Abstract
Ship Shoal is an inner-shelf submarine shoal with large amounts of restoration quality sand that was dredged in 2013–2016 for the Caminada Headland Restoration Project in central Louisiana, USA. Here we provide the first assessment of the characteristics and rate of seasonal sediment infilling the South Pelto dredge pit on eastern Ship Shoal, which will inform future restoration initiatives. Vibracore and multicore samples collected in 2017 and 2018 from within and outside of South Pelto dredge pit revealed new interlaminated silts and clays (median grain size 4.3–6 ϕ, 16–48 µm) deposited at the bottom of the dredge pit, underlain by original Ship Shoal sand and older pro-delta deposits. Through analyzing beryllium-7 (7Be) inventories in multicores, we found that sedimentation rate varied seasonally from 4 to 12 cm (sedimentation rate 0.02–0.06 cm day−1) in fall 2017 to 8 to16 cm (0.05–0.15 cm day−1) in spring 2018. Mapping plume distribution along the continental shelf with satellite imagery corroborated with local wind/wave data revealed that the sediments deposited in South Pelto dredge pit are likely sourced from a combination of the Atchafalaya and Mississippi River plumes during the study period, in addition to possible resuspension from the ambient inner continental shelf and fine-grained material exported from proximal bays. Sedimentation in the dredge pit is not greatly affected by wall slope failure or bedload influx of ambient Ship Shoal sand. Infilling rate and material are slower and finer than past model prediction. Restoration quality sand on this sandy shoal in Louisiana is thus not renewable.

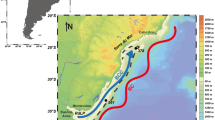
Modified from Xu et al. (2016)

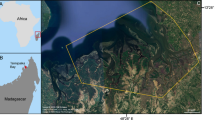
modified from Liu et al. 2019)












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison, M.A., G.C. Kineke, E.S. Gordon, and M.A. Goni. 2000. Development and reworking of a seasonal flood deposit on the inner continental shelf off the Atchafalaya River. Continental Shelf Research 20 (16): 2267–2294.
Allison, M.A., C.R. Demas, B.A. Ebersole, B.A. Kleiss, C.D. Little, E.A. Meselhe, N.J. Powell, T.C. Pratt, and B.M. Vosburg. 2012. A water and sediment budget for the lower Mississippi-Atchafalaya River in flood years 2008–2010: Implications for sediment discharge to the oceans and coastal restoration in Louisiana. Journal of Hydrology 432–433: 84–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.02.020.
Baskaran, M., C.H. Coleman, and P.H. Santschi. 1993. Atmospheric depositional fluxes of 7Be and 210Pb at Galveston and College Station. Texas. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres 98 (D11): 20555–20571.
Baustian, M.M., and N.N. Rabalais. 2009. Seasonal composition of benthic macroinfauna exposed to hypoxia in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Estuaries and Coasts 32 (5): 975–983.
Bentley, S.J., Y. Furukawa, and W.C. Vaughan. 2000. Record of event sedimentation in Mississippi Sound. Gulf Coast Association of Geological Societies Transactions 50: 715–723.
Bentley, S.J. 2002. Dispersal of fine sediments from river to shelf: Process and product. Gulf Coast Association of Geological Societies Transactions 52: 1055–1067.
Bentley, S.J., T.R. Keen, C.A. Blain, and W.C. Vaughan. 2002. The origin and preservation of a major hurricane event bed in the northern Gulf of Mexico: Hurricane Camille, 1969. Marine Geology 186 (3–4): 423–446.
Bouma, A.H. 1968. Distribution of minor structures in Gulf of Mexico sediments. Gulf Coast Association of Geological Societies Transactions 18: 26–33.
Chamberlain, E.L., T.E. Törnqvist, Z. Shen, B. Mauz, and J. Wallinga. 2018. Anatomy of Mississippi Delta growth and its implications for coastal restoration. Science advances 4(4): eaar4740. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aar4740.
Coastal Engineering Consultant Inc. 2017. Project Completion Report - Caminada Headland Beach and Dune Restoration Project, BA-45/BA-143.
Cobb, M., T.R. Keen, and N.D Walker. 2008. Modeling the circulation of the Atchafalaya Bay system. Part 2: river plume dynamics during cold fronts. Journal of Coastal Research 24(4(244)): 1048–1062.
Cochran, J.K., and P. Masque. 2003. Short-lived U/Th series radionuclides in the ocean: Tracers for scavenging rates, export fluxes and particle dynamics. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry 52 (1): 461–492.
Corbett, D.R., B. McKee, and D. Duncan. 2004. An evaluation of mobile mud dynamics in the Mississippi River deltaic region. Marine Geology 209 (1–4): 91–112.
Courtois, A. 2018. A regional survey of river-plume sedimentation on the Mississippi River Delta Front. M.S. Thesis, Louisiana State University.
CPRA (Coastal Protection and Restoration Authority). 2017. Caminada Headland Beach and Dune Restoration – Increment II (BA-143) completion report. Baton Rouge, Louisiana: CPRA, 187p.
Denommee, K.C., S.J. Bentley, D. Harazim, and J.H. Macquaker. 2016. Hydrodynamic controls on muddy sedimentary-fabric development on the Southwest Louisiana subaqueous delta. Marine Geology 382: 162–175.
DiMego, G.J., L.F. Bosart, and G.W. Endersen. 1976. An examination of the frequency and mean conditions surrounding frontal incursions into the Gulf of Mexico and Caribbean Sea. Monthly Weather Review 104 (6): 709–718.
Frazier, D.E. 1967. Recent deltaic deposits of the Mississippi River: Their development and chronology. Gulf Coast Association of Geological Societies Transactions 17: 287–315.
Geotek Ltd. (2018). Gamma Density. Retrieved Oct 05, 2018, from https://www.geotek.co.uk/sensors/gammadensity/.
Goni, M.A., Y. Alleau, R. Corbett, J.P. Walsh, D. Mallinson, M.A. Allison, E. Gordon, S. Petsch, and T.M. Dellapenna. 2007. The effects of Hurricanes Katrina and Rita on the seabed of the Louisiana shelf. The Sedimentary Record 5 (1): 4–9.
Jose, F., D. Kobashi, and G.W. Stone. 2007. Spectral wave transformation over an elongated sand shoal off south-central Louisiana. USA, Journal of Coastal Research, Special Issue 50: 757–761.
Kaste J.M., and M. Baskaran. 2012. Meteoric 7Be and 10Be as Process Tracers in the Environment. In: Baskaran M. (eds) Handbook of Environmental Isotope Geochemistry. Advances in Isotope Geochemistry. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-10637-8_5.
Keller, G., S.J. Bentley, K. Xu, J. Maloney, M. Miner, and I. Georgiou. 2016. River-plume sedimentation and 210Pb/7Be seabed delivery on the Mississippi River delta front. Geo Marine Letters. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-016-0476-0.
Khalil, S.M., C.W. Finkl, J. Andrews, and C.P. Knotts. 2007a. Restoration-quality sand from Ship Shoal, Louisiana: geotechnical investigation for sand on a drowned barrier island. In Coastal Sediments’ 07 (pp. 685–698).
Khalil, S.M., C.P. Knotts, and B. Tate. 2007b. Restoration of Louisiana barrier islands: engineering approaches to hazard mitigation by modulating coastal environments. In Coastal Engineering 2006: (In 5 Volumes) (pp. 1951–1963).
Khalil, S.M., R.C. Raynie, and J. LeBlanc. 2019. Louisiana’s barrier island system—a programmatic approach to restoration. Coastal Sediments. https://doi.org/10.1142/9789811204487_0023.
Kindinger, J., J. Flocks, M. Kulp, S. Penland, L.D. Britsch, G. Brewer, G.L. Brooks, S. Dadisman, C. Dreher, and N. Ferina, 2001. Sand resources, regional geology, and coastal processes for the restoration of the Barataria barrier shoreline (No. 2001–384).
Kulp, M., S. Penland, S.J. Williams, C. Jenkins, J. Flocks, and J. Kindinger. 2005. Geologic framework, evolution, and sediment resources for restoration of the Louisiana coastal zone. Journal of coastal research pp.56–71.
Liu, H., K.H. Xu, B. Li, Y. Han, and G. Li. 2019. Sediment identification using machine learning classifiers in a mixed-texture dredge pit of Louisiana shelf for coastal restoration. Water 11, 1257. https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4441/11/6/1257.
Liu, H., K. Xu, and C. Wilson. 2020a. Sediment infilling and geomorphological change of a mud-capped Raccoon Island dredge pit near Ship Shoal of Louisiana shelf. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 245, p.106979.
Liu, H., K. Xu, Y. Ou, R. Bales, Z. Zang, and Z.G. Xue. 2020b. Sediment transport near ship shoal for coastal restoration in the Louisiana shelf: A model estimate of the year 2017–2018. Water 12 (8): 2212.
Liu, H. 2020. Sediment transport and geomorphological evolution in the transgressive Ship Shoal, Louisiana: insights from geophysical observation, modeling, and machine learning studies (2020). LSU Doctoral Dissertations 5288. https://digitalcommons.lsu.edu/gradschool_dissertations/5288
Maloney, J.M., S.J. Bentley, K. Xu, J. Obelcz, I.Y. Georgiou, and M.D. Miner. 2018. Mississippi River subaqueous delta is entering a stage of retrogradation. Marine Geology 400: 12–23.
Miner, M.D., M.A. Kulp, D.M. FitzGerald, J.G. Flocks, and H.D. Weathers. 2009. Delta lobe degradation and hurricane impacts governing large-scale coastal behavior, South-central Louisiana, USA. Geo-Marine Letters 29 (6): 441–453.
Moeller, C.C., O.K. Huh, H.H. Roberts, L.E. Gumley, and W.P. Menzel. 1993. Response of Louisiana coastal environments to a cold front passage. Journal of Coastal Research 434–447.
Mossa, J. and H.H. Roberts. 1990. Synergism of riverine and winter storm-related sediment transport processes in Louisiana's coastal wetlands.
Motti, J., and M.A. Kulp. 2003. Descriptive logs and textural analysis data for BSS2000 vibracores: ship shoal area. New Orleans, Louisiana: Louisiana Department of Natural Resources, 15p.
Muhammad, Z., S.J. Bentley, L.A. Febo, A.W. Droxler, G.R. Dickens, L.C. Peterson, and B.N. Opdyke. 2008. Excess 210Pb inventories and fluxes along the continental slope and basins of the Gulf of Papua. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface (2003–2012), v. 113, no. F1.
Murray, S.P. 1998. An observational study of the Mississippi-Atchafalaya coastal plume.
Nairn, R., J.A. Johnson, D. Hardin, and J. Michel. 2004. A biological and physical monitoring program to evaluate long-term impacts from sand dredging operations in the United States outer continental shelf. Journal of Coastal Research pp.126–137.
Nairn, R., Q. Lu, and S. Langendyk. 2005. A study to address the issue of seafloor stability and the impact on oil and gas infrastructure in the Gulf of Mexico. US Dept. of the Interior, MMS, Gulf of Mexico OCS Region, New Orleans, LA OCS Study MMS 43: 179.
O’Connor, M. 2017. Sediment infilling of Louisiana continental-shelf borrow areas: a record of sedimentary processes in the Northern Gulf of Mexico. M.S. Thesis, Louisiana State University, 68pg.
Obelcz, J., K. Xu, S.J. Bentley, M. O’Connor, and M.D. Miner. 2018. Mud-capped dredge pits: An experiment of opportunity for characterizing cohesive sediment transport and slope stability in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 208: 161–169.
Penland, S., J.R. Suter, and T.F. Moslow. 1986. Inner-shelf shoal sedimentary facies and sequences: Ship Shoal, northern Gulf of Mexico.
Penland, S., R. Boyd, and J.R. Suter. 1988. Transgressive depositional systems of the Mississippi delta plain: A model for barrier shoreline and shelf sand development. Journal of Sedimentary Research 58 (6): 932–949.
Penland, S., and K.E. Ramsey. 1990. Relative sea level rise in Louisiana and the Gulf of Mexico: 1908–1988. Journal of Coastal Research 6: 323–342.
Perez, B.C., J.W. Day Jr., L.J. Rouse, R.F. Shaw, and M. Wang. 2000. Influence of Atchafalaya River discharge and winter frontal passage on suspended sediment concentration and flux in Fourleague Bay, Louisiana. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 50 (2): 271–290.
Restreppo, G.A., S.J. Bentley, J. Wang, and K. Xu. 2018. Riverine sediment contribution to distal deltaic wetlands: Fourleague Bay. LA. Estuaries and Coasts 42 (1): 55–67.
Roberts, H.H. 1997. Dynamic changes of the Holocene Mississippi River delta plain: the delta cycle. Journal of Coastal Research pp.605–627.
Robichaux, P., K. Xu, S.J. Bentley, M. Miner, and Z. Xue. 2020. Morphological evolution of a mud-capped borrow area on the Louisiana shelf: Nonlinear infilling and continuing consolidation. Geomorphology 354: 107030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2019.107030.
Rotondo, K.A., and S.J. Bentley. 2003. Deposition and resuspension of fluid muds on the western Louisiana inner continental shelf. Gulf Coast Association of Geological Societies Transactions 53: 722–731.
Stone, G.W. and R.A. McBride. 1998. Louisiana barrier islands and their importance in wetland protection: forecasting shoreline change and subsequent response of wave climate. Journal of Coastal Research pp.900–915.
Stone, G.W., D.A. Pepper, J. Xu, and X. Zhang. 2004. Ship Shoal as a prospective borrow site for barrier island restoration, Coastal south-central Louisiana, USA: numerical wave modeling and field measurements of hydrodynamics and sediment transport. Journal of Coastal Research pp.70–88.
Stone, G.W., R.E. Condrey, J.W. Fleeger, S.M. Khalil, D. Kobashi, F. Jose, E. Evers, S. Dubois, B. Liu, S. Arndt, and C. Gelpi. 2009. Environmental investigation of long-term use of Ship Shoal sand resources for large scale beach and coastal restoration in Louisiana. US Dept. of the Interior, Minerals Management Service, Gulf of Mexico OCS Region, New Orleans, LA. OCS Study MMS, 24, p.278.
Sommerfield, C.K., C.A. Nittrouer, and C.R. Alexander. 1999. 7Be as a tracer of flood sedimentation on the northern California continental margin. Continental Shelf Research 19 (3): 335–361.
Törnqvist, T.E., T.R. Kidder, W.J. Autin, K. van der Borg, A.F. de Jong, C.J. Klerks, E.M. Snijders, J.E. Storms, R.L. van Dam, and M.C. Wiemann. 1996. A revised chronology for Mississippi River subdeltas. Science 273 (5282): 1693–1696.
Van Heerden, I.L. and K. DeRouen Jr. 1997. Implementing a barrier island and barrier shoreline restoration program: the state of Louisiana's perspective. Journal of Coastal Research pp.679–685.
Walker, N.D. and A.B. Hammack. 2000. Impacts of winter storms on circulation and sediment transport: Atchafalaya-Vermilion Bay region, Louisiana, USA. Journal of Coastal Research pp.996–1010.
Wang, J., K. Xu, C. Li, and J. Obelcz. 2018. Forces driving the morphological evolution of a mud-capped borrow area. Northern Gulf of Mexico. Water 10 (8): 1001.
Wells, J.T. and G.P. Kemp. 1981. Atchafalaya mud stream and recent mudflat progradation: Louisiana chenier plain.
Williams, S.J., and M. Kulp, S. Penland, J. Kindinger, and J. Flocks. (2011). Mississippi River delta plain, Louisiana coast, and inner shelf Holocene geologic framework, processes, and resources. Gulf of Mexico Origin, Waters, and Biota: Volume III, Geology 175–193.
Wright, L.D., C.T. Friedrichs, S.C. Kim, and M.E. Scully. 2001. Effects of ambient currents and waves on gravity-driven sediment transport on continental shelves. Marine Geology 175 (1–4): 25–45.
Xu, K., C.K. Harris, R.D. Hetland, and J.M. Kaihatu. 2011. Dispersal of Mississippi and Atchafalaya sediment on the Texas-Louisiana shelf: Model estimates for the year 1993. Continental Shelf Research 31 (15): 1558–1575.
Xu, K., R.C. Mickey, Q. Chen, C.K. Harris, R.D. Hetland, K. Hu, and J. Wang. 2016. Shelf sediment transport during hurricanes Katrina and Rita. Computers & Geosciences 90: 24–39.
Xu, K.H., S.J. Bentley, J.W. Day, and A.M. Freeman. 2019. A review of sediment diversion in the Mississippi River Deltaic Plain, Estuarine. Coastal and Shelf Science 225: 106241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2019.05.023.
Zang, Z., Z.G. Xue, K. Xu, S.J. Bentley, Q. Chen, E.J. D’Sa, and Q. Ge. 2019. A Two Decadal (1993–2012) Numerical assessment of sediment dynamics in the Northern Gulf of Mexico. Water 11 (5): 938.
Acknowledgements
Michael Miner, Christopher DuFore and Tershara Mathews served as the project officers of Bureau of Ocean Energy Management. We are thankful to the Field Support Group of Coastal Studies Institute at Louisiana State University, crew of the R/V Coastal Profiler, and Dr Chunyan Li for WAVCIS data during the study period. We would also like to thank the LSU Earth Scan Lab, in particular Nan Walker and Alaric Haag, for their assistance.
Funding
Funding for this study was provided by the U.S. Department of the Interior, Bureau of Ocean Energy Management, Coastal Marine Institute, Washington DC, under Cooperative Agreement Numbers M14AC00023, M16AC00018, M17AC00019, and M19AC00015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Eduardo Siegle
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, Z., Wilson, C.A., Xu, K.H. et al. Sandy Borrow Area Sedimentation—Characteristics and Processes Within South Pelto Dredge Pit on Ship Shoal, Louisiana Shelf, USA. Estuaries and Coasts 45, 658–676 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-021-00975-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-021-00975-6