Abstract
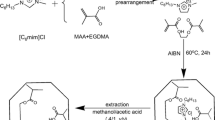
The aim of this paper is to develop a potentiometric sensing methodology for sensitive and selective determination of neutral phenols by using a molecularly imprinted polymer as a receptor. Bisphenol A (BPA), a significant environmental contaminant, is employed as the model target. The BPA-imprinted polymer is synthesized by the semi-covalent technique and incorporated into a plasticized poly(vinyl chloride) membrane doped with the tridodecylmethylammonium salt. The present electrode shows a linear anionic potential response over the concentration range from 0.1 to 1 μM with a detection limit of 0.02 μM, and exhibits an excellent selectivity over other phenols. The proposed approach has been successfully applied to the determination of BPA released from real plastic samples. It offers promising potential in development of potentiometric sensors for measuring neutral phenols at trace levels.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grygolowicz-Pawlak E, Bakker E (2010) Electrochem Commun 12:1195–1198
Liang RN, Song DA, Zhang RM, Qin W (2010) Angew Chem Int Ed 49:2556–2559
Ito T, Radecka H, Tohda K, Odashima K, Umezawa Y (1998) J Am Chem Soc 120:3049–3059
Radecki J, Radecka H, Piotrowski T, Depraetere S, Dehaen W, Plavec J (2004) Electroanalysis 16:2073–2081
Saraswathyamma B, Pajak M, Radecki J, Maes W, Dehaen W, Kumar KG, Radecka H (2008) Electroanalysis 20:2009–2015
Kriz D, Ramstrom O, Mosbach K (1997) Anal Chem 69:A345–A349
Liang RN, Zhang RM, Qin W (2009) Sens Actuators B Chem 141:544–550
Hutchins RS, Bachas LG (1995) Anal Chem 67:1654–1660
Laws SC, Carey SA, Ferrell JM, Bodman GJ, Cooper RL (2000) Toxicol Sci 54:154–167
Alexiadou DK, Maragou NC, Thomaidis NS, Theodoridis GA, Koupparis MA (2008) J Sep Sci 31:2272–2282
Kawaguchi M, Hayatsu Y, Nakata H, Ishii Y, Ito R, Saito K, Nakazawa H (2005) Anal Chim Acta 539:83–89
San Vicente B, Navarro Villoslada F, Moreno-Bondi MC (2004) Anal Bioanal Chem 380:115–122
Tan F, Zhao HX, Li XN, Quan X, Chen JW, Xiang XM, Zhang X (2009) J Chromatogr A 1216:5647–5654
Chen LX, Xu SF, Li JH (2011) Chem Soc Rev 40:2922–2942
Ye QS, Meyerhoff ME (2001) Anal Chem 73:332–336
Ceresa A, Sokalski T, Pretsch E (2001) J Electroanal Chem 501:70–76
Fu B, Bakker E, Yun JH, Yang VC, Meyerhoff ME (1994) Anal Chem 66:2250–2259
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Instrument Developing Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (YZ201161), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (20977073, 41206087), and the Taishan Scholar Program of Shandong Province (TS20081159).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kou, LJ., Liang, RN., Wang, XW. et al. Potentiometric sensor for determination of neutral bisphenol A using a molecularly imprinted polymer as a receptor. Anal Bioanal Chem 405, 4931–4936 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-6877-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-6877-2