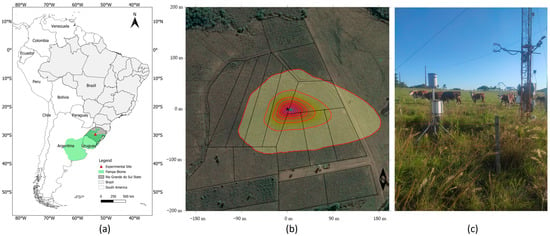
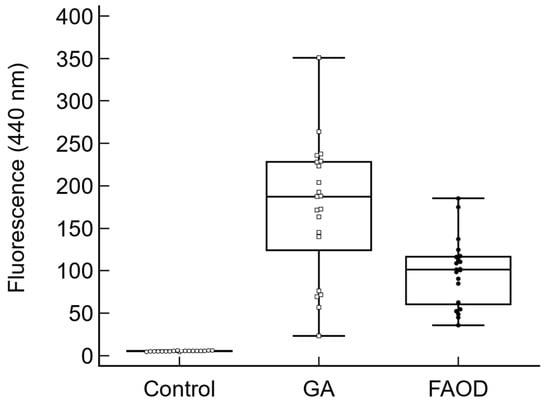
Technological and climatic factors significantly influence the expression of quality and quantity properties of spring wheat. This study aims to quantify the effects of weather conditions and fertilizer systems on spring wheat yield, quality (protein content), and physiological indicators (leaf vapor pressure deficit,
[...] Read more.
Technological and climatic factors significantly influence the expression of quality and quantity properties of spring wheat. This study aims to quantify the effects of weather conditions and fertilizer systems on spring wheat yield, quality (protein content), and physiological indicators (leaf vapor pressure deficit, evapotranspiration, surface temperature of the flag leaf) and to identify a suitable spring wheat genotype for the Transylvanian Plain. The experimental factors were: Y represents the year (Y
1, 2019; Y
2, 2020); F represents the fertilizer variant (F
1, a single rate of fertilization: 36 kg ha
−1 of nitrogen; F
2, two rates of fertilization: 36 kg ha
−1 of nitrogen + 72 kg ha
−1 of nitrogen; F
3, two rates of fertilization: 36 kg ha
−1 of nitrogen + 105 kg ha
−1 of nitrogen); and S represents the genotype (S1, Pădureni; S2, Granny; S3, Triso; S4, Taisa; S5, Ciprian; and S6, Lennox). This multifactorial experiment with three factors was conducted on Phaeozem soil. Regardless of weather conditions, fertilization with N
100–110 at the head swollen sheath (stage 10, Feeks Growth Scale for Wheat) is deemed the most suitable variant because it yields an average grain yield of 5000 kg ha
−1 of good quality (13.84% protein) with a considerable flag leaf area (29 cm
2) where physiological processes can optimally support the well-being of the spring wheat plants. Beyond this level of fertilization, the average grain yield tends to plateau, but the protein content considerably increases by 13–23%, depending on the genotype. High yields were achieved in the Lennox and Triso genotypes.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT