Bromus japonicus is a common monocot weed that occurs in major winter wheat fields in the Huang–Huai–Hai region of China. Pyroxsulam is a highly efficient and safe acetolactate synthase (ALS)-inhibiting herbicide that is widely used to control common weeds in wheat fields. However,
B. japonicus populations in China have evolved resistance to pyroxsulam by different mutations in the
ALS gene. To understand the resistance distribution, target-site resistance mechanisms, and cross-resistance patterns, 208
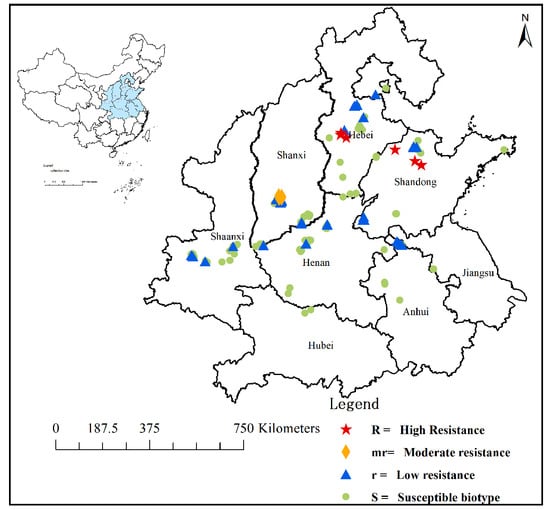
B. japonicus populations were collected from eight provinces. In the resistant population screening experiment, 59 populations from six provinces showed different resistance levels to pyroxsulam compared with the susceptible population, of which 17
B. japonicus populations with moderate or high levels of resistance to pyroxsulam were mainly from the Hebei (4), Shandong (4) and Shanxi (9) Provinces. Some resistant populations were selected to investigate the target site-resistance mechanism to the ALS-inhibiting herbicide pyroxsulam. Three pairs of primers were designed to amplify the
ALS sequence, which was assembled into the complete
ALS sequence with a length of 1932 bp. DNA sequencing of
ALS revealed that four different
ALS mutations (Pro-197-Ser, Pro-197-Thr, Pro-197-Phe and Asp-376-Glu) were found in 17 moderately or highly resistant populations. Subsequently, five resistant populations, QM21-41 with Pro-197-Ser, QM20-8 with Pro-197-Thr and Pro-197-Phe, and QM21-72, QM21-76 and QM21-79 with Asp-376-Glu mutations in
ALS genes, were selected to characterize their cross-resistance patterns to ALS inhibitors. The QM21-41, QM20-8, QM21-72, QM21-76 and QM21-79 populations showed broad-spectrum cross-resistance to pyroxsulam, mesosulfuron–methyl and flucarbazone–sodium. This study is the first to report evolving cross-resistance to ALS-inhibiting herbicides due to Pro-197-Phe mutations in
B. japonicus.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT