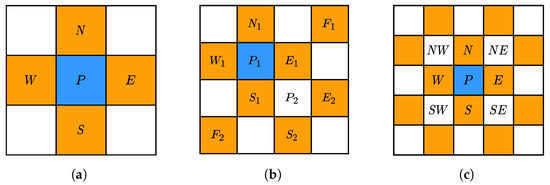
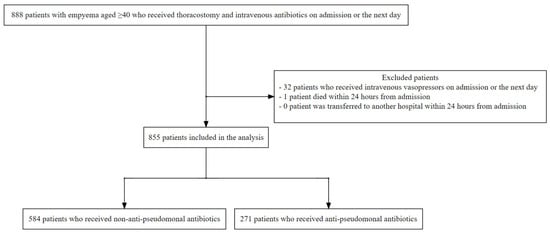
Forest ecosystems are essential to the global carbon cycle because they are the biggest terrestrial carbon reserves. In the management of forests, thinning is a commonly employed strategy, impacting the respiration and biomass loss of trees, thereby modifying forest carbon dynamics. However, there
[...] Read more.
Forest ecosystems are essential to the global carbon cycle because they are the biggest terrestrial carbon reserves. In the management of forests, thinning is a commonly employed strategy, impacting the respiration and biomass loss of trees, thereby modifying forest carbon dynamics. However, there is a lack of scientific research to confirm the impacts of thinning intensities on carbon storage in trees, soil layers, shrubs, and ground vegetation layers as well as its impact on wood production and growth rate. The goal of this study was to find the optimal thinning levels for increasing carbon sequestration during the growth stage of the Korean pine (
Pinus koraiensis) middle-aged plantations in Northeast China. In this study, thinning intensity (0, 10, 11, 16, 18, and 22%) affected the carbon storage of trees, tree growth, volume, and, we suspected, soil layer, shrubs, and vegetation (herbs, litter, and grass) also. Specifically, after four years of thinning, the 18% treatment significantly increased total carbon storage, individual organ storage, growth, and tree volume (
p < 0.05). These results give us abundant information about how thinning affects the dynamics of carbon storage, wood production, and the interactions between soil and plants in
P. koraiensis plantations, contributing to multi-objective management strategies for optimizing carbon sequestration, wood production, and ecosystem health.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT