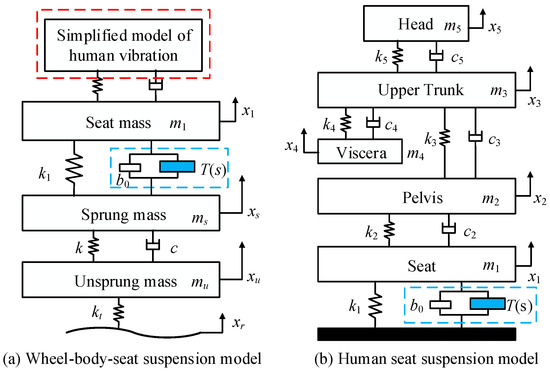
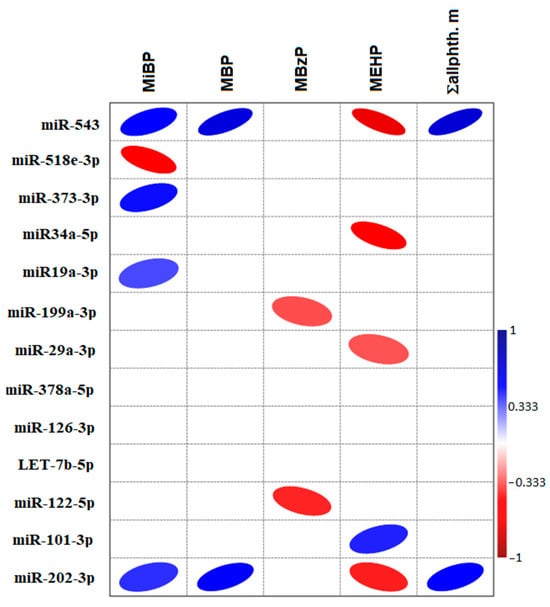
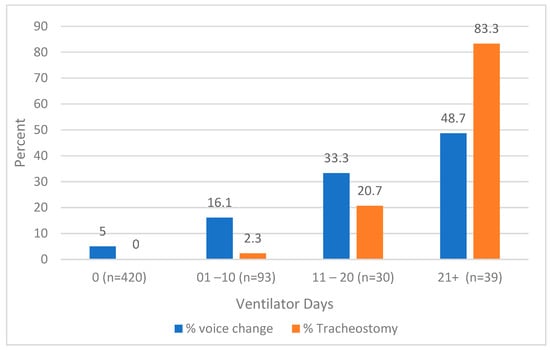
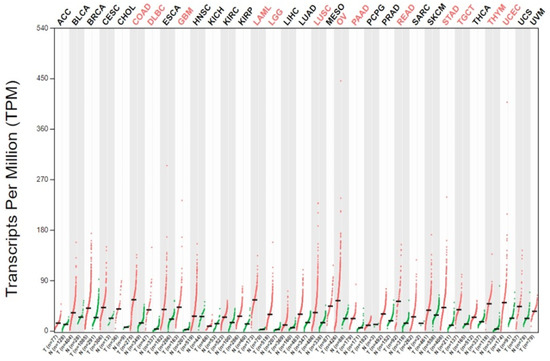
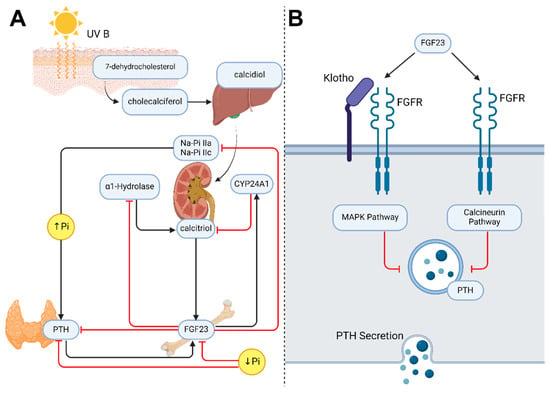
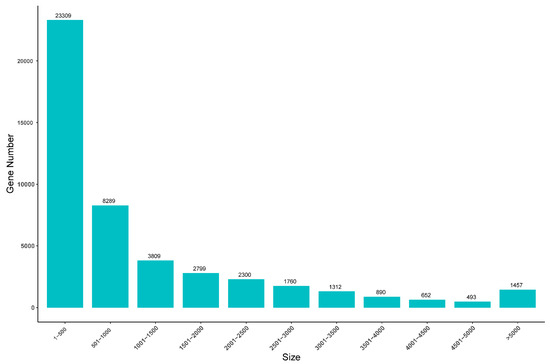
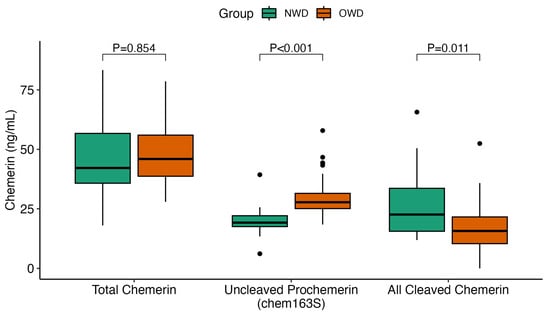
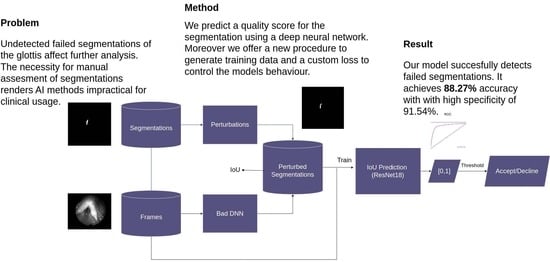
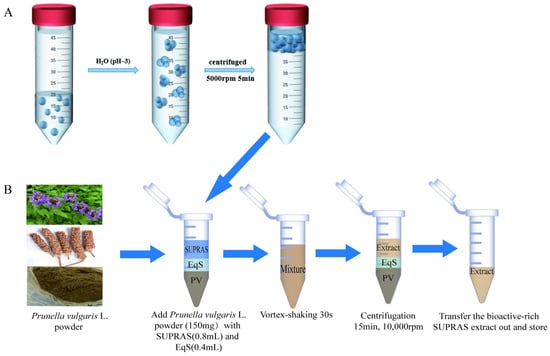
P53 overexpression plays a critical role in cancer pathogenesis by disrupting the intricate regulation of cellular proliferation. Despite its firmly established function as a tumor suppressor, elevated p53 levels can paradoxically contribute to tumorigenesis, influenced by factors such as exposure to carcinogens, genetic mutations, and viral infections. This phenomenon is observed across a spectrum of cancer types, including bladder (BLCA), ovarian (OV), cervical (CESC), cholangiocarcinoma (CHOL), colon adenocarcinoma (COAD), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBC), esophageal carcinoma (ESCA), head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSC), kidney chromophobe (KICH), kidney renal clear cell carcinoma (KIRC), liver hepatocellular carcinoma (LIHC), lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC), and uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma (UCEC). This broad spectrum of cancers is often associated with increased aggressiveness and recurrence risk. Effective therapeutic strategies targeting tumors with p53 overexpression require a comprehensive approach, integrating targeted interventions aimed at the p53 gene with conventional modalities such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted drugs. In this extensive