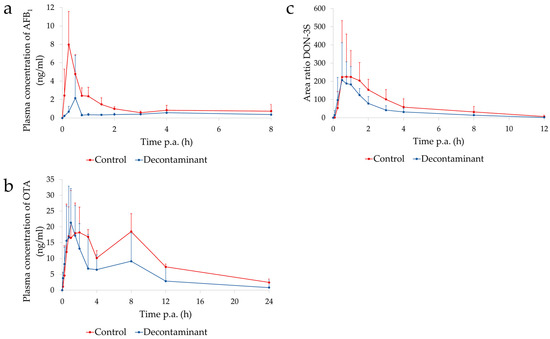
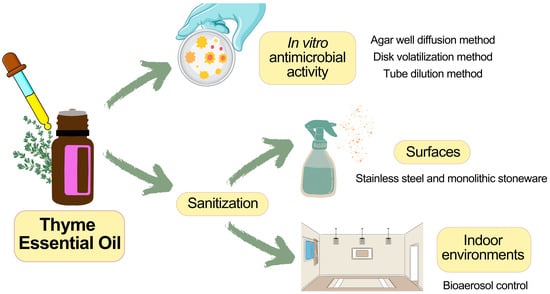
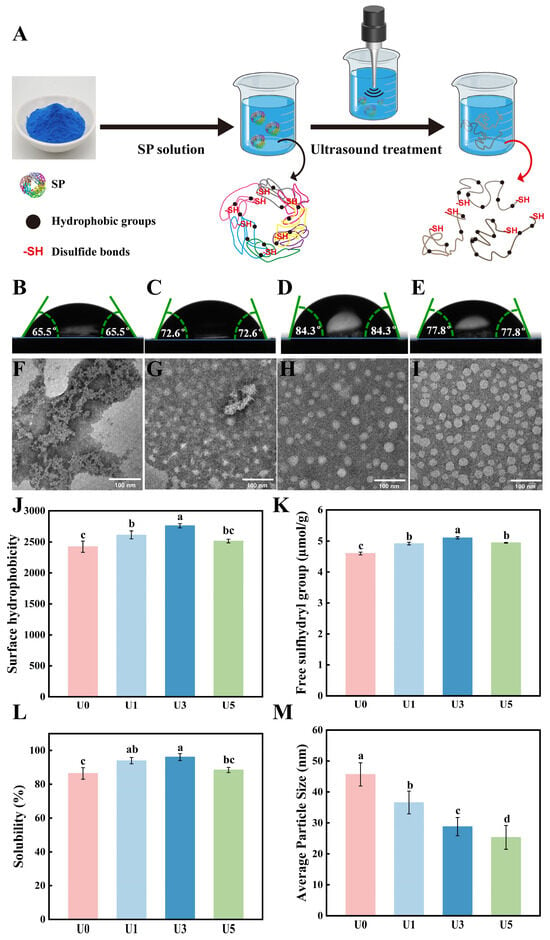
The aims of this study were (i) to determine the effect of an algoclay-based decontaminant on the oral availability of three mycotoxins (deoxynivalenol; DON, ochratoxin A; OTA, and aflatoxin B
1; AFB
1) using an oral bolus model and (ii) to
[...] Read more.
The aims of this study were (i) to determine the effect of an algoclay-based decontaminant on the oral availability of three mycotoxins (deoxynivalenol; DON, ochratoxin A; OTA, and aflatoxin B
1; AFB
1) using an oral bolus model and (ii) to determine the effect of this decontaminant on the performance, intestinal morphology, liver oxidative stress, and metabolism, in broiler chickens fed a diet naturally contaminated with DON. In experiment 1, sixteen 27-day-old male chickens (approximately 1.6 kg body weight; BW) were fasted for 12 h and then given a bolus containing either the mycotoxins (0.5 mg DON/kg BW, 0.25 mg OTA/kg BW, and 2.0 mg AFB
1/kg BW) alone (
n = 8) or combined with the decontaminant (2.5 g decontaminant/kg feed; circa 240 mg/kg BW) (
n = 8). Blood samples were taken between 0 h (before bolus administration) and 24 h post-administration for DON-3-sulphate, OTA, and AFB
1 quantification in plasma. The algoclay decontaminant decreased the relative oral bioavailability of DON (39.9%), OTA (44.3%), and AFB
1 (64.1%). In experiment 2, one-day-old male Ross broilers (
n = 600) were divided into three treatments with ten replicates. Each replicate was a pen with 20 birds. The broiler chickens were fed a control diet with negligible levels of DON (0.19–0.25 mg/kg) or diets naturally contaminated with moderate levels of DON (2.60–2.91 mg/kg), either supplemented or not with an algoclay-based decontaminant (2 g/kg diet). Jejunum villus damage was observed on day 28, followed by villus shortening on d37 in broiler chickens fed the DON-contaminated diet. This negative effect was not observed when the DON-contaminated diet was supplemented with the algoclay-based decontaminant. On d37, the mRNA expression of glutathione synthetase was significantly increased in the liver of broiler chickens fed the DON-contaminated diet. However, its expression was similar to the control when the birds were fed the DON-contaminated diet supplemented with the algoclay-based decontaminant. In conclusion, the algoclay-based decontaminant reduced the systemic exposure of broiler chickens to DON, OTA, and AFB
1 in a single oral bolus model. This can be attributed to the binding of the mycotoxins in the gastrointestinal tract. Moreover, dietary contamination with DON at levels between 2.69 and 2.91 mg/kg did not impair production performance but had a negative impact on broiler chicken intestinal morphology and the liver redox system. When the algoclay-based decontaminant was added to the diet, the harm caused by DON was no longer observed. This correlates with the results obtained in the toxicokinetic assay and can be attributed to a decreased absorption of DON.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT