-producing gene cluster. Physiology, nutrient requirement, and molecular genetics analyses of tacrolimus biosynthesis in ‘S. tsukubaensis’ necessitate chemically defined or semi-defined media, which work as a jigsaw puzzle and allow for pieces (nutrients) exchange. To date, studies related to ‘S. tsukubaensis’ have been mainly focused in the improvement of tacrolimus production using complex industrial fermentation media, which difficulty allows testing of tacrolimus overproduction enhancers or inhibitors because of the presence of non‐defined substances. In the present work, two semi-defined media were developed in order to study the main factors involved in tacrolimus production in ‘S. tsukubaensis’.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharonowitz Y (1980) Nitrogen metabolite regulation of antibiotic biosynthesis. Annu Rev Microbiol 34:209–233
Aidoo KA, Wong A, Alexander DC, Rittammer RA, Jensen SE (1994) Cloning, sequencing and disruption of a gene from Streptomyces clavuligerus involved in clavulanic acid biosynthesis. Gene 147(1):41–46
Barreiro C, Prieto C, Sola-Landa A, Solera E, Martínez-Castro M, Perez-Redondo R, Garcia-Estrada C, Aparicio JF, Fernandez-Martínez LT, Santos-Aberturas J, Salehi-Najafabadi Z, Rodríguez-García A, Tauch A, Martín JF (2012) Draft genome of ‘Streptomyces tsukubaensis’ NRRL 18488, the producer of the clinical immnunosuppressant tacrolimus (FK506). J Bacteriol 194(14):3756–3757
Baumann K, Emmer G (1999) Heteroatoms-containing tricyclic compounds. US Patent 5,912,238
Becker B, Lechevalier MP, Gordon RE, Lechevalier HA (1964) Rapid differentiation between Nocardia and Streptomyces by paper chromatography of whole-cell hydrolysates. Appl Microbiol 12:421–423
Burget U, Zundel G (1986) Lysine–phosphate hydrogen bonds and hydrogen-bonded chains with large proton polarizability in polylysine–phosphate systems: IR investigations. J Mol Struct 145(1–2):93–109
Butler AR, Cundliffe E (2001) Influence of dimethylsulfoxide on tylosin production in Streptomyces fradiae. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 27(1):46–51
Chen G, Wang GY, Li X, Waters B, Davies J (2000) Enhanced production of microbial metabolites in the presence of dimethyl sulfoxide. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 53(10):1145–1153
Cheng YR, Hauck L, Demain AL (1995) Phosphate, ammonium, magnesium and iron nutrition of Streptomyces hygroscopicus with respect to rapamycin biosynthesis. J Ind Microbiol 14(5):424–427
De Ley J, Cattoir H, Reynaerts A (1970) The quantitative measurement of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates. Eur J Biochem 12:133–142
Doull JL, Vining LC (1990) Nutritional control of actinorhodin production by Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2): suppressive effects of nitrogen and phosphate. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 32(4):449–454
Dumont F, Garrity GM, Fernandez IM, Matas TD (1992) Process for producing FK-506. US Patent 5,116,756
Euzéby JP (1997) List of bacterial names with standing in nomenclature: a folder 243 available on the Internet. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:590–592
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39(4):783–791
Fireman M, Di Martini AF, Armstrong SC, Cozza KL (2004) Immunosuppressants. Psychosomatics 45:354–360
Garrity GM, Heimbuch BK, Motamedi H, Shafiee A (1993) Genetic relationships among actinomycetes that produce the immunosuppressant macrolides FK506, FK520/FK523 and rapamycin. J Ind Microbiol 12(1):42–47
Goranovic D, Kosec G, Mrak P, Fujs S, Horvat J, Kuscer E, Kopitar G, Petkovic H (2010) Origin of the allyl group in FK506 biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 285(19):14292–14300
Hasegawa T, Takizawa M, Tanida S (1983) A rapid analysis for chemical grouping of aerobic actinomycetes. J Gen Appl Microbiol 29:319–322
Hodgson DA (2000) Primary metabolism and its control in streptomycetes: a most unusual group of bacteria. Adv Microb Physiol 42:47–238
Huss VAR, Festl H, Schleifer KH (1983) Studies on the spectrophotometric determination of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates. Syst Appl Microbiol 4:184–192
Jhang J, Wolfe S, Demain AL (1989) Phosphate regulation of ACV synthetase and cephalosporin biosynthesis in Streptomyces clavuligerus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 48(2):145–150
Jones KL (1949) Fresh isolates of actinomycetes in which the presence of sporogenous aerial mycelia is a fluctuating characteristic. J Bacteriol 57:141–145
Kim HS, Park YI (2008) Isolation and identification of a novel microorganism producing the immunosuppressant tacrolimus. J Biosci Bioeng 105(4):418–421
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Kino T, Hatanaka H, Hashimoto M, Nishiyama M, Goto T, Okuhara M, Kohsaka M, Aoki H, Imanaka H (1987) FK-506, a novel immunosuppressant isolated from a Streptomyces. I. Fermentation, isolation, and physico-chemical and biological characteristics. J Antibiot 40:1249–1255
Kumar P, Sharma S, Shukla A, Kumar S, Maurya RK, Katial V, Mitra A, Gigras P (2005) Production of tacrolimus (FK-506) using new Streptomyces species. WO 2005/038009 A2
Lanzetta PA, Alvarez LJ, Reinach PS, Candia OA (1979) Improved assay for nanomole amounts of inorganic phosphate. Anal Biochem 100:95–97
Lechevalier MP, Lechevalier H (1970) Chemical composition as a criterion in the classification of aerobic actinomycetes. Int J Syst Bacteriol 20:435–443
Lee MS, Kojima I, Demain AL (1997) Effect of nitrogen source on biosynthesis of rapamycin by Streptomyces hygroscopicus. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 19(2):83–86
Locci R (1989) Streptomyces and related genera. In: Williams ST, Sharpe ME, Holt JG (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 4. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 2451–2508
Martín JF (2004) Phosphate control of the biosynthesis of antibiotics and other secondary metabolites is mediated by the PhoR–PhoP system: an unfinished story. J Bacteriol 186(16):5197–5201
Martínez-Castro M, Barreiro C, Romero F, Fernández-Chimeno RI, Martín JF (2011) Streptomyces tacrolimicus sp. nov., a low producer of the immunosuppressant tacrolimus (FK506). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61(Pt 5):1084–1088
Medema MH, Trefzer A, Kovalchuk A, van den Berg M, Müller U, Heijne W, Wu L, Alam MT, Ronning CM, Nierman WC, Bovenberg RA, Breitling R, Takano E (2010) The sequence of a 1.8-mb bacterial linear plasmid reveals a rich evolutionary reservoir of secondary metabolic pathways. Genome Biol Evol 2:212–224
Meier-Kriesche HU, Li S, Gruessner RW, Fung JJ, Bustami RT, Barr ML, Leichtman AB (2006) Immunosuppression: evolution in practice and trends, 1994–2004. Am J Transplant 6(5 Pt 2):1111–1131
Mendes MV, Tunca S, Antón N, Recio E, Sola-Landa A, Aparicio JF, Martín JF (2007) The two-component phoR-phoP system of Streptomyces natalensis: inactivation or deletion of phoP reduces the negative phosphate regulation of pimaricin biosynthesis. Metab Eng 9(2):217–227
Miller LT (1982) Single derivatization method for routine analysis of bacterial whole-cell fatty acid methyl esters, including hydroxyl acids. J Clin Microbio 16:584–586
Miller L, Berger T (1985) Bacteria identification by gas chromatography of whole cell fatty acids, Hewlett-Packard application note 228–241. Hewlett-Packard, Avondale
Mo S, Kim DH, Lee JH, Park JW, Basnet DB, Ban YH, Yoo YJ, Chen SW, Park SR, Choi EA, Kim E, Jin YY, Lee SK, Park JY, Liu Y, Lee MO, Lee KS, Kim SJ, Kim D, Park BC, Lee SG, Kwon HJ, Suh JW, Moore BS, Lim SK, Yoon YJ (2011) Biosynthesis of the allylmalonyl–CoA extender unit for the FK506 polyketide synthase proceeds through a dedicated polyketide synthase and facilitates the mutasynthesis of analogues. J Am Chem Soc 133(4):976–985
Mo S, Yoo YJ, Ban YH, Lee SK, Kim E, Suh JW, Yoon YJ (2012) Roles of fkbN in positive regulation and tcs7 in negative regulation of FK506 biosynthesis in Streptomyces sp. KCTC 11604BP. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(7):2249–2255
Motamedi H, Shafiee A (1998) The biosynthetic gene cluster for the macrolactone ring of the immunosuppressant FK506. Eur J Biochem 256(3):528–534