study, we present a detailed analysis shedding light on the multifaceted role of TP53 across various cancers, with a specific emphasis on its impact on disease-free survival (DFS). Leveraging data from the TCGA database and the GTEx dataset, along with GEPIA, UALCAN, and STRING, we identify TP53 overexpression as a significant prognostic indicator, notably pronounced in prostate adenocarcinoma (PRAD). Supported by compelling statistical significance (
p < 0.05), our analysis reveals the distinct influence of TP53 overexpression on DFS outcomes in PRAD. Additionally, graphical representations of overall survival (OS) underscore the notable disparity in OS duration between tumors exhibiting elevated TP53 expression (depicted by the red line) and those with lower TP53 levels (indicated by the blue line). The hazard ratio (HR) further emphasizes the profound impact of TP53 on overall survival. Moreover, our investigation delves into the intricate TP53 protein network, unveiling genes exhibiting robust positive correlations with TP53 expression across 13 out of 27 cancers. Remarkably, negative correlations emerge with pivotal tumor suppressor genes. This network analysis elucidates critical proteins, including SIRT1, CBP, p300, ATM, DAXX, HSP 90-alpha, Mdm2, RPA70, 14-3-3 protein sigma, p53, and ASPP2, pivotal in regulating cell cycle dynamics, DNA damage response, and transcriptional regulation. Our study underscores the paramount importance of deciphering TP53 dynamics in cancer, providing invaluable insights into tumor behavior, disease-free survival, and potential therapeutic avenues.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT