Article contents
Cation-Exchange Constants for Clays from Electrochemical Measurements
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 01 January 2024
Abstract
Ion exchange constants for various cations adsorbed on clays were determined using compacted-clay samples as membrane electrodes and theory for the membrane response of glass electrodes. The electrochemical cell used is conventionally written: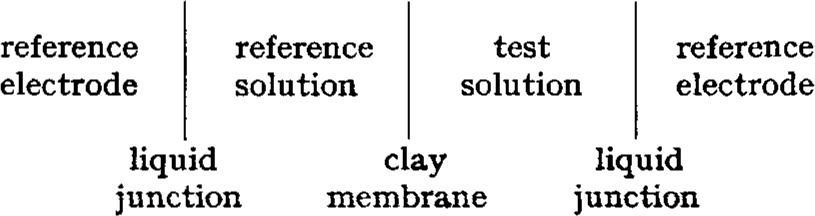 A static electrical potential is developed between the reference electrodes. The potential is a function of the cation species and of the cation activities in the two solutions and is given by an adaptation of the Nernst equation. From measurements of the electrical potential, the free energy of reactions or exchange constants for a series of reactions between various cation species were obtained. These determinations indicate that compacted clays prefer monovalent over divalent cations.
A static electrical potential is developed between the reference electrodes. The potential is a function of the cation species and of the cation activities in the two solutions and is given by an adaptation of the Nernst equation. From measurements of the electrical potential, the free energy of reactions or exchange constants for a series of reactions between various cation species were obtained. These determinations indicate that compacted clays prefer monovalent over divalent cations.
Some exchange constants were determined for the same clays in a non-compacted state. Not only the magnitude but also the order of cation selectivity changed for the same clay when determinations were made in the dispersed state and compared with those obtained by electrochemical means using compacted clay. Publication authorized by the Director, U.S. Geological Survey.
- Type
- General
- Information
- Clays and Clay Minerals (National Conference on Clays and Clay Minerals) , Volume 12 , February 1963 , pp. 397 - 421
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Clay Minerals Society 1963
References
- 5
- Cited by