Muramatsu H, Mokhtar SI, Katsuoka M, Ezaki M (2005) Phylogenetic analysis of immunosuppressant FK506-producing streptomycete strains. Actinomycetologica 19(2):33–39
Nárdiz N, Santamarta I, Lorenzana LM, Martín JF, Liras P (2011) A rhodanese‐like protein is highly overrepresented in the mutant S. clavuligerus oppA2::aph: effect on holomycin and other secondary metabolites production. Microb Biotechnol 4(2):216–225
Okuhara M, Tanaka H, Goto T, Kino T, Hatanaka H (1990) Tricyclo compounds, a process for their production and a pharmaceutical composition containing the same. US Patent 4,894,366
Rodríguez-García A, Barreiro C, Santos-Beneit F, Sola-Landa A, Martín JF (2007) Genome-wide transcriptomic and proteomic analysis of the primary response to phosphate limitation in Streptomyces coelicolor M145 and in a DeltaphoP mutant. Proteomics 7(14):2410–2429
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Santos-Beneit F, Rodríguez-García A, Franco-Domínguez E, Martín JF (2008) Phosphate-dependent regulation of the low- and high-affinity transport systems in the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor. Microbiology 154(Pt8):2356–2370.
Shirling SB, Gottlieb D (1966) Methods for characterization of Streptomyces species. Int J Syst Bacteriol 16:313–340
Sigmund JM, Clark DC, Rainey FA, Anderson AS (2003) Detection of eubacterial 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme a reductases from natural populations of actinomycetes. Microb Ecol 46(1):106–112
Singh BP, Behera BK (2009) Regulation of tacrolimus production by altering primary source of carbons and amino acids. Lett Appl Microbiol 49(2):254–259
Staneck JL, Roberts GD (1974) Simplified approach to identification of aerobic actinomycetes by thin-layer chromatography. Appl Microbiol 28:226–231
Tamaoka J, Komagata K (1984) Determination of DNA base composition by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. FEMS Microbiol Lett 25:125–128
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Tresner HD, Backus EJ (1963) System of color wheels for streptomycete taxonomy. Appl Microbiol 11:335–338
Turło J, Gutkowska B, Gajzlerska W (2006) Submerged cultivation of ‘Streptomyces tsukubaensis’ in media composed of waste products of food industry. Acta Pol Pharm 63(5):463–465
Vandamme P, Pot B, Gillis M, de Vos P, Kersters K, Swings J (1996) Polyphasic taxonomy, a consensus approach to bacterial systematics. Microbiol Rev 60(2):407–438
Wayne LG, Brenner DJ, Colwell RR, Grimont PAD, Kandler O, Krichevsky MI, Moore LH, Moore WEC, Murray RGE, Stackebrandt E, Starr MP, Trüper HG (1987) International Committee on Bacterial Systematics. Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:463–464
Williams ST, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Wellington EMH, Sneath PHA, Sackin MJ (1983) Numerical classification of Streptomyces and related genera. J Gen Microbiol 129:1743–1813
Yoon YJ, Choi CY (1997) Nutrient effects on FK-506, a new immunosuppressant, production by Streptomyces sp. in a defined medium. J Ferment Bioeng 83(6):599–603
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant of the CICYT Ministry of Innovation and Science (Madrid, Spain) [BIO2006-14853-C02-01 (CONSOLIDER)] and by the European Union through an ERA-IB (PIM2010EEI-00677) international cooperation project. M. Martínez-Castro received a PFU fellowship of the Ministry of Education and Science. C. Barreiro was supported by the European Union program ERA-IB [BioProChemBB project (EIB.08.008)]. We acknowledge the scientific assistance of S. Albillos and the excellent technical support of B. Martín, J. Merino, A. Casenave, and A. Mulero (INBIOTEC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martínez-Castro, M., Salehi-Najafabadi, Z., Romero, F. et al. Taxonomy and chemically semi-defined media for the analysis of the tacrolimus producer ‘Streptomyces tsukubaensis’ . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 2139–2152 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4364-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4364-x